Abstract
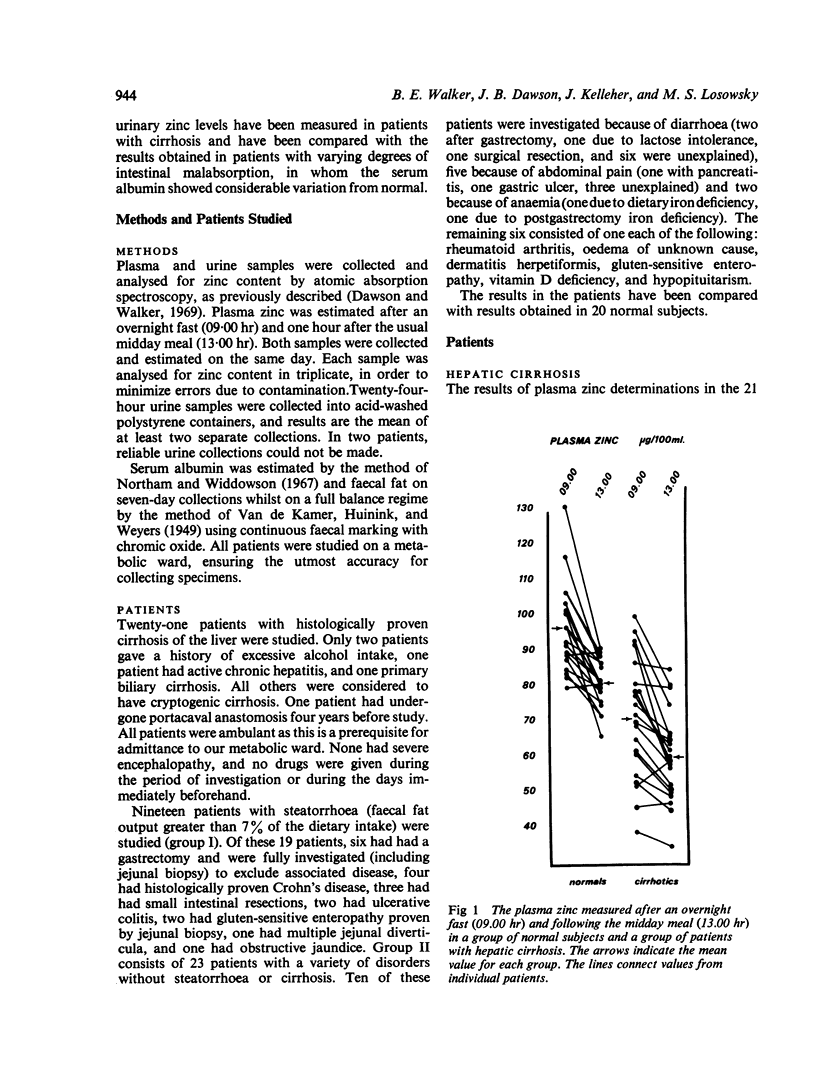
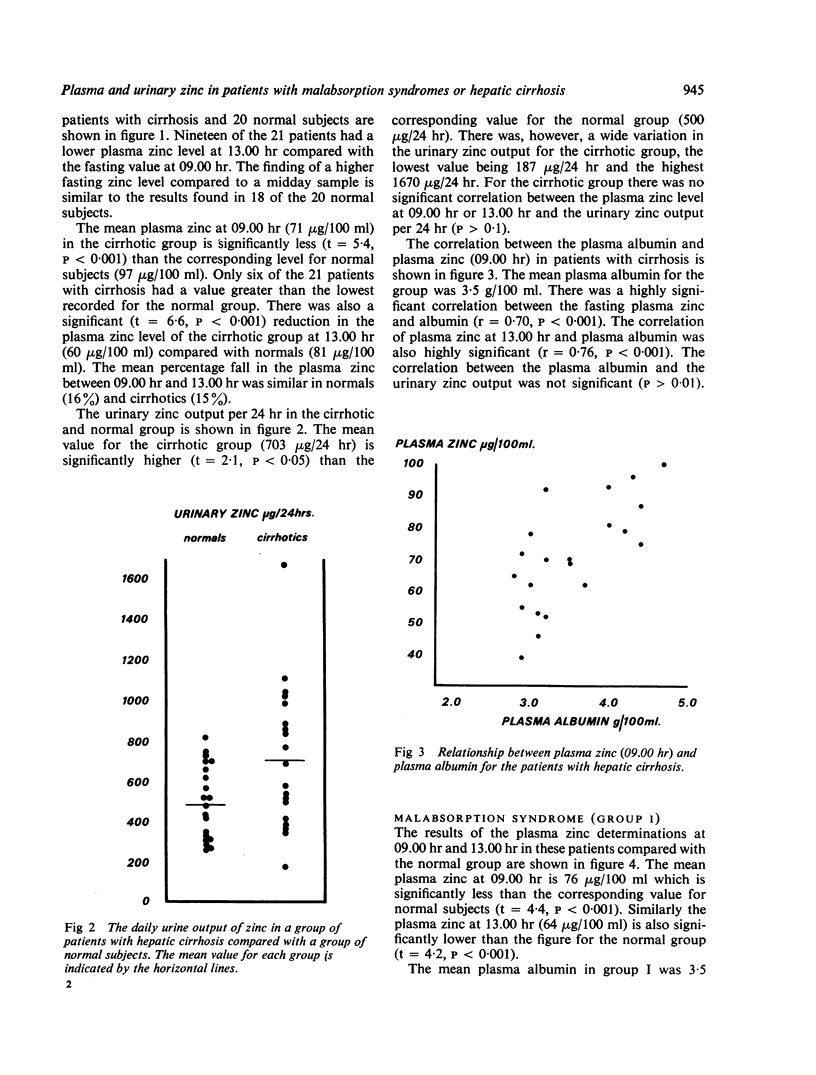
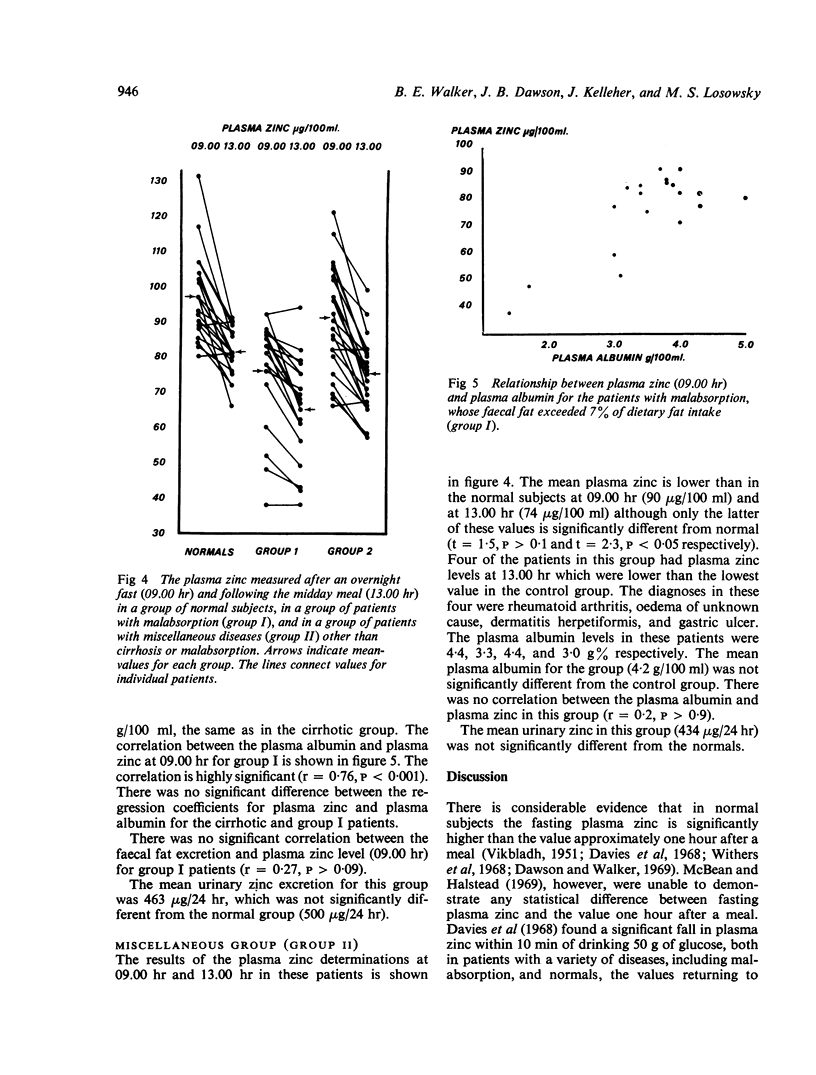
Plasma and urinary zinc have been measured in 19 patients with malabsorption and 21 patients with hepatic cirrhosis. The results have been compared with those of 20 control subjects and 23 patients with a variety of other diseases. The diurnal variation in plasma zinc levels has been confirmed and is of such magnitude that this must be taken into account in comparing results in groups of subjects. Plasma zinc levels, both fasting and after a meal, are significantly lower in patients with cirrhosis (71 and 60 μg/100 ml) and malabsorption (76 and 64 μg/100 ml) than in controls (97 and 81 μg/100 ml). In the patients with cirrhosis or malabsorption similar correlations exist between plasma zinc and plasma albumin, suggesting that the low plasma zinc levels may be, at least in part, dependent on the plasma albumin level. Urinary zinc excretion is increased in cirrhosis, but not in malabsorption, indicating that increased urinary loss is unlikely to explain the low plasma levels.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTHOLOMAY A. F., ROBIN E. D., VALLEE R. L., WACKER W. E. Zinc metabolism in hepatic dysfunction. I. Serum zinc concentrations in Laënnec's cirrhosis and their validation by sequential analysis. N Engl J Med. 1956 Aug 30;255(9):403–408. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195608302550901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyett J. D., Sullivan J. F. Distribution of protein-bound zinc in normal and cirrhotic serum. Metabolism. 1970 Feb;19(2):148–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyett J. D., Sullivan J. F. Zinc and collagen content of cirrhotic liver. Am J Dig Dis. 1970 Sep;15(9):797–802. doi: 10.1007/BF02236039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies I. J., Musa M., Dormandy T. L. Measurements of plasma zinc. II. In malignant disease. J Clin Pathol. 