Abstract
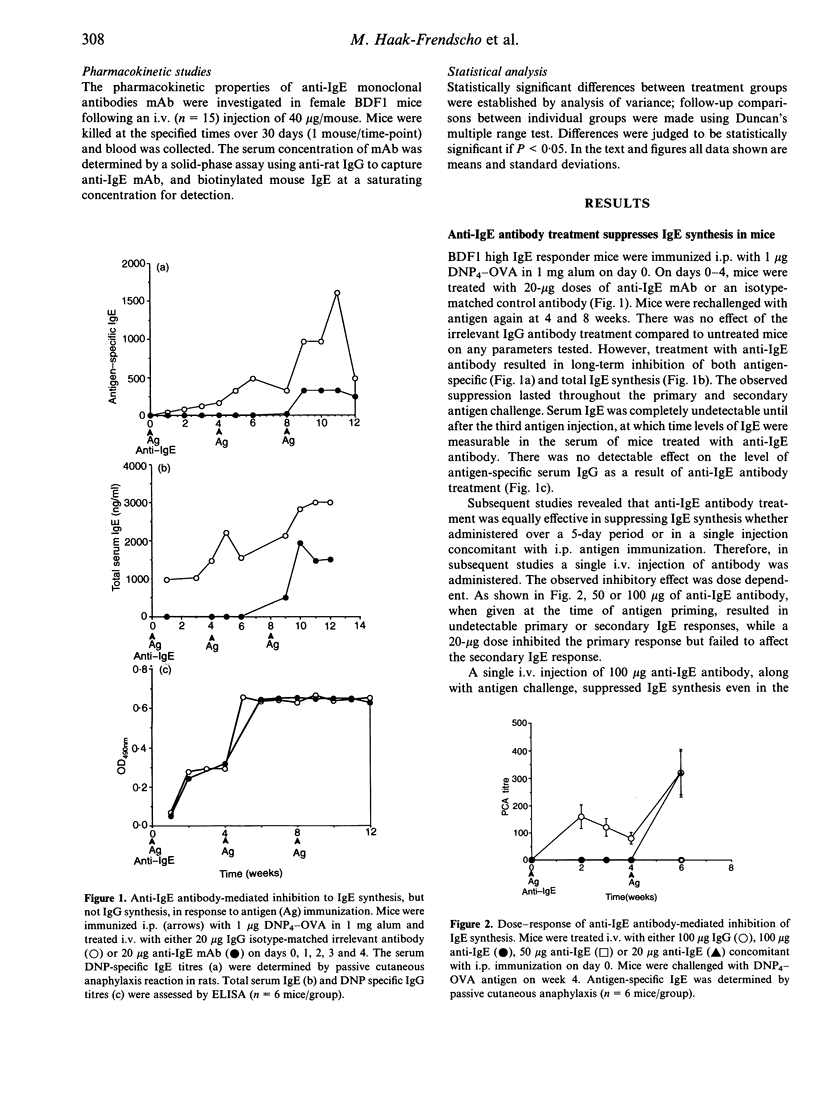
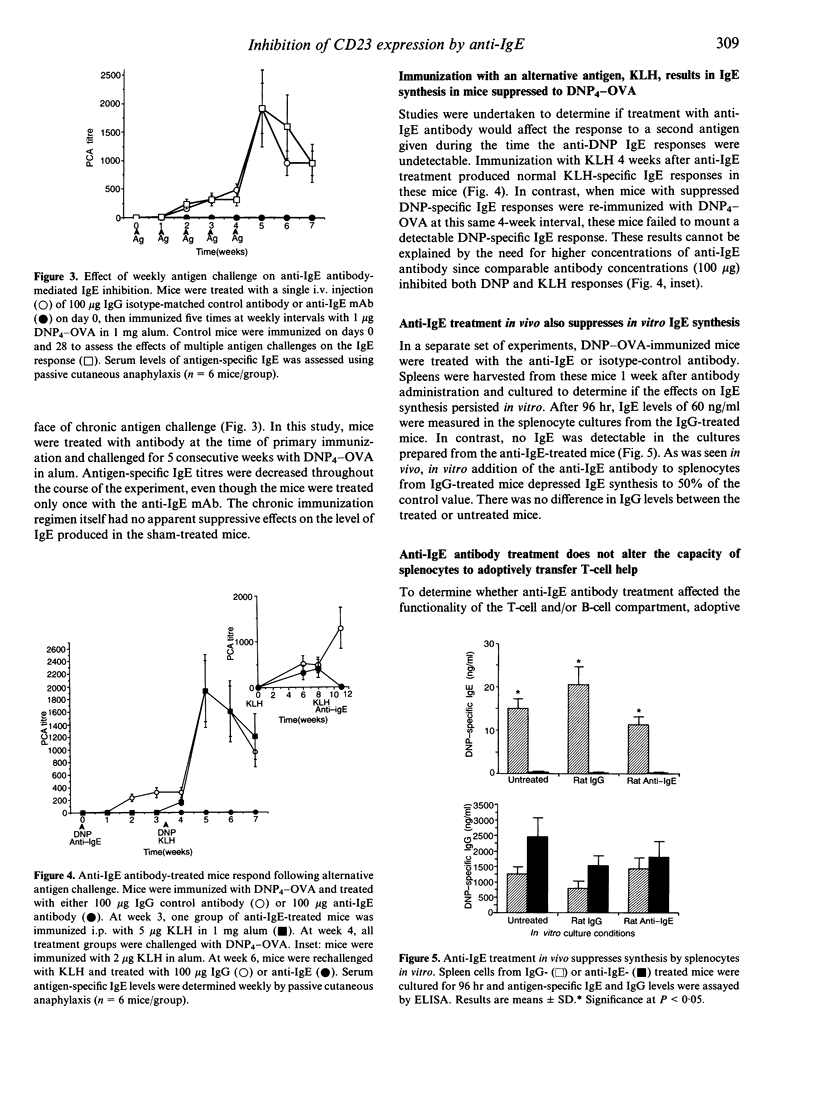
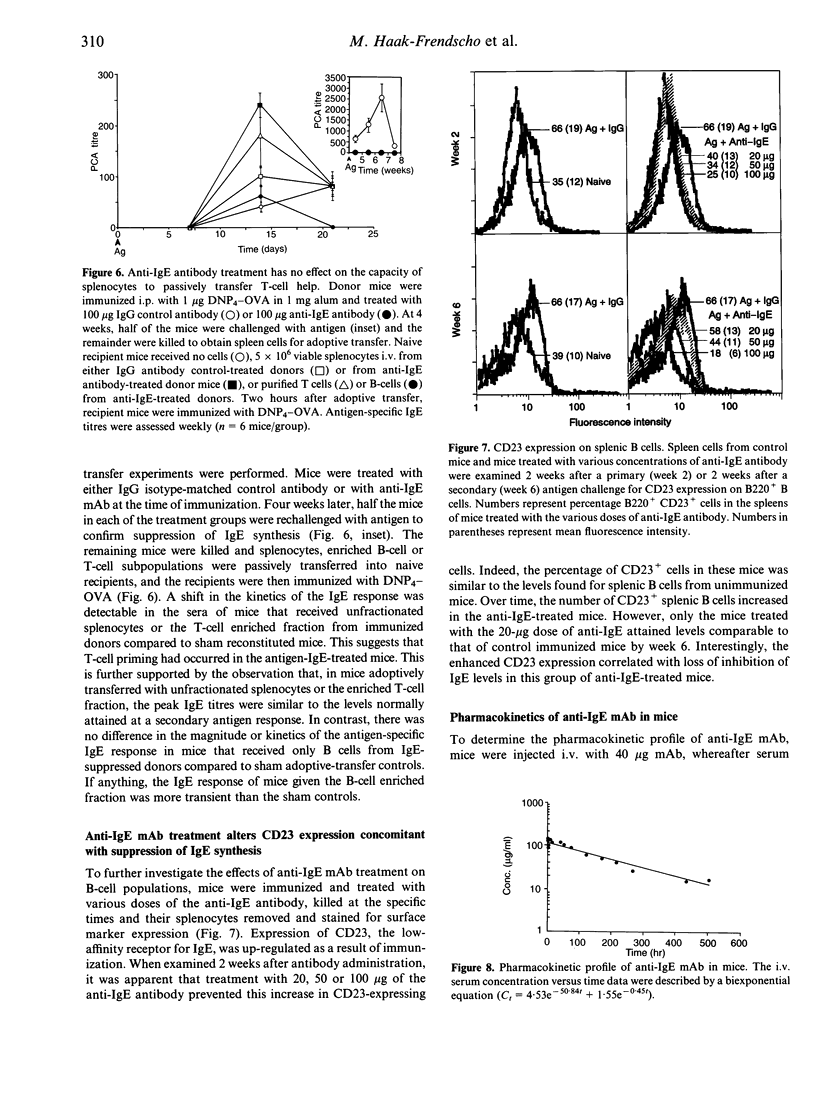
High IgE responder BDF1 mice were immunized intraperitoneally (i.p.) with dinitrophenol4 (DNP4)-ovalbumin (OVA) in alum concomitant with intravenous (i.v.) administration of an anti-IgE monoclonal antibody (mAb). IgE levels were undetectable in mice treated with the anti-IgE antibody, whereas mice treated with isotype-matched irrelevant mAb had IgE levels comparable to that of untreated, immunized mice. Subsequent antigen challenges with DNP4-OVA, either at weekly or monthly intervals, failed to evoke an IgE response for greater than 2 months in mice treated with anti-IgE during the primary sensitization, even though the terminal half-life of the anti-IgE antibody was 7 days. This inhibition was specific for DNP4-OVA since the DNP4-OVA-suppressed mice were able to respond to keyhole limpet haemocyanin (KLH). To investigate the effects of antibody treatment at the cellular level, passive transfer experiments were performed. The primary DNP-specific IgE response of adoptive transfer recipient mice was the same whether the donor cells were from mice treated with IgG or anti-IgE. Transfer of enriched T- or B-cell populations indicated that T-cell help was not compromised by administration of the anti-IgE mAb. However, splenocytes from the anti-IgE-treated mice failed to synthesize IgE in vitro, and flow cytometric analysis of B cells from anti-IgE-treated mice showed a dose-dependent decrease in CD23+ cells following antibody treatment, which correlated with decreased serum IgE levels. Taken together, the results of these studies suggest that anti-IgE treatment suppresses IgE responses via effects on B cells rather than T cells, possibly through effects on CD23-dependent pathways.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubry J. P., Pochon S., Graber P., Jansen K. U., Bonnefoy J. Y. CD21 is a ligand for CD23 and regulates IgE production. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):505–507. doi: 10.1038/358505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R. IgE antibody-specific abrogation of an established immune response in mice by modified antigens. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1799–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., Platteau B., Beckers A., Pauwels R. Differential effect of neonatal injections of anti-mu or anti-delta antibodies on the synthesis of IgM, IgD, IgE, IgA, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG2c immunoglobulin classes. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2083–2087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozelka B. E., McCants M. L., Salvaggio J. E., Lehrer S. B. IgE isotype suppression in anti-epsilon-treated mice. Immunology. 1982 Jul;46(3):527–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S. Genesis of host IgE competence: perinatal IgE tolerance induced by IgE processed and presented by IgE Fc receptor (CD23)-bearing B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):343–348. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Katz D. H. IgE class-restricted tolerance induced by neonatal administration of soluble or cell-bound IgE. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):772–788. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen U., Scheuermann R. H., Wirth T., Gerster T., Roeder R. G., Harshman K., Berger C. Anti-IgM antibodies down modulate mu-enhancer activity and OTF2 levels in LPS-stimulated mouse splenic B-cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5981–5989. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad D. H. Fc epsilon RII/CD23: the low affinity receptor for IgE. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:623–645. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dintzis H. M., Dintzis R. Z. Profound specific suppression by antigen of persistent IgM, IgG, and IgE antibody production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1113–1117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filion L. G., Lee W. Y., Sehon A. H. Suppression of the IgE antibody response to ovalbumin in mice with a conjugate of ovalbumin and isologous gamma-globulins. Cell Immunol. 1980 Aug 15;54(1):115–128. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Romo L., Shields J., Humbert Y., Graber P., Aubry J. P., Gauchat J. F., Ayala G., Allet B., Chavez M., Bazin H. Inhibition of an in vivo antigen-specific IgE response by antibodies to CD23. Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1038–1041. doi: 10.1126/science.8351517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gause A., Yoshida N., Kappen C., Rajewsky K. In vivo generation and function of B cells in the presence of a monoclonal anti-IgM antibody: implications for B cell tolerance. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jul;17(7):981–990. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier-Brossette N., Bourget I., Akoundi C., Bonnefoy J. Y., Cousin J. L. Spontaneous and ligand-induced endocytosis of CD23 (Fc epsilon receptor II) from the surface of B lymphocytes generates a 16-kDa intracellular fragment. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1573–1577. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Gordon J. Coordinated action of IgE and a B-cell-stimulatory factor on the CD23 receptor molecule up-regulates B-lymphocyte growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6239–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haak-Frendscho M., Ridgway J., Shields R., Robbins K., Gorman C., Jardieu P. Human IgE receptor alpha-chain IgG chimera blocks passive cutaneous anaphylaxis reaction in vivo. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):351–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Nisonoff A. Induction of high titers of anti-IgE by immunization of inbred mice with syngeneic IgE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5009–5013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HayGlass K. T., Naides S. J., Benacerraf B., Sy M. S. T cell development in B cell deficient mice. III. Restriction specificity of suppressor T cell factor(s) produced in mice treated chronically with rabbit anti-mouse mu chain antibody. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1985;2(2):107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HayGlass K. T., Stefura W. Isotype-selective abrogation of established IgE responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Dec;82(3):429–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05466.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Biological function of gamma E antibodies and mechanisms of reaginic hypersensitivity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jan;6(1):25–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. Y., Sehon A. H. Abrogation of reaginic antibodies with modified allergens. Nature. 