Abstract
The agglutinating antibody responses in duodenal fluid and serum were measured serially in 15 infants with enteropathogenic E. coli gastroenteritis. Peak levels of duodenal agglutinins were recorded eight to 18 days after the onset of symptoms, and the titres fell within the next seven to 14 days. These antibodies were mainly of the IgA class but IgM antibodies were detected early in the response, especially in the youngest infants. Serum antibody responses were detected in eight patients, but they correlated poorly with the titres of intestinal antibodies. No rise in serum antibodies was found in six infants. Further studies are required to determine whether these differences are host-derived or whether they reflect different pathogenic properties of the infecting organisms.
Full text
PDF
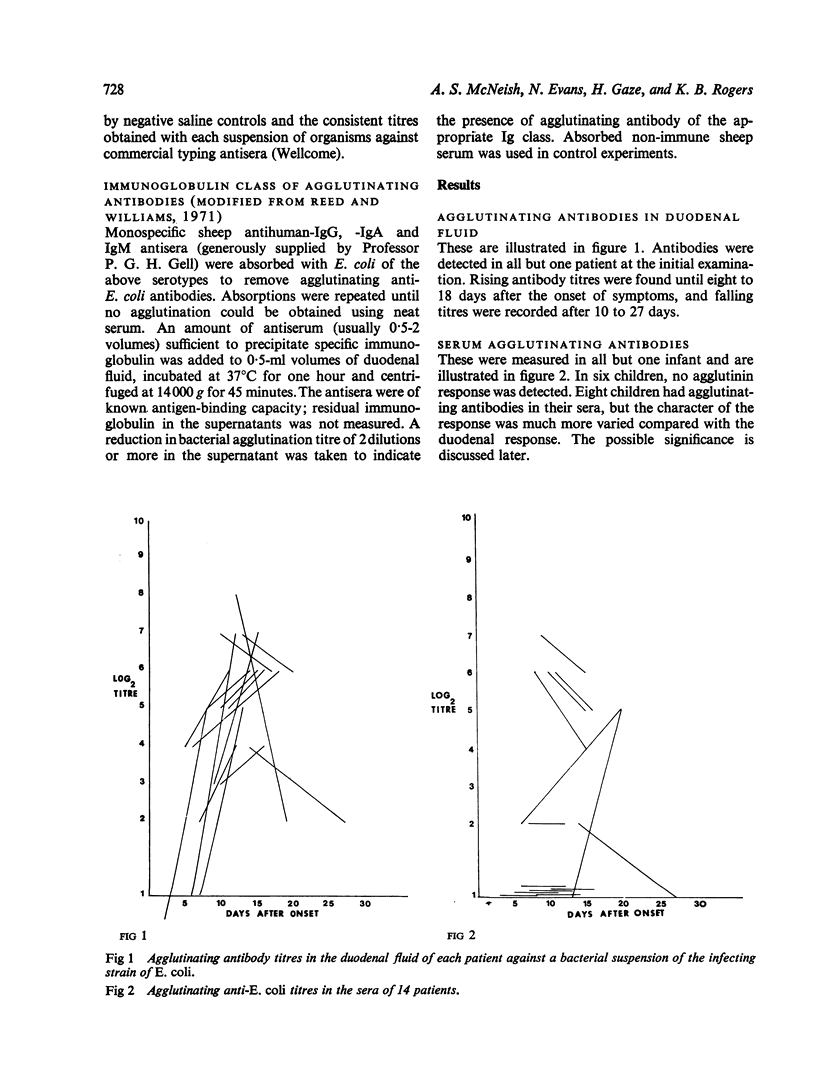
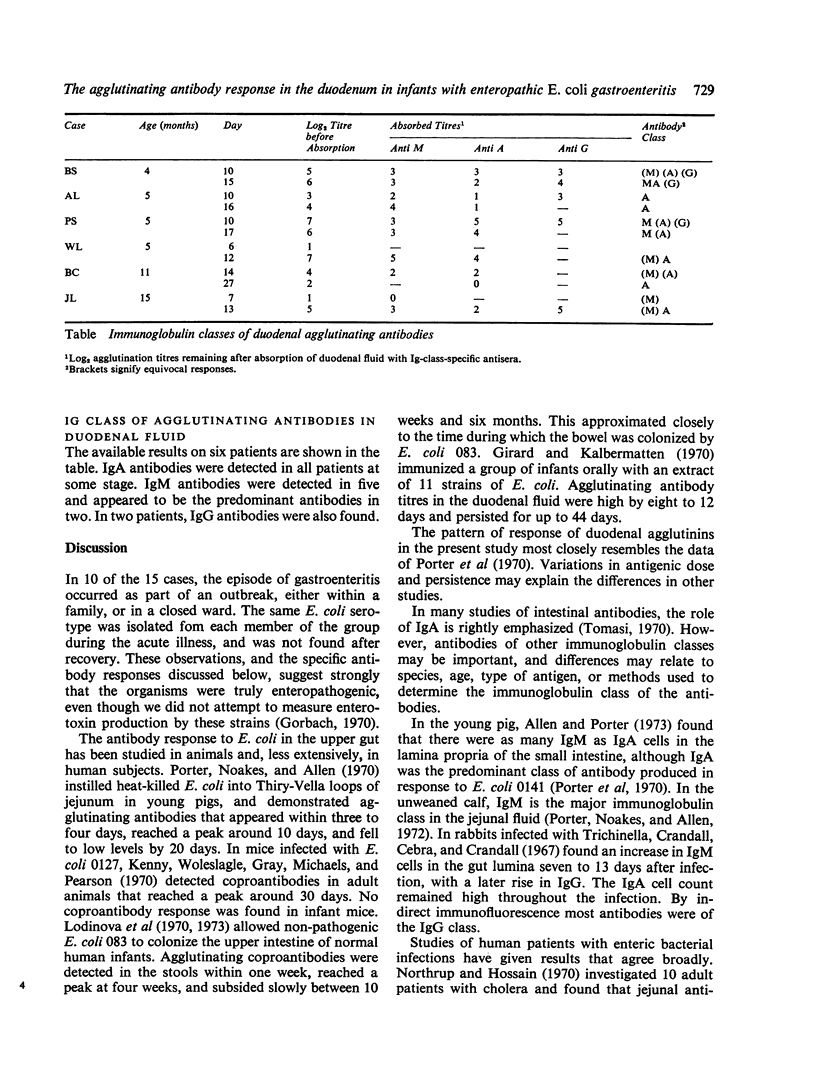


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen W. D., Porter P. The relative distribution of IgM and IgA cells in intestinal mucosa and lymphoid tissues of the young unweaned pig and their significance in ontogenesis of secretory immunity. Immunology. 1973 Mar;24(3):493–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall R. B., Cebra J. J., Crandall C. A. The relative proportions of IgG-, IgAand IgM-containing cells in rabbit tissues during experimental trichinosis. Immunology. 1967 Feb;12(2):147–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P., Sheahan D. G., LaBrec E. H., Kalas J. P. Pathogenesis of Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 1;285(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107012850101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Availability of locally synthesized and systemic antibodies in the intestine. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):965–981. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.965-981.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. P., de Kalbermatten A. Antibody activity in human duodenal fluid. Eur J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;1(3):188–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1970.tb00616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L. Acute diarrhea--a "toxin" disease? N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 2;283(1):44–45. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007022830111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny J. F., Weinert D. W., Gray J. A. Enteric infection with Escherichia coli O127 in the mouse. II. Failure of specific immunity to alter intestinal colonization of infants and adults. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):10–20. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny J. F., Woleslagle D. L., Gray J. A., Michaels R. H., Pearson M. A. Enteric infection with Escherichia coli O127 in the mouse. I. Characteristics of infection and systemic and local immune responses in mice of different ages. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):528–540. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodinová R., Jouja V., Wagner V. Serum immunoglobulins and coproantibody formation in infants after artificial intestinal colonization with Escherichia coli 083 and oral lysozyme administration. Pediatr Res. 1973 Jul;7(7):659–669. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197307000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodinová R., Wagner V. Development of faecal immunoglobulins and coproantibodies in infants after artificial oral colonization with E. coli 083. Experientia. 1970;26(2):188–188. doi: 10.1007/BF01895573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeish A. S., Gaze H., Evans N. Proceedings: Agglutinating antibodies in the duodenal secretions of infants with enteropathic E. coli gastroenteritis. Gut. 1974 Oct;15(10):834–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup R. S., Hossain S. A. Immunoglobulins and antibody activity in the intestine and serum in cholera. II. Measurement of antibody activity in jejunal aspirates and sera of cholera patients by radioimmunodiffusion. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(Suppl):142+–142+. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.supplement.s142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Kenworthy R., Holme D. W., Horsfield S. Escherichia coli antigens as dietary additives for oral immunisation of pigs: trials with pig creep feeds. Vet Rec. 1973 Jun 16;92(24):630–636. doi: 10.1136/vr.92.24.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Noakes D. E., Allen W. D. Intestinal secretion of immunoglobulins and antibodies to Escherichia coli in the pig. Immunology. 1970 Jun;18(6):909–920. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Noakes D. E., Allen W. D. Intestinal secretion of immunoglobulins in the preruminant calf. Immunology. 1972 Sep;23(3):299–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Williams R. C., Jr Intestinal immunoglobulins in shigellosis. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jul;61(1):35–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Linggood M. A. The effect of antisera in protecting pigs against experimental Escherichia coli diarrhoea and oedema disease. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Nov;4(4):487–493. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-4-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr Structure and function of mucosal antibodies. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:281–298. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


