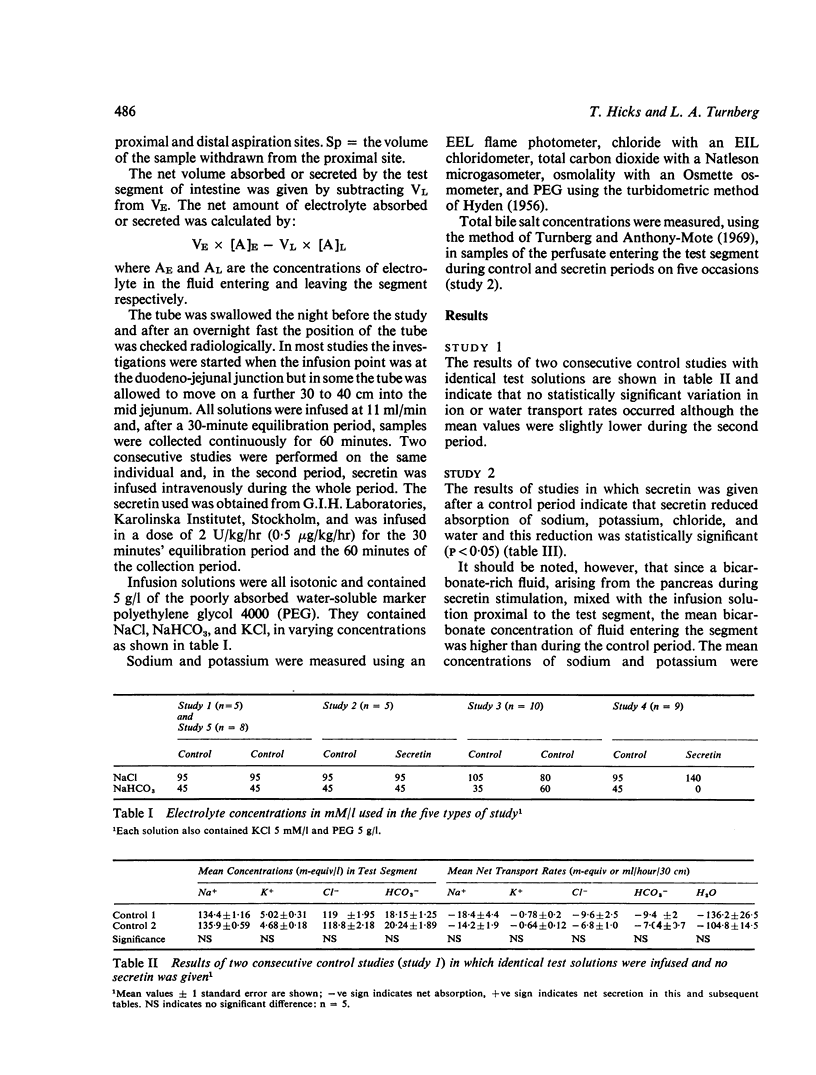
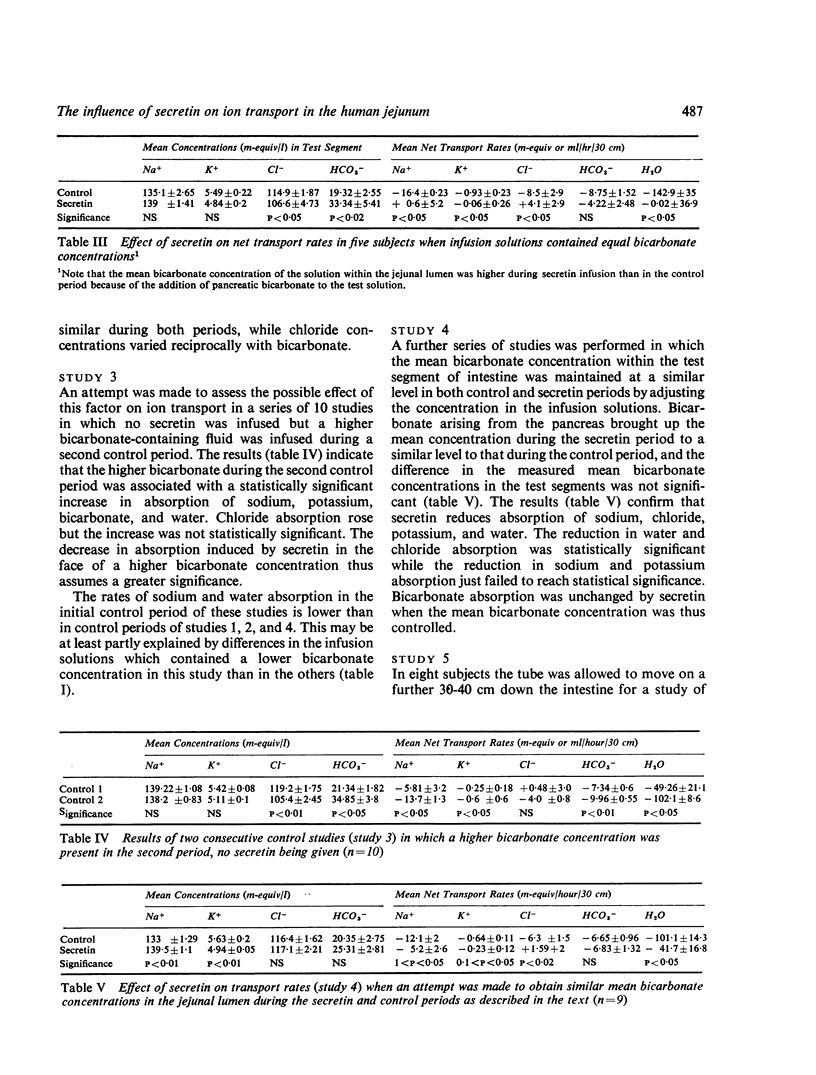
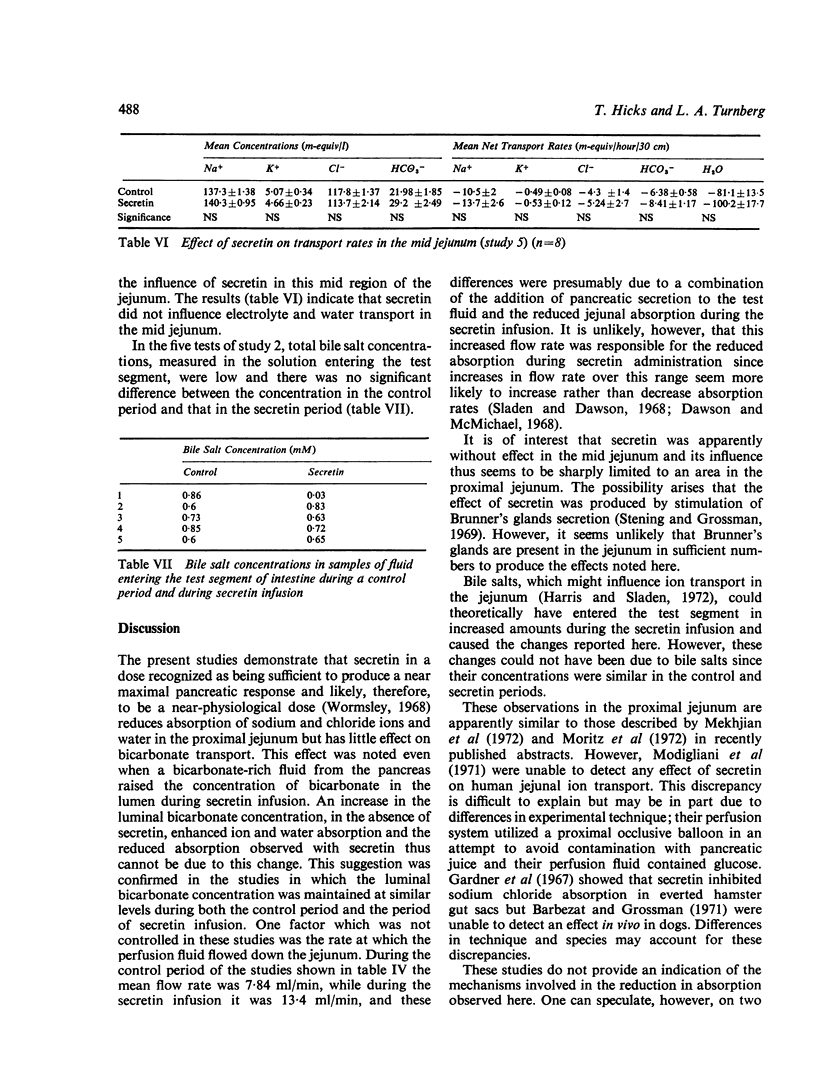
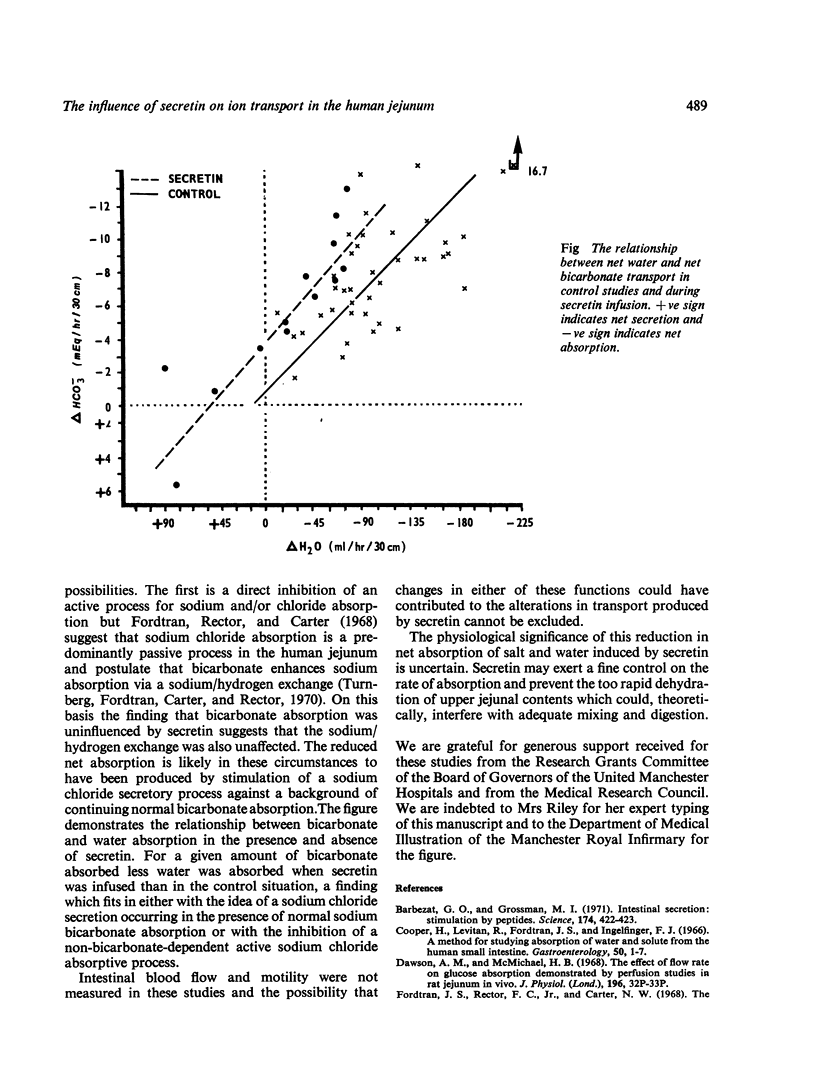
Abstract
Using a triple-lumen tube perfusion technique in normal human subjects secretin (2U/kg/hour intravenously) was shown to reduce the absorption of sodium, potassium, and chloride in the most proximal 30 cm of jejunum but it had no effect on bicarbonate absorption. This effect was not due to an artefact produced by the entry of secretin-stimulated, bicarbonate-rich, pancreatic juice into the test segment. Absorption of sodium chloride and water was stimulated rather than inhibited by higher bicarbonate concentrations and the effect of secretin was obvious even when this factor was controlled by adjusting the bicarbonate concentrations of the test fluids. Secretin did not influence ion transport in the mid-jejunum. It is suggested that the effects described may indicate a physiological role for secretin in the intestine where it could prevent the too rapid dehydration of upper jejunal contents which might interfere with adequate mixing and digestion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbezat G. O., Grossman M. I. Intestinal secretion: stimulation by peptides. Science. 1971 Oct 22;174(4007):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4007.