Abstract
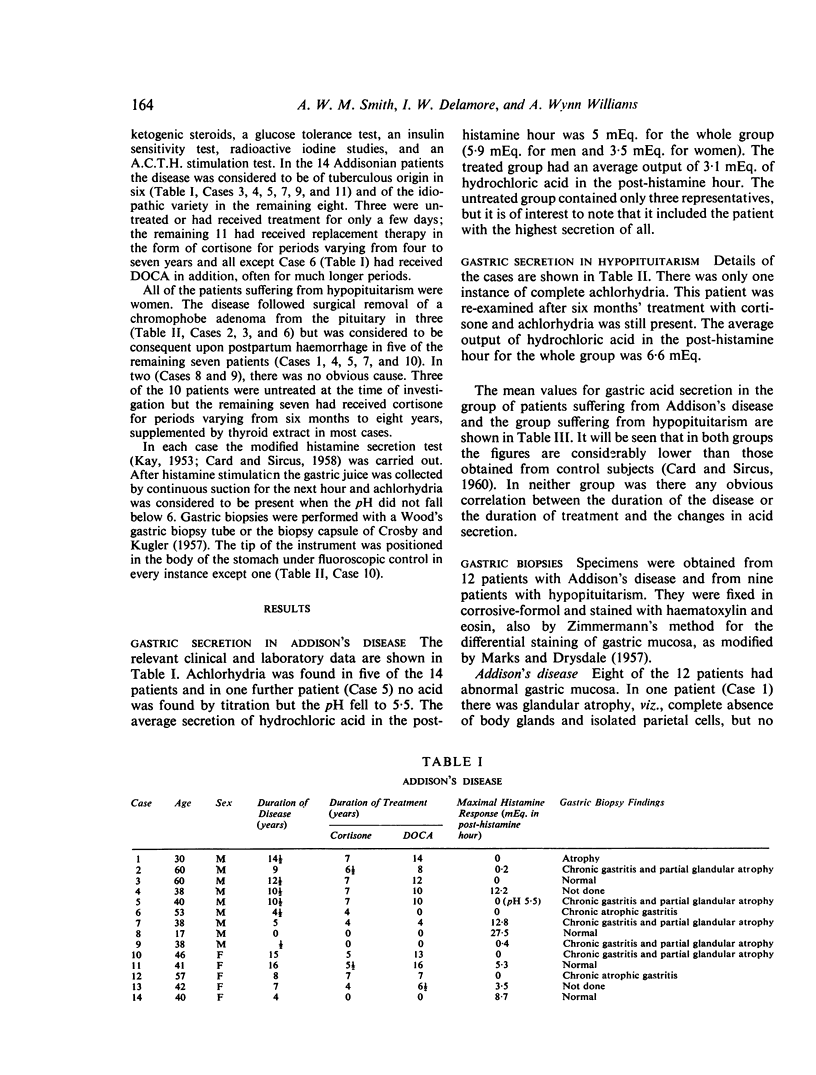
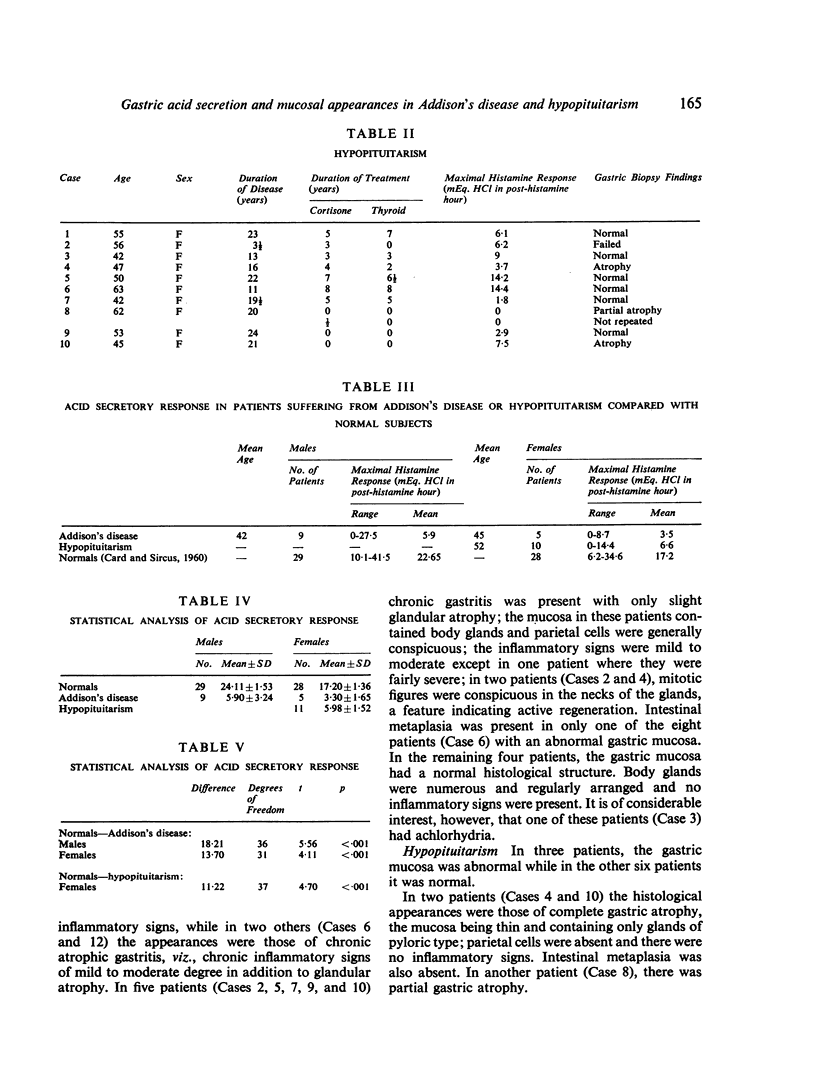
Studies of gastric acid secretion and mucosal appearances have been made in a group of 14 patients suffering from hypopituitarism. Achlorhydria was found in six of the patients suffering from Addison's disease but in only one patient suffering from hypopituitarism. In both groups the mean gastric secretion of hydrochloric acid was considerably lower than in a group of control subjects and replacement therapy with cortisone and DOCA in Addison's disease and cortisone and thyroid extract in hypopituitarism failed to restore gastric function to normal. A constant correlation was not found between gastric acid secretion and mucosal appearances.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER B. L., ABRAMS G. D. Effect of hypophysectomy on the cytology of the fundic glands of the stomach and on the secretion of pepsin. Am J Physiol. 1954 Jun;177(3):409–412. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.177.3.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER B. L., BRIDGMAN R. M. The histology of the gastro-intestinal mucosa (rat) after adrenalectomy or administration of adrenocortical hormones. Am J Anat. 1954 May;94(3):363–397. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000940303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARD W. I., MARKS I. N. The relationship between the acid output of the stomach following "maximal" histamine stimulation and the parietal cell mass. Clin Sci. 1960 Feb;19:147–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSBY W. H., KUGLER H. W. Intraluminal biopsy of the small intestine; the intestinal biopsy capsule. Am J Dig Dis. 1957 May;2(5):236–241. doi: 10.1007/BF02231100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRYSDALE K. M., MARKS I. N. A modification of Zimmermann's method for differential staining of gastric mucosa. Stain Technol. 1957 Jan;32(1):48–48. doi: 10.3109/10520295709111398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEYRTER F., KLIMA R. Uber die Magenveränderungen bei der Addisonschen Krankheit. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1952 Sep 26;77(39):1173–1175. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1117185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M. H. F. The response to different regions of the gastrointestinal tract to normal and abnormal stimuli; influence of feeding inert bulk material and of hypophysectomy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1953 Feb;13(4):1035–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY S. J., BENSON J. A., Jr, SPIRO H. M., REIFENSTEIN R. W. Effects of ACTH and cortisone upon the stomach: its significance in the normal and in peptic ulcer. Gastroenterology. 1951 Dec;19(4):658–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAEGER K., JACOBSOHN D., KAHLSON G. Atrophy of the gastrointestinal mucosa following hypophysectomy or adrenalectomy. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1953;111:161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAY A. W. Effect of large doses of histamine on gastric secretion of HCI; an augmented histamine test. Br Med J. 1953 Jul 11;2(4827):77–80. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4827.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSNER J. B., KLOTZ A. P., PALMER W. L. Unfavorable course of gastric ulcer during administration of ACTH and cortisone. Gastroenterology. 1952 Jan;20(1):27–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SORKIN S. Z. Addison's disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1949 Dec;28(4):371–425. doi: 10.1097/00005792-194912000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEMPIEN S. J., DAGRADI A. The histamine response of the gastric mucosa in a patient with adrenal insufficiency: effect of cortisone administration. Gastroenterology. 1954 Sep;27(3):358–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELBOURN R. B., CODE C. F. Effects of cortisone and of adrenalectomy of secretion of gastric acid and on occurrence of gastric ulceration in the pylorus-ligated rat. Gastroenterology. 1953 Mar;23(3):356–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


