Abstract
The toxicity of three fractions (A, B, and C) obtained by ultrafiltration of a peptic: tryptic digest of gluten has been assessed by serial feeding experiments in patients with treated coeliac disease.
The first fraction (A), which contains amino acids and oligopeptides, produced no damage to the jejunal mucosa.
The other two fractions (B and C) both caused mucosal damage.
Fraction B, which contains the products of digestion of smaller molecular weight, consists of polypeptides which are concentrated in the region of 8000 molecular weight. It contains no gliadin (molecular weight 50 000) or gluten.
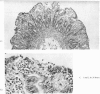
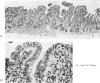
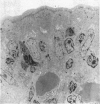
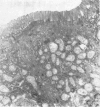
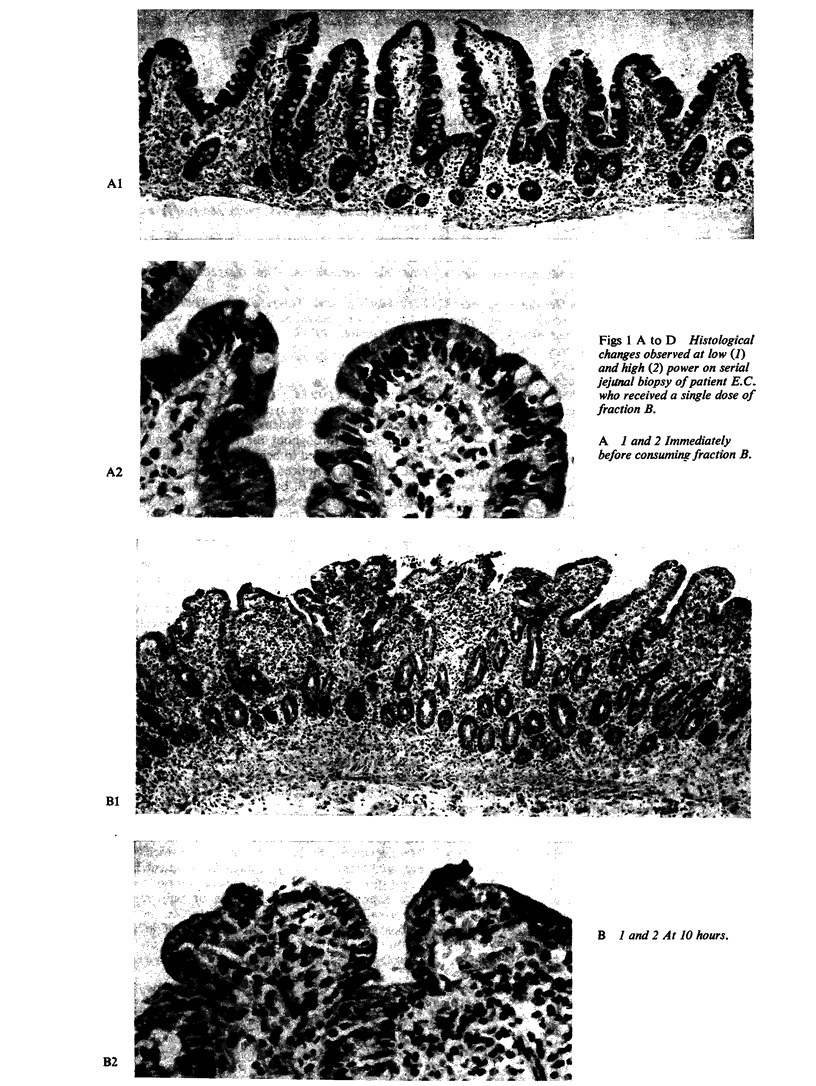
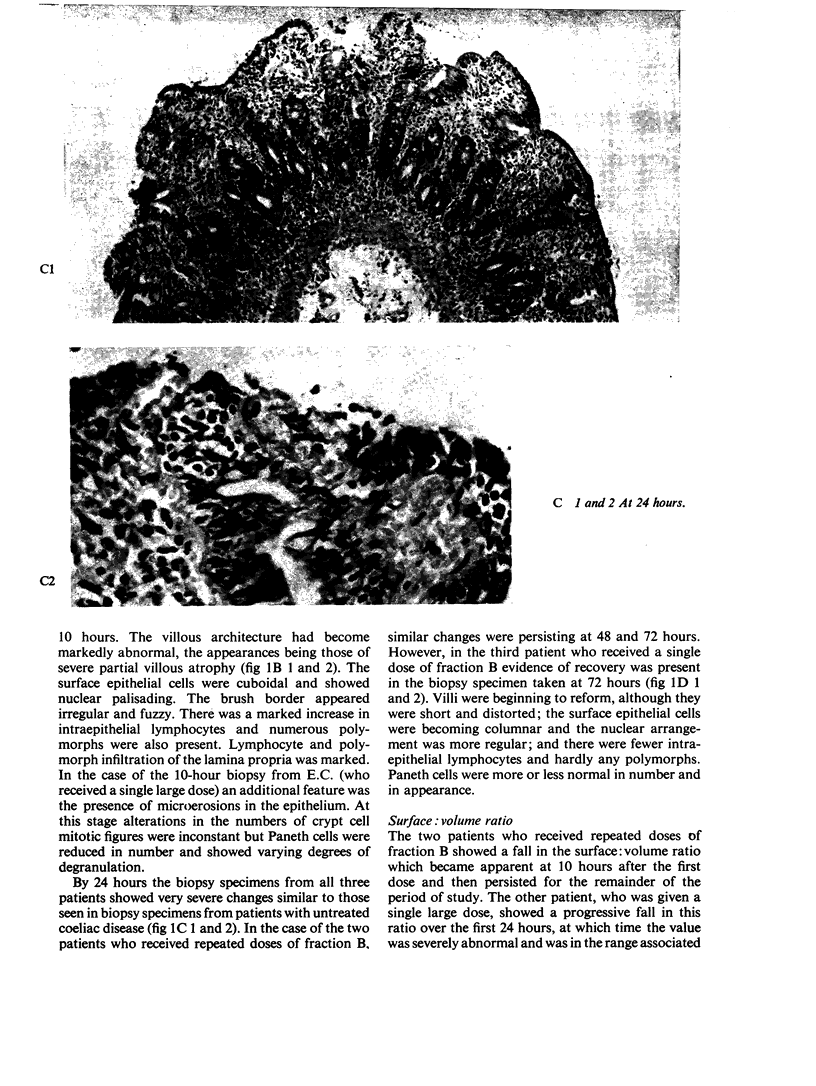
