Abstract
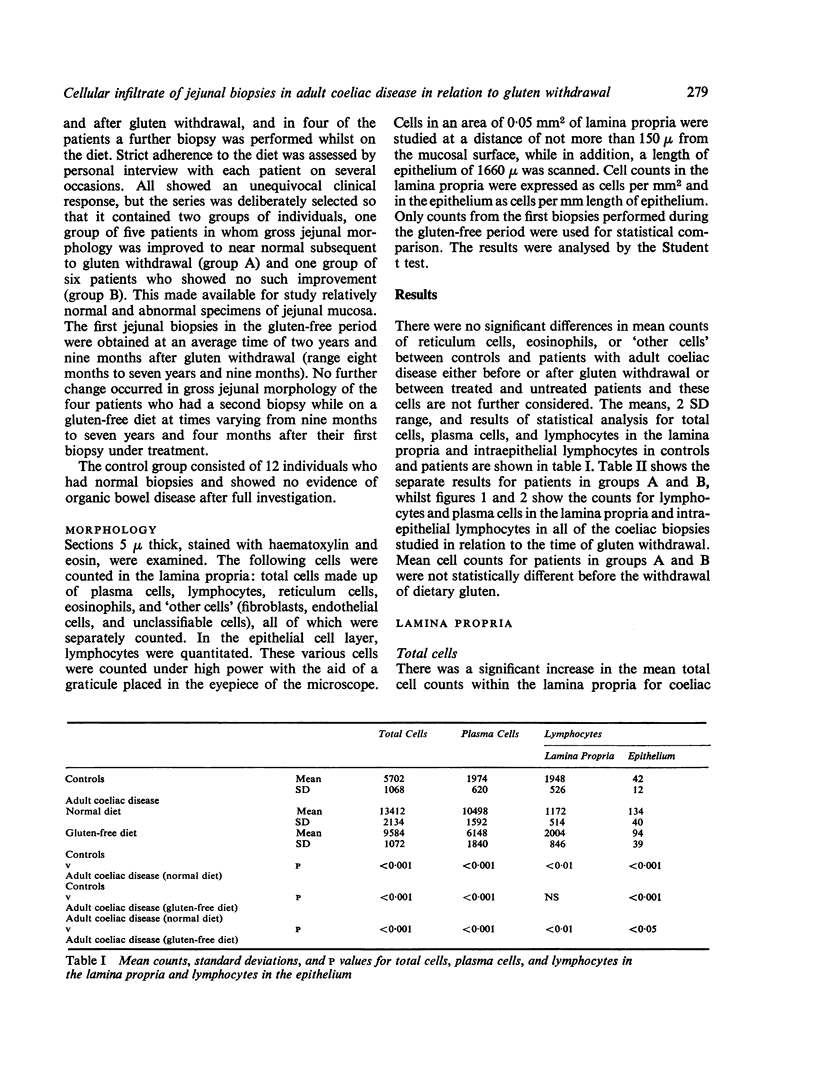
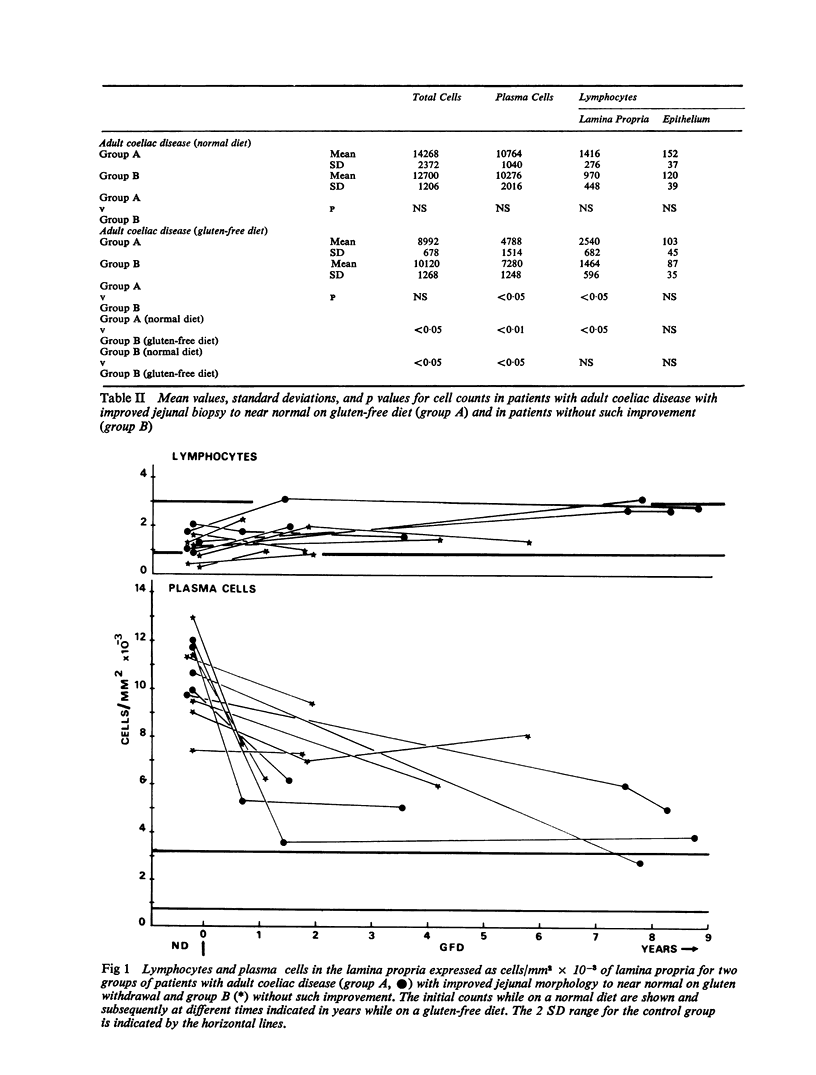
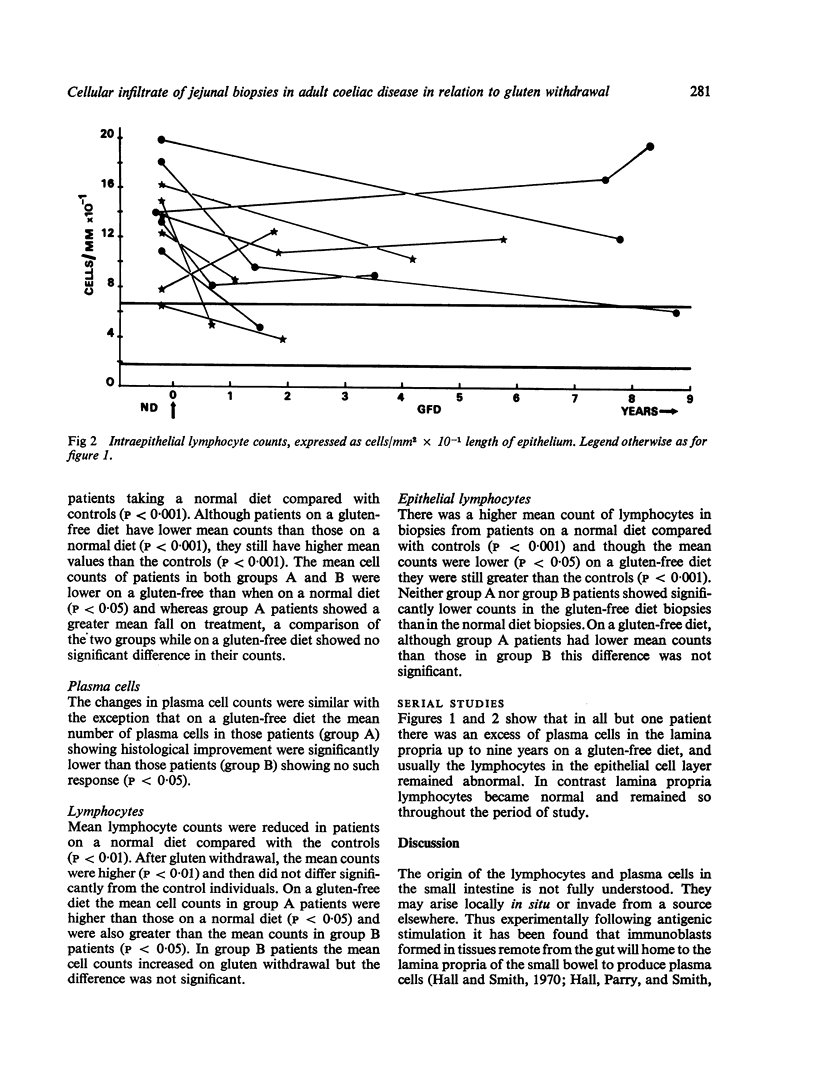
A comparison has been made of inflammatory cell counts in the lamina propria and epithelium of jejunal biopsies in 11 patients with adult coeliac disease with those found in 12 control subjects. In the coeliac patients, there were significant increases in the numbers of total cells, plasma cells, and intraepithelial lymphocytes, but a significant reduction in lamina propria lymphocytes. Following clinical improvement on a strict gluten-free diet, significant changes in cell counts occurred, but with the exception of lymphocytes in the lamina propria, the counts were still abnormal. Analysis of five patients in whom the biopsy improved to near normal morphology and of six in whom there was no such improvement showed that significant falls in plasma cells and rises in lymphocytes in the lamina propria could occur without improvement in other morphological appearances. These results seem relevant to the problem of diagnosing coeliac disease in patients who, on gluten withdrawal, show an unequivocal clinical response, but no gross morphological improvement in the jejunal biopsy. On the basis of the observed changes in cell counts, there seems little justification in questioning the diagnosis of coeliac disease in such patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON C. M. Histological changes in the duodenal mucosa in coeliac disease. Reversibility during treatment with a wheat gluten free diet. Arch Dis Child. 1960 Oct;35:419–427. doi: 10.1136/adc.35.183.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austad W. I., Cornes J. S., Gough K. R., McCarthy C. F., Read A. E. Steatorrhea and malignant lymphoma. The relationship of malignant tumors of lymphoid tissue and celiac disease. Am J Dig Dis. 1967 May;12(5):475–490. doi: 10.1007/BF02233180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLT R. J., PARRISH J. A., FRENCH A. B., POLLARD H. M. ADULT COELIAC DISEASE. HISTOLOGIC RESULTS OF LONG-TERM LOW GLUTEN DIET. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Apr;60:581–586. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-4-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHAN D. J., GERRARD J. W. Celiac disease. Problems in diagnosis and effects of a gluten free diet. Ann Intern Med. 1962 Jul;57:85–95. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-57-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONIACH I., SHINER M. Histopathology of the stomach in pernicious anaemia and jejunum in steatorrhoea. Br J Radiol. 1960 Apr;33:238–242. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-33-388-238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Carswell F. Precipitins to dietary proteins in serum and upper intestinal secretions of coeliac children. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 8;1(5792):75–77. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5792.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Murray D. Quantitation of intraepithelial lymphocytes in human jejunum. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):988–994. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry L., Seah P. P., McMinn R. M., Hoffbrand A. V. Lymphocytic infiltration of epithelium in diagnosis of gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Br Med J. 1972 Aug 12;3(5823):371–374. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5823.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Parry D. M., Smith M. E. The distribution and differentiation of lymph-borne immunoblasts after intravenous injection into syngeneic recipients. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1972 May;5(3):269–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1972.tb00365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Smith M. E. Homing of lymph-borne immunoblasts to the gut. Nature. 1970 Apr 18;226(5242):262–263. doi: 10.1038/226262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris O. D., Cooke W. T., Thompson H., Waterhouse J. A. Malignancy in adult coeliac disease and idiopathic steatorrhoea. Am J Med. 1967 Jun;42(6):899–912. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD W. C., BRANDBORG L. L., FLICK A. L., TRIER J. S., RUBIN C. E. STUDIES OF CELIAC SPRUE. IV. THE RESPONSE OF THE WHOLE LENGTH OF THE SMALL BOWEL TO A GLUTEN-FREE DIET. Gastroenterology. 1964 Dec;47:573–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meader R. D., Landers D. F. Electron and light microscopic observations on relationships between lymphocytes and intestinal epithelium. Am J Anat. 1967 Nov;121(3):763–773. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULLEY J. W. Observation on the aetiology of idiopathic steatorrhoea; jejunal and lymph-node biopsies. Br Med J. 1954 Dec 4;2(4900):1318–1321. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4900.1318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pink I. J., Croft D. N., Creamer B. Cell loss from small intestinal mucosa: a morphological study. Gut. 1970 Mar;11(3):217–222. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.3.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN C. E., BRANDBORG L. L., FLICK A. L., PHELPS P., PARMENTIER C., VAN NIEL S. Studies of celiac sprue. III. The effect of repeated wheat instillation into the proximal ileum of patients on a gluten free diet. Gastroenterology. 1962 Dec;43:621–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN C. E., BRANDBORG L. L., PHELPS P. C., TAYLOR H. C., Jr Studies of celiac disease. I. The apparent identical and specific nature of the duodenal and proximal jejunal lesion in celiac disease and idiopathic sprue. Gastroenterology. 1960 Jan;38:28–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUFFIN J. M., KURTZ S. M., BORLAND J. L., Jr, BAIN C. R., ROUFAIL W. M. GLUTEN-FREE DIET FOR NONTROPICAL SPRUE. IMMEDIATE AND PROLONGED EFFECTS. JAMA. 1964 Apr 6;188:42–44. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060270048011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHINER M. EFFECT OF A GLUTEN-FREE DIET IN 17 PATIENTS WITH IDIOPATHIC STEATORRHEA; A FOLLOW-UP STUDY. Am J Dig Dis. 1963 Dec;8:969–983. doi: 10.1007/BF02239489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR K. B., TRUELOVE S. C., THOMSON D. L., WRIGHT R. An immunological study of coeliac disease and idiopathic steatorrhoea. Serological reactions to gluten and milk proteins. Br Med J. 1961 Dec 30;2(5269):1727–1731. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5269.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THURLBECK W. M., BENSON J. A., Jr, DUDLEY H. R., Jr The histopathologic changes of sprue and their significance. Am J Clin Pathol. 1960 Aug;34:108–117. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/34.2.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toner P. G., Ferguson A. Intraepithelial cells in the human intestinal mucosa. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Feb;34(3):329–344. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YARDLEY J. H., BAYLESS T. M., NORTON J. H., HENDRIX T. R. Celiac disease. A study of the jejunal epithelium before and after a gluten-free diet. N Engl J Med. 1962 Dec 6;267:1173–1179. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196212062672303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


