Abstract
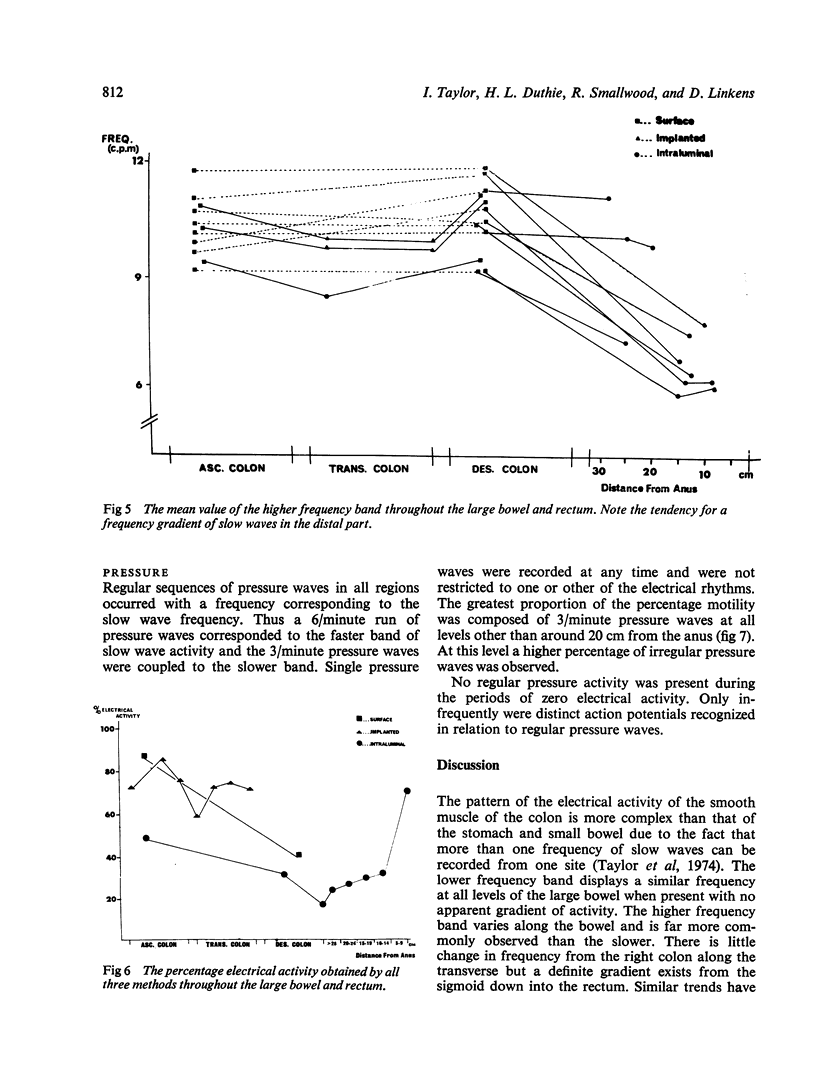
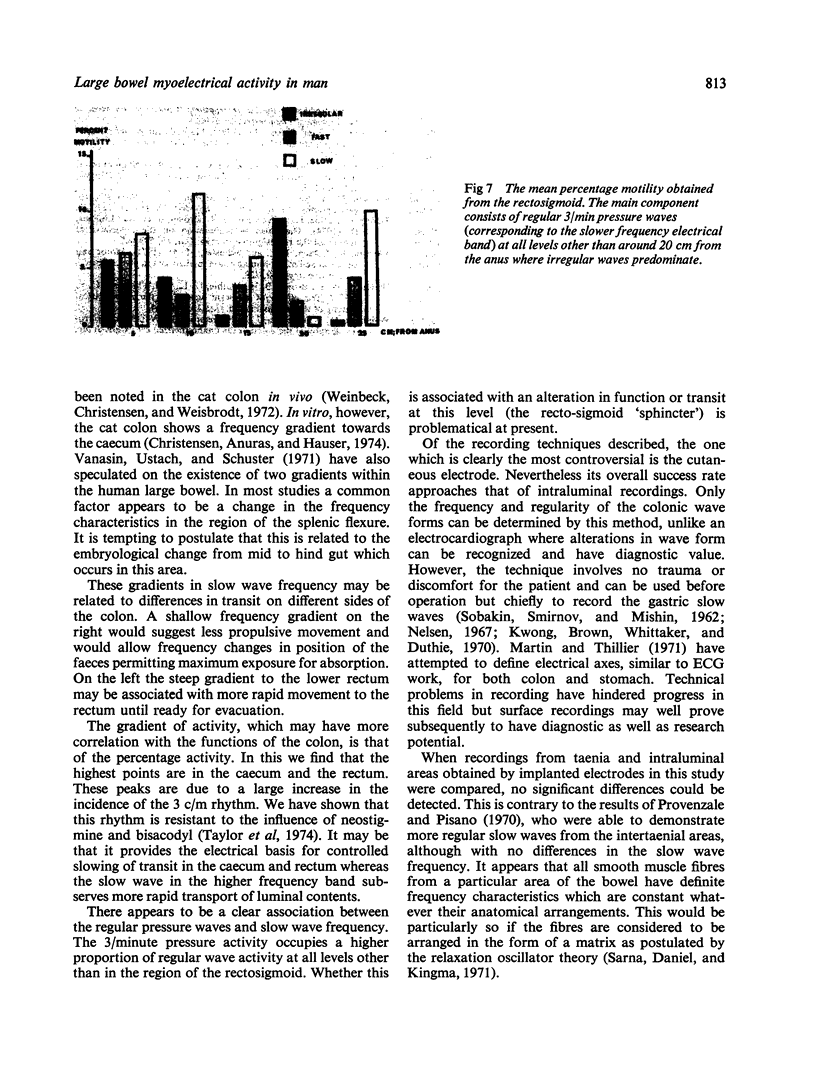
The myoelectrical activity of human colon and rectum has been studied by three types of electrode in man--intraluminal (suction), serosal and cutaneous. The patterns obtained indicate a high degree of consistency between the methods and the value of surface electrodes is emphasized. Gradient along the large bowel of both frequency and percentage electrical activity have been observed and possible physiological roles are postulated for them. By correlating the features of regular electrical and corresponding regular motor waves an alteration in the myoelectrical pattern is observed in the region of the rectosigmoid junction.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BASS P., CODE C. F., LAMBERT E. H. Motor and electric activity of the duodenum. Am J Physiol. 1961 Aug;201:287–291. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Anuras S., Hauser R. L. Migrating spike bursts and electrical slow waves in the cat colon: effect of sectioning. Gastroenterology. 1974 Feb;66(2):240–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL E. E., WACHTER B. T., HONOUR A. J., BOGOCH A. The relationship between electrical and mechanical activity of the small intestine of dog and man. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1960 Jul;38:777–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duthie H. L., Brown B. H., Robertson-Dunn B., Kwong N. K., Whittaker G. E., Waterfall W. Electrical activity in the gastroduodenal area--slow waves in the proximal duodenum. A comparison of man and dog. Am J Dig Dis. 1972 Apr;17(4):344–351. doi: 10.1007/BF02231736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong N. K., Brown B. H., Whittaker G. E., Duthie H. L. Electrical activity of the gastric antrum in man. Br J Surg. 1970 Dec;57(12):913–916. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800571211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Thillier J. L. L'electro-gastroentero-graphie (E.GE.G.) Presse Med. 1971 May 29;79(27):1235–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provenzale L., Pisano M. Methods for recording electrical activity of the human colon in vivo. Clinical applications. Am J Dig Dis. 1971 Aug;16(8):712–722. doi: 10.1007/BF02239596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBAKIN M. A., SMIRNOVIP, MISHIN L. N. Electrogastrography. Ire Trans Biomed Electron. 1962 Apr;BME-9:129–132. doi: 10.1109/tbmel.1962.4322977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna S. K., Daniel E. E., Kingma Y. J. Simulation of slow-wave electrical activity of small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):166–175. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I., Duthie H. L., Smallwood R., Brown B. H., Linkens D. The effect of stimulation on the myoelectrical activity of the rectosigmoid in man. Gut. 1974 Aug;15(8):599–607. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.8.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfall W. E., Brown B. H., Duthie H. L., Whittaker G. E. The effects of humoral agents on the myoelectrical activity of the terminal ileum. Gut. 1972 Jul;13(7):528–534. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.7.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienbeck M., Christensen J., Weisbrodt N. W. Electromyography of the colon in the unanesthetized cat. Am J Dig Dis. 1972 Apr;17(4):356–362. doi: 10.1007/BF02231738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]