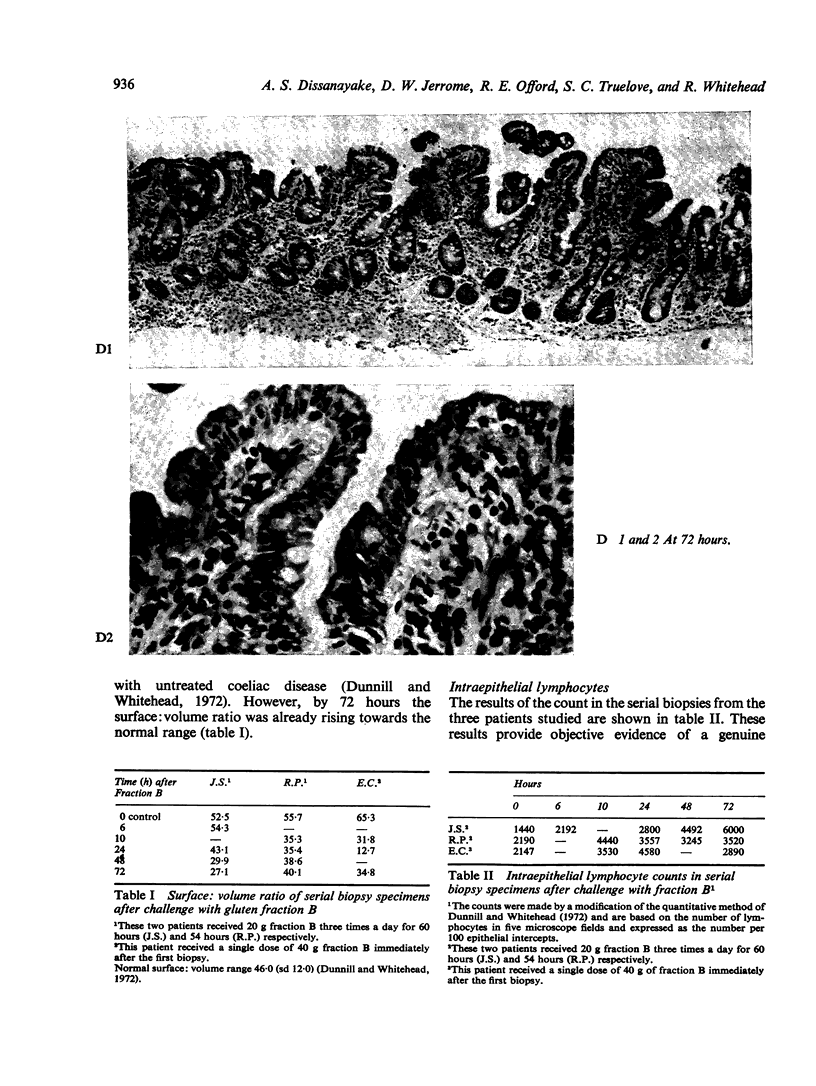
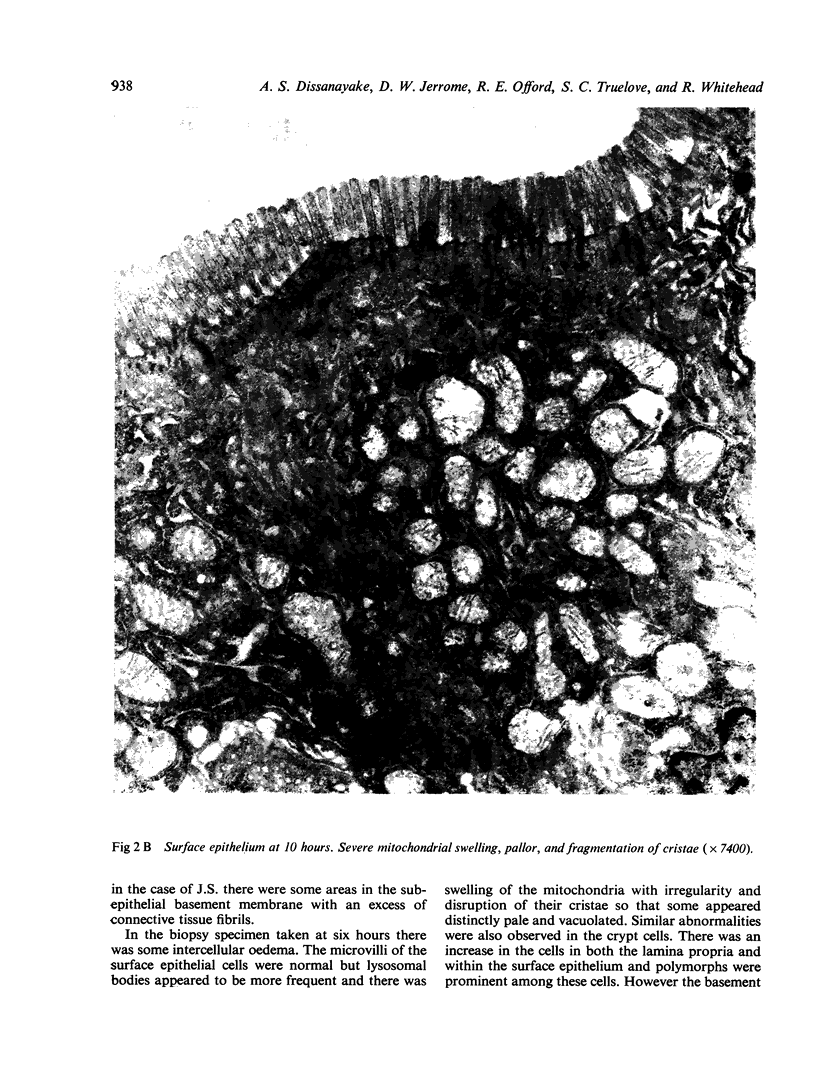
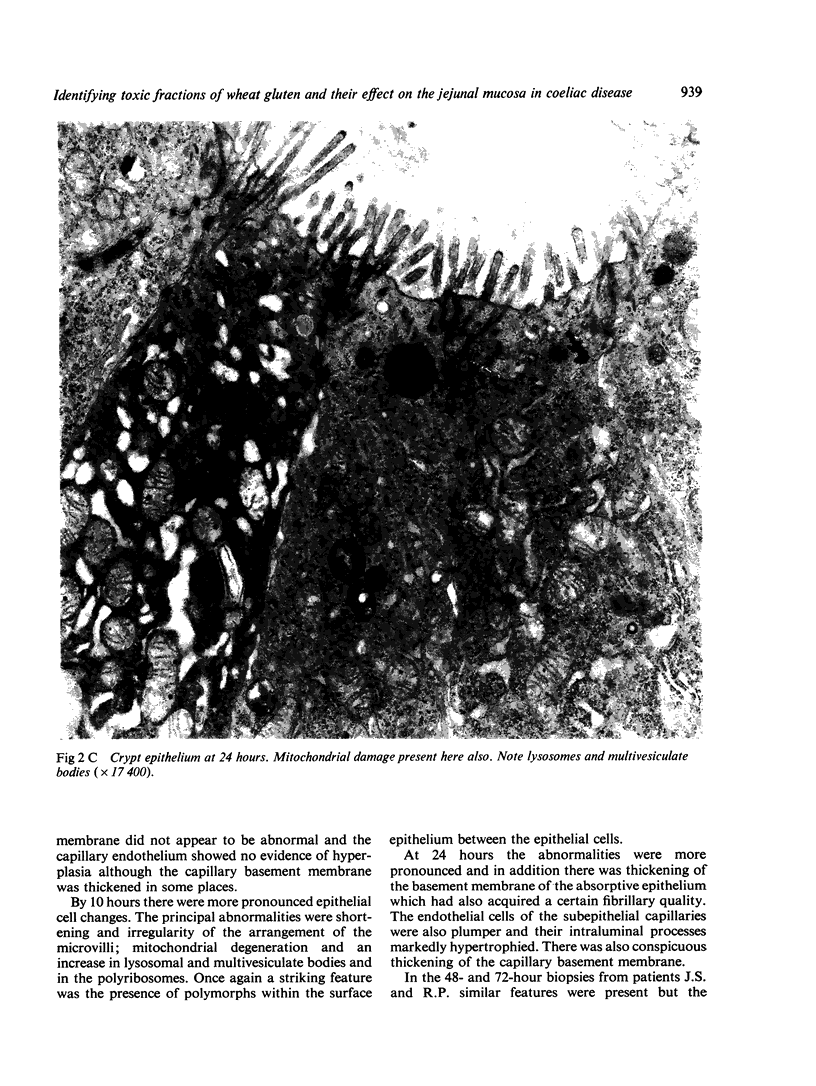
Ultrastructural evidence of damage was visible six hours after challenge with fraction B and by 10 hours histological abnormalities were also present.