1968 May;21(3):363–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. B., Walker B. E. Direct determination of zinc in whole blood, plasma and urine by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Dec;26(3):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDRICKS R. E., TANAKA K. R., VALENTINE W. N. Zinc in human blood cells: normal values and abnormalities associated with liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1960 Nov;39:1651–1656. doi: 10.1172/JCI104188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Boyde T. R. Plasma-zinc concentrations in patients with psoriasis, other dermatoses, and venous leg ulceration. Lancet. 1967 Nov 11;2(7524):1019–1020. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. D., Lehmann B. H. Serum zinc and copper concentrations in children with protein-calorie malnutrition. S Afr Med J. 1969 Oct 11;43(41):1248–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henzel J. H., DeWeese M. S., Pories W. J. Significance of magnesium and zinc metabolism in the surgical patient. II. Zinc. Arch Surg. 1967 Dec;95(6):991–999. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1967.01330180139023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEEJEEBHOY K. N. HYPOANABOLIC HYPOALBUMINAEMIA IN GASTRO-INTESTINAL DISEASE. Br Med J. 1964 Jan 4;1(5374):30–35. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5374.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. M., Helwig H. L., Redeker A. G., Reynolds T. B. Urine and serum zinc abnormalities in disease of the liver. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Oct;44(4):426–435. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.4.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losowsky M. S., Walker B. E. Liver disease and malabsorption. Gastroenterology. 1969 Mar;56(3):589–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon R. A., Parker M. L., McKinnon M. C. Zinc treatment in malabsorption. Med J Aust. 1968 Aug 3;2(5):210–212. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1968.tb82733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBean L., Halsted J. A. Fasting versus postprandial plasma zinc levels. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Sep;22(5):623–623. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.5.623-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. P., Jemec B. Zinc metabolism in patients with severe burns. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1968;2(1):47–52. doi: 10.3109/02844316809026205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SULLIVAN J. F., LANKFORD H. G. ZINC METABOLISM AND CHRONIC ALCOHOLISM. Am J Clin Nutr. 1965 Aug;17:57–63. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/17.2.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SULLIVAN J. F. The relation of zincuria to water and electrolyte excretion in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1962 Apr;42:439–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. F., Heaney R. P. Zinc metabolism in alcoholic liver disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Feb;23(2):170–177. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLEE B. L., WACKER W. E., BARTHOLOMAY A. F., HOCH F. L. Zinc metabolism in hepatic dysfunction. II. Correlation of metabolic patterns with biochemical findings. N Engl J Med. 1957 Nov 28;257(22):1055–1065. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195711282572201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIKBLADH I. Studies on zinc in blood II. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1951;3 (Suppl 2):1–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON P., MENDENHALL C. L. SERUM ALBUMIN TURNOVER IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS MEASURED BY 131I-LABELLED HUMAN ALBUMIN. Clin Sci. 1963 Oct;25:281–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers A. F., Baker H., Musa M., Dormandy T. L. Plasma-zinc in psoriasis. Lancet. 1968 Aug 3;2(7562):278–278. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


