Abstract
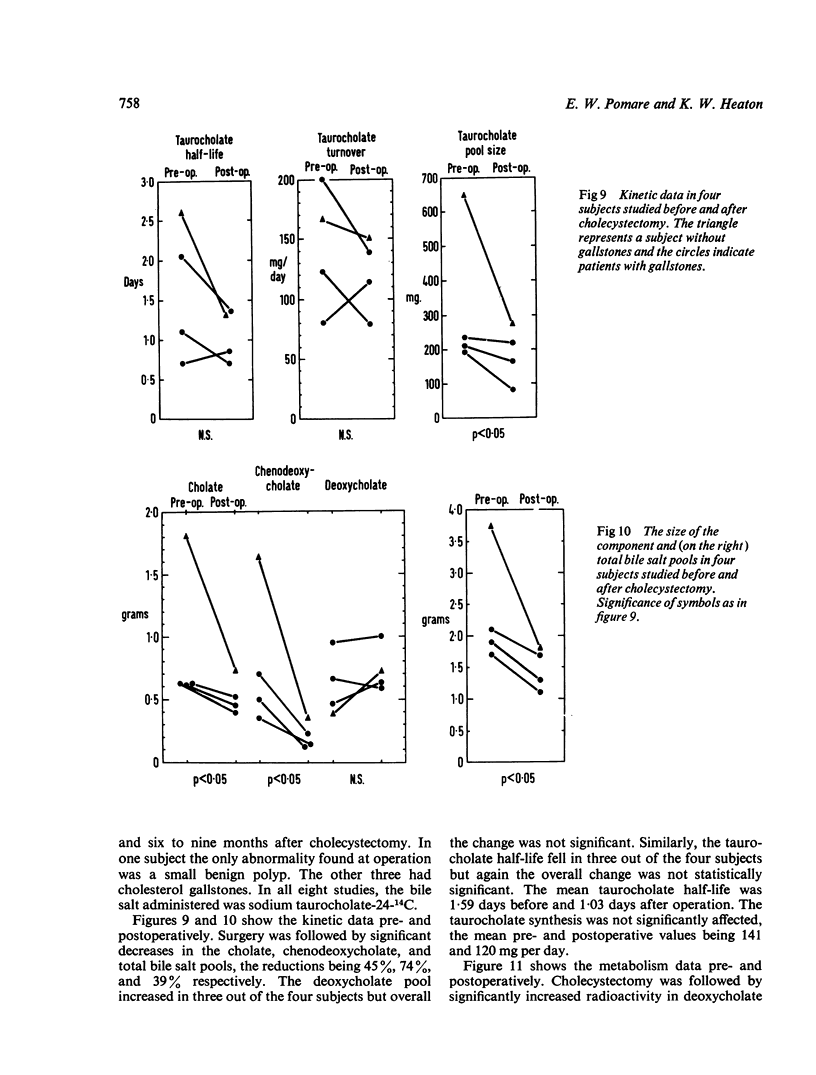
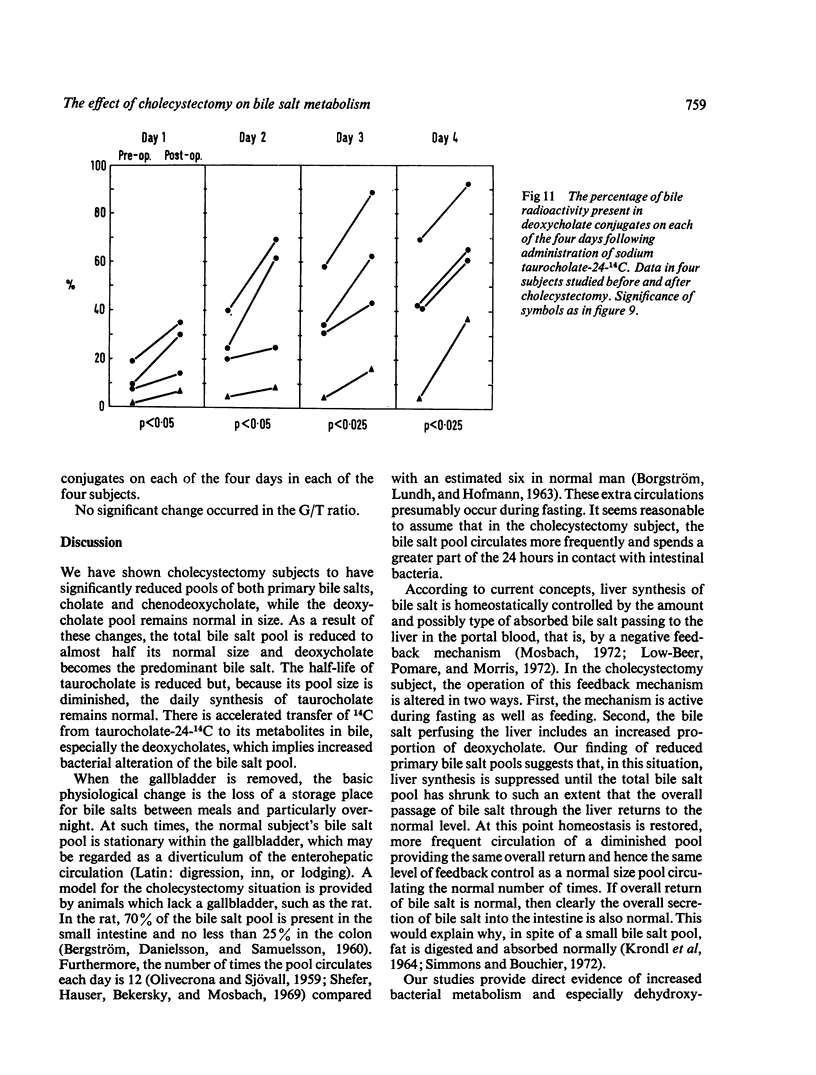
Isotopic bile salt studies have been performed in 13 cholecystectomy patients and 10 matched controls using labelled taurocholate and deoxycholic acid. Cholecystectomy subjects have reduced pools of both primary bile salts, cholate and chenodeoxycholate, while the deoxycholate pool remains normal in size. As a result of these changes, the total bile salt pool is reduced to almost half its normal size and deoxycholate becomes the predominant bile salt. The half-life of taurocholate is reduced but, because its pool size is diminished, the daily synthesis of taurocholate remains normal. There is accelerated transfer of 14C from taurocholate-24-14C to its metabolites in bile, especially deoxycholate conjugates. In four subjects studied pre- and postoperatively similar changes occurred in all the above parameters.