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H., Levitan R., Fordtran J. S., Ingelfinger F. J. A method for studying absorption of water and solute from the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jan;50(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Carter N. W. The mechanisms of sodium absorption in the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):884–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI105781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Peskin G. W., Cerda J. J., Brooks F. P. Alterations of in vitro fluid and electrolyte absorption by gastrointestinal hormones. Am J Surg. 1967 Jan;113(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(67)90257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries J. T., Sladen G. E. The effects of different bile salts on the absorption of fluid, electrolytes, and monosaccharides in the small intestine of the rat in vivo. Gut. 1972 Aug;13(8):596–603. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.8.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONSON G., SUNDMAN L., THULIN L. THE INFLUENCE OF CHEMICALLY PURE SECRETIN ON HEPATIC BILE OUTPUT. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Nov;62:287–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1964.tb03976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. R., Grossman M. I. Intestinal hormones as inhibitors of gastric secretion. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jan;60(1):120–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modigliani R., Huet P. M., Rambaud J. C., Bernier J. J. Effect of secretin upon movements of water and electrolytes across the small intestine in man. Rev Eur Etud Clin Biol. 1971 Apr;16(4):361–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Dawson A. M. An evaluation of perfusion techniques in the study of water and electrolyte absorption in man: the problem of endogenous secretions. Gut. 1968 Oct;9(5):530–535. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.5.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stening G. F., Grossman M. I. Hormonal control of Brunner's glands. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jun;56(6):1047–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Anthony-Mote A. The quantitative determination of bile salts in bile using thin-layer chromatography and 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 May;24(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Fordtran J. S., Carter N. W., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):548–556. doi: 10.1172/JCI106265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormsley K. G. Response to secretin in man. Gastroenterology. 1968 Feb;54(2):197–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