1977 Jun 16;267(5612):618–619. doi: 10.1038/267618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo H. Y., Hofstetter H., Banchereau J., Delespesse G. Cross-linking of CD23 antigen by its natural ligand (IgE) or by anti-CD23 antibody prevents B lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2122–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D. Induction of temporary IgA deficiency in mice injected with heterologous anti-immunoglobulin heavy chain antisera. J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):1152–1155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D., Jutila J. W. Immunosuppression of mice injected with heterologous anti-immunoglobulin heavy chain antisera. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1316–1333. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D., Manning J. K., Reed N. D. Suppression of reaginic antibody (IgE) formation in mice by treatment with anti-mu antiserum. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):288–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R., Suszko I. M., McIntire F. C. Polymerized ragweed antigen E. I. Preparation and immunologic studies. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1402–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Interleukin-4: a prototypic immunoregulatory lymphokine. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):1859–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Kurbe-Leamer M., Behle K., Max E. E., Zhang K. Inhibition of human IgE production via Fc epsilon R-II stimulation results from a decrease in the mRNA for secreted but not membrane epsilon H chains. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):4000–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehon A. H. Suppression of IgE antibody responses with tolerogenic conjugates of allergens and haptens. Prog Allergy. 1982;32:161–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhove B., Bazin H. Differentiation of membrane IgE+ rat B cells into IgE-secreting cells. Immunology. 1993 Aug;79(4):580–586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D. Molecular basis for the inhibition of LPS induced differentiation by anti-immunoglobulin. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1987;3(3):133–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