All these data can be explained by the fact that the bile salt pool circulates during fasting as well as during digestion. The consequences of this are (1) increased exposure of bile salts to intestinal bacteria and hence increased bacterial degradation; (2) continuous passage of the bile salt pool through the liver, and therefore continuous and presumably enhanced feedback inhibition of hepatic bile salt synthesis.
The reservoir function of the gallbladder influences the size, kinetics, metabolism, and composition of the bile salt pool. We suggest that no study of bile salt metabolism is complete without some assessment of gallbladder status.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austad W. I., Lack L., Tyor M. P. Importance of bile acids and of an intact distal small intestine for fat absorption. Gastroenterology. 1967 Apr;52(4):638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROEM B., LUNDH G., HOFMANN A. THE SITE OF ABSORPTION OF CONJUGATED BILE SALTS IN MAN. Gastroenterology. 1963 Aug;45:229–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruusgaard A. Quantitative determination of the major 3-hydroxy bile acids in biological material after thin-layer chromatographic separation. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Jun;28(3):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H. The enterohepatic circulation. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jan;62(1):122–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton K. W., Austad W. I., Lack L., Tyor M. P. Enterohepatic circulation of C14-labeled bile salts in disorders of the distal small bowel. Gastroenterology. 1968 Jul;55(1):5–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. II. Glycine-conjugated dihydroxy bile acids. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1898–1905. doi: 10.1172/JCI106992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRONDL A., VAVRINKOVA H., MICHALEC C. EFFECT OF CHOLECYSTECTOMY ON THE ROLE OF THE GALL BLADDER IN FAT ABSORPTION. Gut. 1964 Dec;5:607–610. doi: 10.1136/gut.5.6.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kottke B. A. Difference in bile acid excretion. Primary hypercholesteremia compared to combined hypercholesteremia and hypertriglyceridemia. Circulation. 1969 Jul;40(1):13–20. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.40.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Heaton K. W., Heaton S. T., Read A. E. Gallbladder inertia and sluggish enterohepatic circulation of bile-salts in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1971 May 15;1(7707):991–994. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91387-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Heaton K. W., Pomare E. W., Read A. E. The effect of coeliac disease upon bile salts. Gut. 1973 Mar;14(3):204–208. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.3.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Pomare E. W., Morris J. S. Control of bile salt synthesis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 16;238(85):215–216. doi: 10.1038/newbio238215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. S., Low-Beer T. S., Heaton K. W. Bile salt metabolism and the colon. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1973;8(5):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosbach E. H. Hepatic synthesis of bile acids. Biochemical steps and mechanisms of rate control. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):478–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVECRONA T., SJOVALL J. Bile acids in rat portal blood: bile acids and steroids 77. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Jun 24;46:284–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1959.tb01758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SJOVALL J. On the concentration of bile acids in the human intestine during absorption. Bile acids and sterioids 74. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Aug 31;46:339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1959.tb01763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer E. A., Braasch J. W., Small D. M. Bile composition at and after surgery in normal persons and patients with gallstones. Influence of cholecystectomy. N Engl J Med. 1972 Dec 28;287(26):1317–1322. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197212282872603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Bekersky I., Mosbach E. H. Feedback regulation of bile acid biosynthesis in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1969 Nov;10(6):646–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons F., Bouchier I. A. Intraluminal bile salt concentrations and fat digestion after cholecystectomy. S Afr Med J. 1972 Dec 30;46(52):2089–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons F., Ross A. P., Bouchier I. A. Alterations in hepatic bile composition after cholecystectomy. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(3):466–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Grahame G. Bile salt secretion in cirrhosis of the liver. Gut. 1970 Feb;11(2):126–133. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahcevic Z. R., Bell C. C., Jr, Buhac I., Farrar J. T., Swell L. Diminished bile acid pool size in patients with gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1970 Aug;59(2):165–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber J., Kottke B. A., Owen C. A., Jr Effect of nicotinic acid on pool size and turnover of taurocholic acid in normal and hypothyroid dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Aug-Sep;122(4):1070–1075. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber J., Kottke B. A., Owen C. A., Jr Pool size and turnover of bile acids in six hypercholesteremic patients with and without administration of nicotinic acid. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):584–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