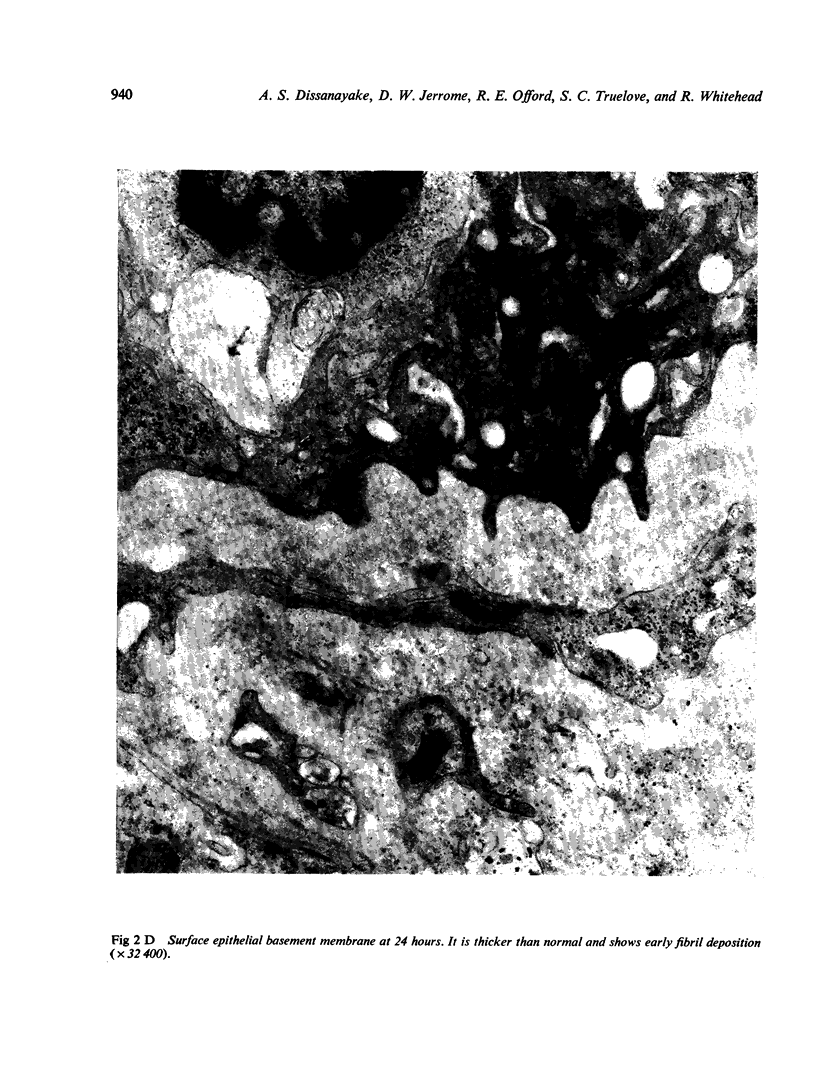
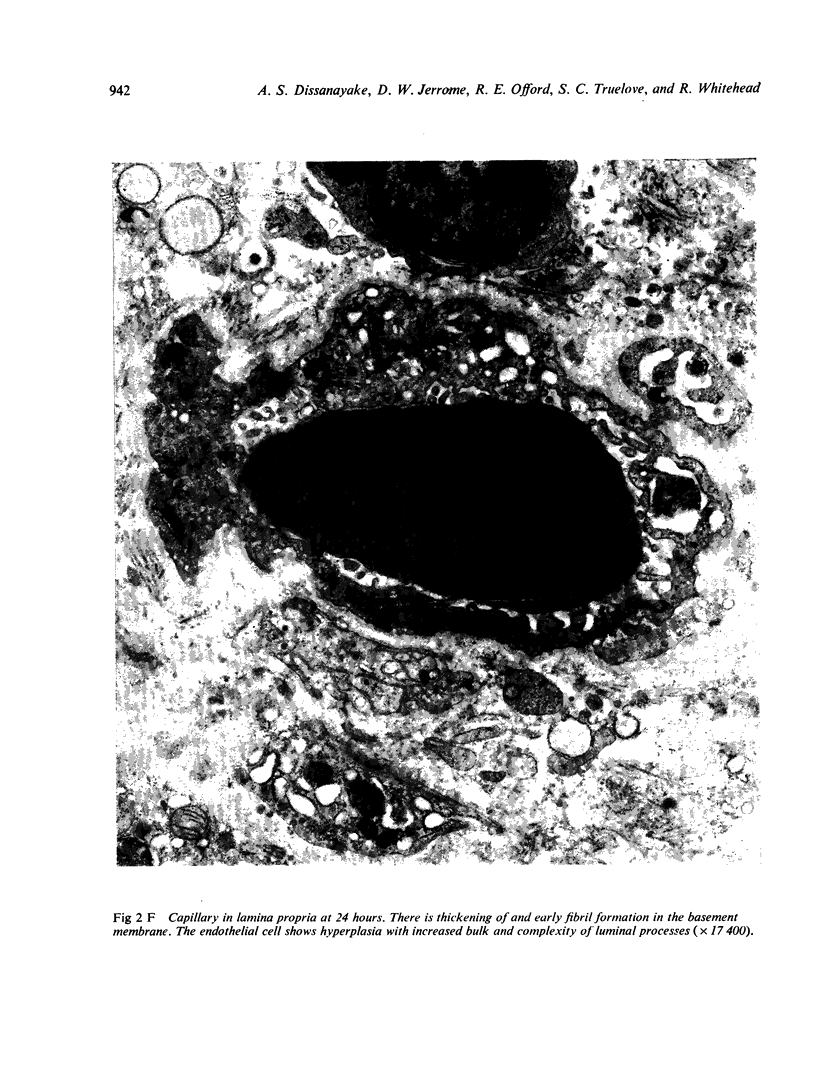
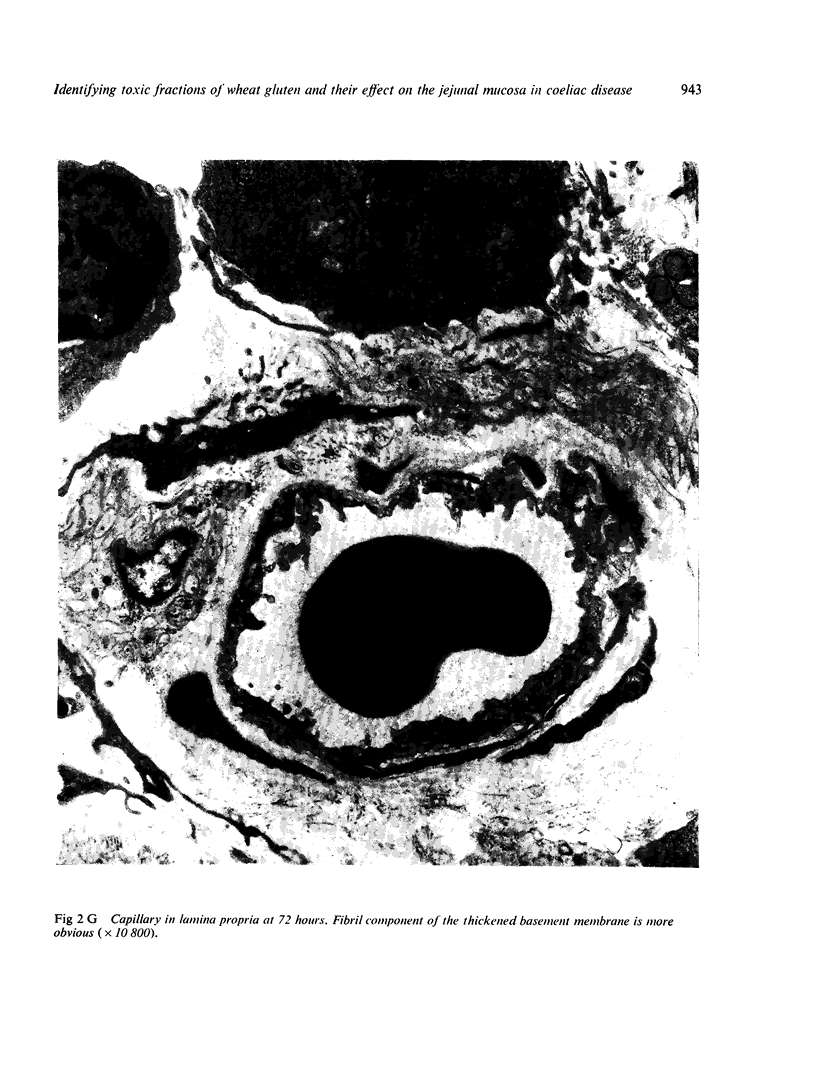
Ultrastructural abnormalities occurred early in the epithelial cells and preceded changes in the basement membrane and capillaries.
