Abstract
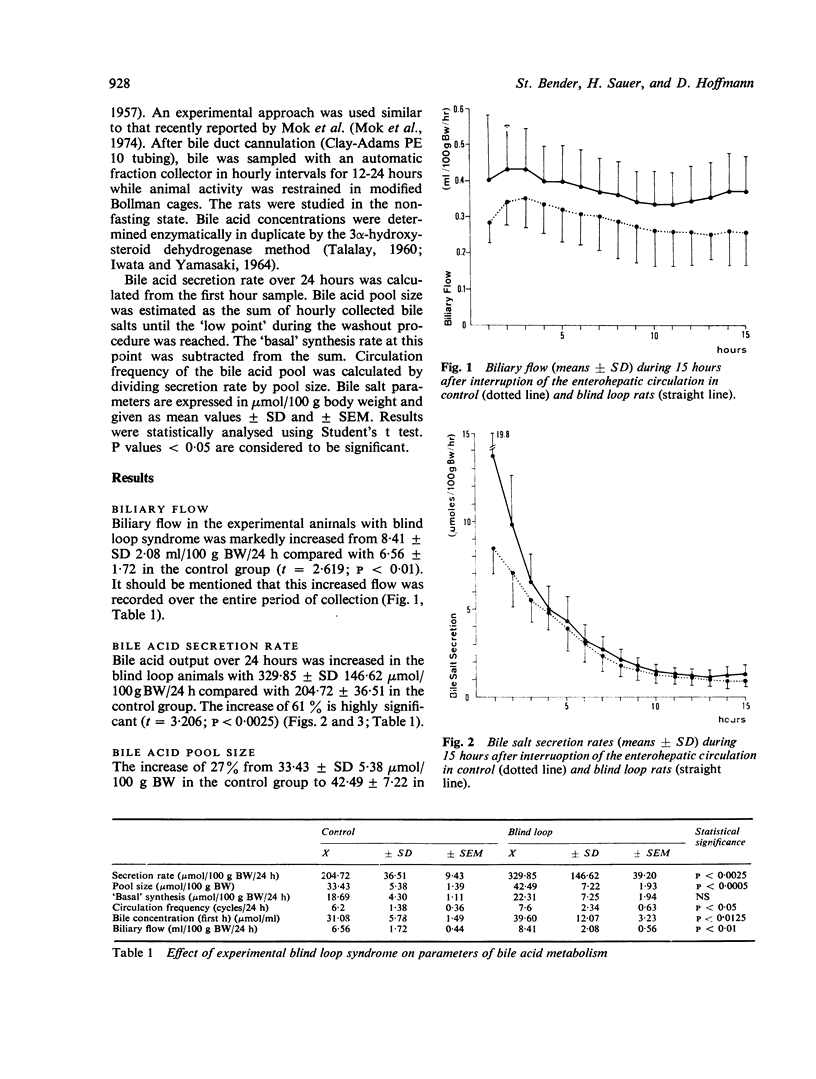
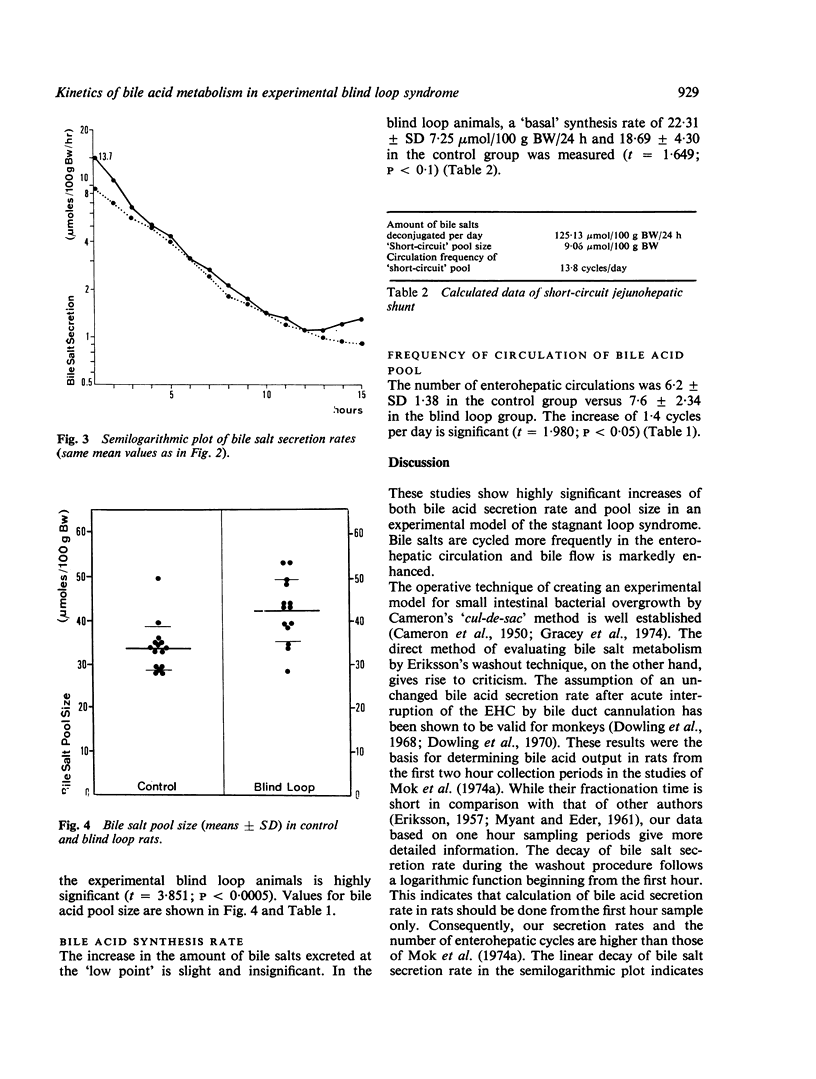
In an experimental model of the contaminated small bowel syndrome, Eriksson's washout technique was used to study bile salt metabolism. Bile salt secretion rate was increased from 204-7 +/- SD 36-5 mumol/100 g body weight/24 h to 329-9 +/- 146-6, pool size from 33-4 +/- 5-4 mumol/100 g BW to 42-5 +/- 7-2, and biliary flow from 6-6 +/- 1-72 ml/100 g BW/24 h to 8-4 +/- 2.1. Detailed analysis of the washout curves gave indirect evidence of a short-circuit jejunohepatic shunt in the model contaminated small bowel syndrome. Parameters of this shunt were calculated with 9-1 mumol/100 g BW for 'short-circuit' pool size and 13-8 for its circulation frequency.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ament M. E., Shimoda S. S., Saunders D. R., Rubin C. E. Pathogenesis of steatorrhea in three cases of small intestinal stasis syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):728–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMERON D. G., WATSON G. M., WITTS L. J. The alimentary tract of rats with intestinal culs-de-sac. Br J Exp Pathol. 1950 Jun;31(3):349–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Salomon H. S., Siperstein M. D. Bile acid metabolism. I. Studies on the mechanisms of intestinal transport. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):832–846. doi: 10.1172/JCI105399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of steatorrhea in the blind loop syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1815–1825. doi: 10.1172/JCI105289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H., Mack E., Picott J., Berger J., Small D. M. Experimental model for the study of the enterohepatic circulation of bile in rhesus monkeys. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jul;72(1):169–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H., Mack E., Small D. M. Effects of controlled interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile salts by biliary diversion and by ileal resection on bile salt secretion, synthesis, and pool size in the rhesus monkey. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):232–242. doi: 10.1172/JCI106232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Hill M. J., Shiner M. The deconjugation of bile salts by human intestinal bacteria. Lancet. 1966 Jun 4;1(7449):1237–1238. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90242-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSSON S. Biliary excretion of bile acids and cholesterol in bile fistula rats; bile acids and steroids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Mar;94(3):578–582. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-23018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Tabaqchali S. Bacteria, bile, and the small bowel. Gut. 1969 Dec;10(12):963–972. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.12.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Papadimitriou J., Bower G. Ultrastructural changes in the small intestines of rats with self-filling blind loops. Gastroenterology. 1974 Oct;67(4):646–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Papadimitriou J., Burke V., Thomas J., Bower G. Effects on small-intestinal function and structure induced by feeding a deconjugated bile salt. Gut. 1973 Jul;14(7):519–528. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.7.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATA T., YAMASAKI K. ENZYMATIC DETERMINATION AND THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS IN BLOOD. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:424–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSTEDT S. The turnover of cholic acid in man: bile acids and steroids. Acta Physiol Scand. 1957 Sep 17;40(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1957.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Norman A., Nygaard K. Bile acid transforming micro-organisms in rats with an intestinal blind segment. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;77(1):162–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1969.tb04217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok H. Y., Perry P. M., Dowling R. H. The control of bile acid pool size: effect of jejunal resection and phenobarbitone on bile acid metabolism in the rat. Gut. 1974 Apr;15(4):247–253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg I. H., Hardison W. G., Bull D. M. Abnormal bile-salt patterns and intestinal bacterial overgrowth associated with malabsorption. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jun 22;276(25):1391–1397. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196706222762501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P. Enzymic analysis of steroid hormones. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:119–143. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Booth C. C. Jejunal bacteriology and bile-salt metabolism in patients with intestinal malabsorption. Lancet. 1966 Jul 2;2(7453):12–15. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91744-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Hatzioannou J., Booth C. C. Bile-salt deconjugation and steatorrhoea in patients with the stagnant-loop syndrome. Lancet. 1968 Jul 6;2(7558):12–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92888-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


