Abstract
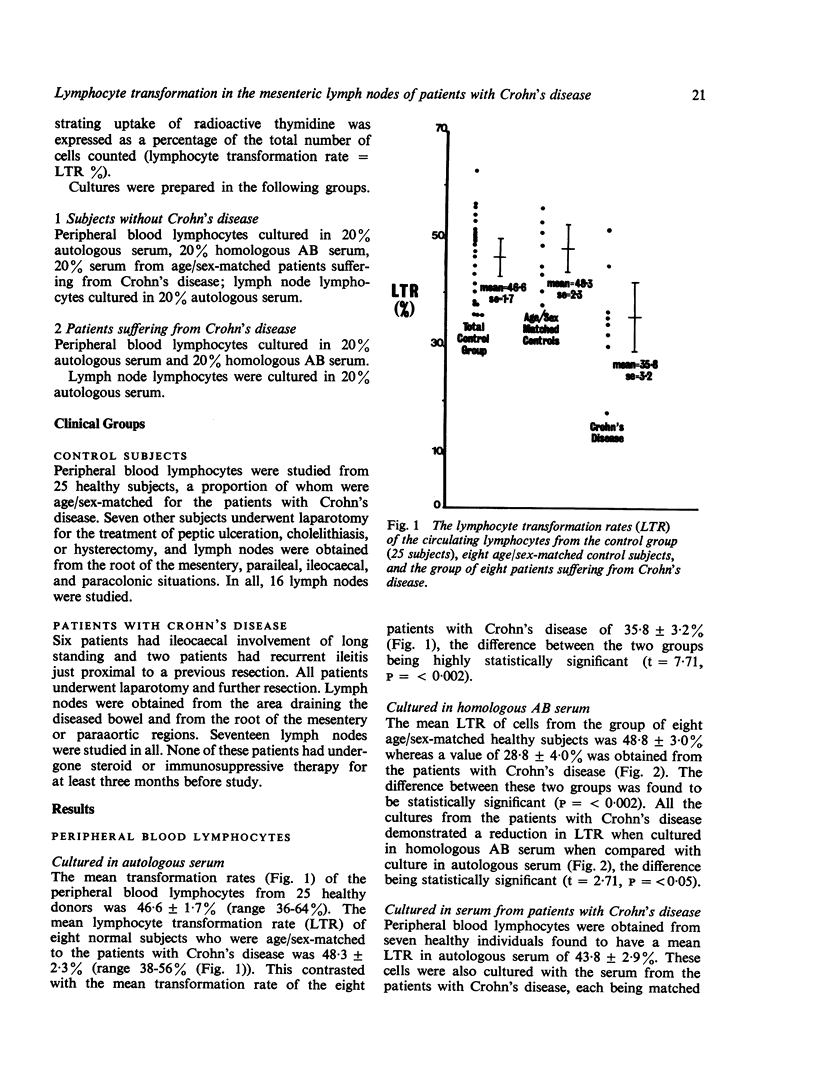
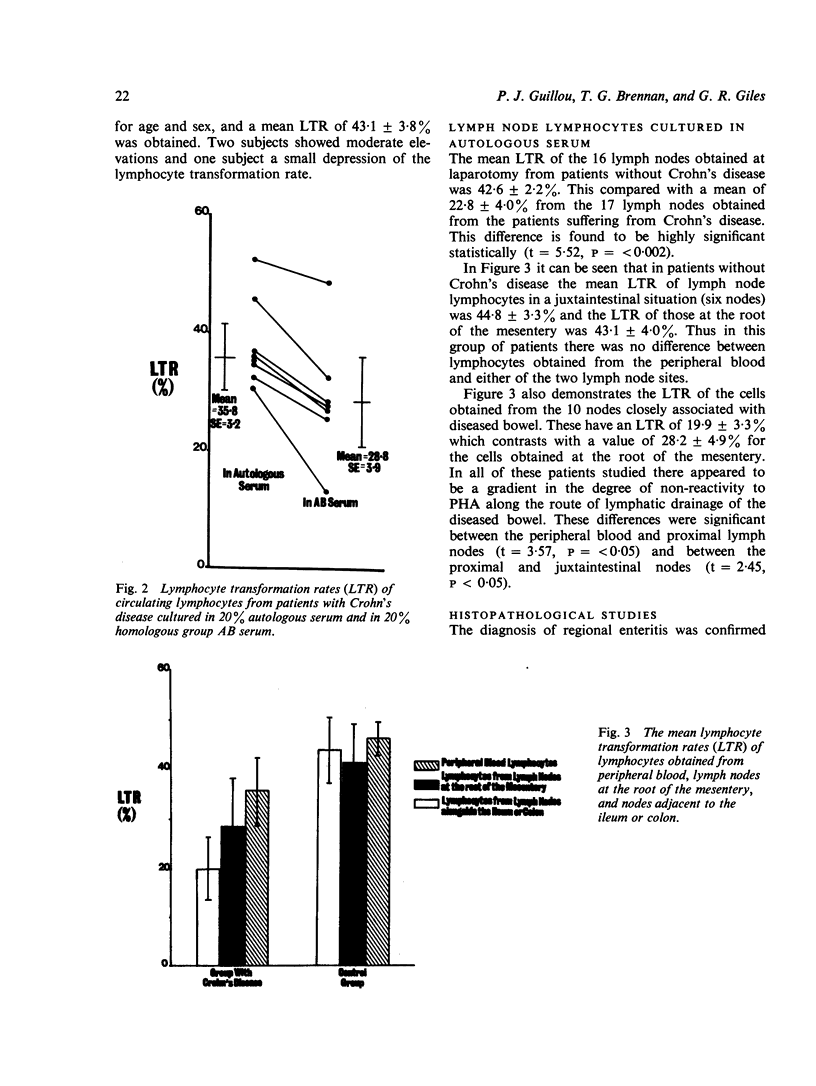
The response of lymphocytes from peripheral blood and mesenteric lymph nodes to stimulation with phytohaemagglutinin in vitro has been studied in eight patients suffering from active Crohn's disease. Patients with Crohn's disease exhibited reduced responses when compared with similar studies performed in control subjects. The impaired responses of circulating lymphocytes from these patients were marked on culture in autologous serum and were not improved by culture in homologous AB serum. Lymphocytes from lymph nodes directly draining diseased bowel exhibited lower responses than those from nodes at the root of the mesentery, which in turn were lower than those of circulating lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aas J., Huizenga A., Newcomer A. D., Shorter R. G. Inflammatory bowel disease: lymphocytic responses to nonspecific stimulation in vitro. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1972;7(4):299–303. doi: 10.3109/00365527209180746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Spiro H. M., Thayer W. R., Jr Delayed hypersensitivity in regional enteritis and ulcerative colitis. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Jul;11(7):572–574. doi: 10.1007/BF02233570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Taub R. N., Present D. H., Janowitz H. D. Short-term lymphocyte cultures in regional enteritis. Lancet. 1970 May 23;1(7656):1112–1112. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92776-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COULSON A. S., CHALMERS D. G. SEPARATION OF VIABLE LYMPHOCYTES FROM HUMAN BLOOD. Lancet. 1964 Feb 29;1(7331):468–469. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90799-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J., Hinton J. M. Tuberculin sensitivity in Crohn's disease. A controlled study. Lancet. 1967 Oct 7;2(7519):753–754. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91949-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. V., Housley J., Ashurst P. M., Hawkins C. F. Development of delayed hypersensitivity to dinitrochlorobenzene in patients with Crohn's disease. Gut. 1969 Jan;10(1):52–56. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHEAR D. N. The relation between regional ileitis and sarcoidosis. Lancet. 1958 Dec 13;2(7059):1250–1251. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)91387-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail M., Brown J. C., Holborow E. J. Immunoglobulins on the surface of human lymphocytes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 16;2(7729):850–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichert F. L., Mathes M. E. EXPERIMENTAL LYMPHEDEMA OF THE INTESTINAL TRACT AND ITS RELATION TO REGIONAL CICATRIZING ENTERITIS. Ann Surg. 1936 Oct;104(4):601–616. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193610440-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. R., Jr Crohn's disease (regional enteritis). A look at the last four years. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1970;6:165–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN PATTER W. N., BARGEN J. A., DOCKERTY M. B., FELDMAN W. H., MAYO C. W., WAUGH J. M. Regional enteritis. Gastroenterology. 1954 Mar;26(3):347–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN S., SOMMERS S. C. Cicatrizing enteritis as a pathologic entity; analysis of 120 cases. Am J Pathol. 1948 May;24(3):475–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. G., Greaves M. F. Delayed hypersensitivity and lymphocyte transformation in Crohn's disease and proctocolitis. Gut. 1969 May;10(5):414–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker M. G., Rees K., Clark C. G. Reduced lymphocyte transformation in breast cancer. Lancet. 1971 May 1;1(7705):892–893. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92448-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. J. The Laboratory Diagnosis of Crohn's Syndrome. Proc R Soc Med. 1963 Jun;56(6):490–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