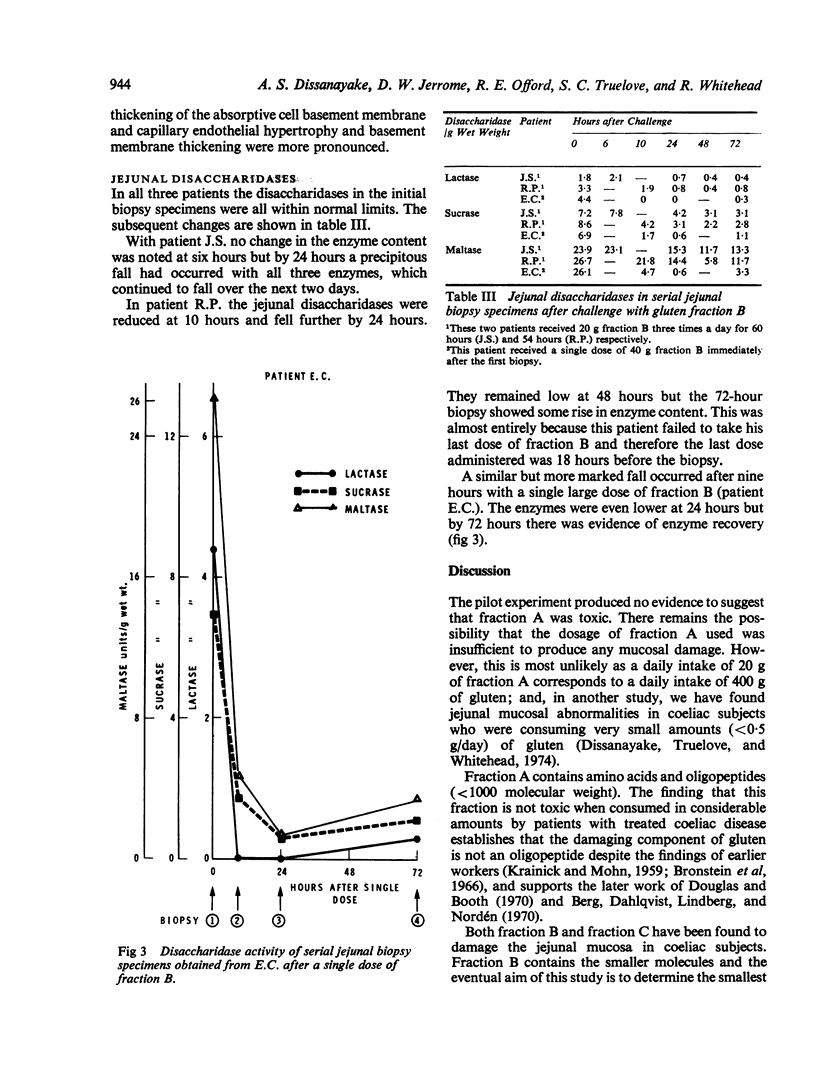
The disaccharidases showed a pronounced depression in all three subjects by 24 hours.
The rapid onset of damage after challenge, coupled with the evidence of recovery as soon as 72 hours later, is more in keeping with a direct action on the surface epithelial cells rather than an immune mechanism.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVEY C., ANDERSON C. M., FREEMAN M. Wheat gluten and coeliac disease. Arch Dis Child. 1957 Oct;32(165):434–437. doi: 10.1136/adc.32.165.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGESS E. A., LEVIN B., MAHALANABIS D., TONGE R. E. HEREDITARY SUCROSE INTOLERANCE: LEVELS OF SUCRASE ACTIVITY IN JEJUNAL MUCOSA. Arch Dis Child. 1964 Oct;39:431–443. doi: 10.1136/adc.39.207.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg N. O., Dahlqvist A., Lindberg T., Nordén A. Intestinal dipeptidases and disaccharidases in celiac disease in adults. Gastroenterology. 1970 Oct;59(4):575–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronstein H. D., Haeffner L. J., Kowlessar O. D. Enzymatic digestion of gliadin: the effect of the resultant peptides in adult celiac disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Aug;14(2):141–155. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake A. S., Truelove S. C., Whitehead R. Jejunal mucosal recovery in coeliac disease in relation to the degree of adherence to a gluten-free diet. Q J Med. 1974 Apr;43(170):161–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas A. P., Booth C. C. Digestion of gluten peptides by normal human jejunal mucosa and by mucosa from patients with adult coeliac disease. Clin Sci. 1970 Jan;38(1):11–25. doi: 10.1042/cs0380011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnill M. S., Whitehead R. A method for the quantitation of small intestinal biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Mar;25(3):243–246. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.3.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAZER A. C., FLETCHER R. F., ROSS C. A., SHAW B., SAMMONS H. G., SCHNEIDER R. Gluten-induced enteropathy: the effect of partially digested gluten. Lancet. 1959 Sep 5;2(7097):252–255. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)92051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G., Offord R. E. The subunit structure of prealbumin. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):309–317. doi: 10.1042/bj1250309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James W. P., Alpers D. H., Gerber J. E., Isselbacher K. J. The turnover of disaccharidases and brush border proteins in rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 23;230(2):194–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAINICK H. G., MOHN G. Weitere Untersuchungen über den schädlichen Weizenmehleffekt bei der Cöliakie. 2. Die Wirkung der enzymatischen Abbauprodukte des Gliadin. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1959 Jun;14(2):124–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall M. J., Schneider R., Cox P. S., Hawkins C. F. Gluten subfractions in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1065–1067. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Grady G. F., Takeuchi A., Sprinz H. The pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea. II. Enterotoxin-induced acute enteritis in the rabbit ileum. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):92–95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan K. A., Vogel M., Lawrence J. M. Disk electrophoresis of wheat flour proteins with a modified apparatus utilizing gels of rectangular cross section. Anal Biochem. 1965 Sep;12(3):526–541. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALEM S. N., SALT R. H., TRUELOVE S. C. CROSBY SMALL-INTESTINAL CAPSULE WITH RADIO-OPAQUE TUBE AND LATEX SHEATH. Gut. 1965 Feb;6:99–100. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiner M., Shmerling D. H. The immunopathology of coeliac disease. Digestion. 1972;5(2):69–88. doi: 10.1159/000197178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiner M. Ultrastructural changes suggestive of immune reactions in the jejunal mucosa of coeliac children following gluten challenge. Gut. 1973 Jan;14(1):1–12. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townley R. R., Cornell H. J., Bhathal P. S., Mitchell J. D. Toxicity of wheat gliadin fractions in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1973 Jun 16;1(7816):1363–1364. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91679-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DE KAMER J. H., WEIJERS H. A., DICKE W. K. Coeliac disease. IV. An investigation into the injurious constituents of wheat in connection with their action on patients with coeliac disease. Acta Paediatr. 1953 May;42(3):223–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1953.tb05586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van ROON J., HAEX A. J., SEEDER W. A., de JONG Clinical and biochemical analysis of gluten toxicity. I. Experientia. 1960 May 15;16:209–209. doi: 10.1007/BF02178994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]