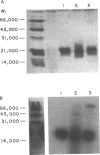
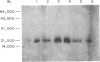
Abstract
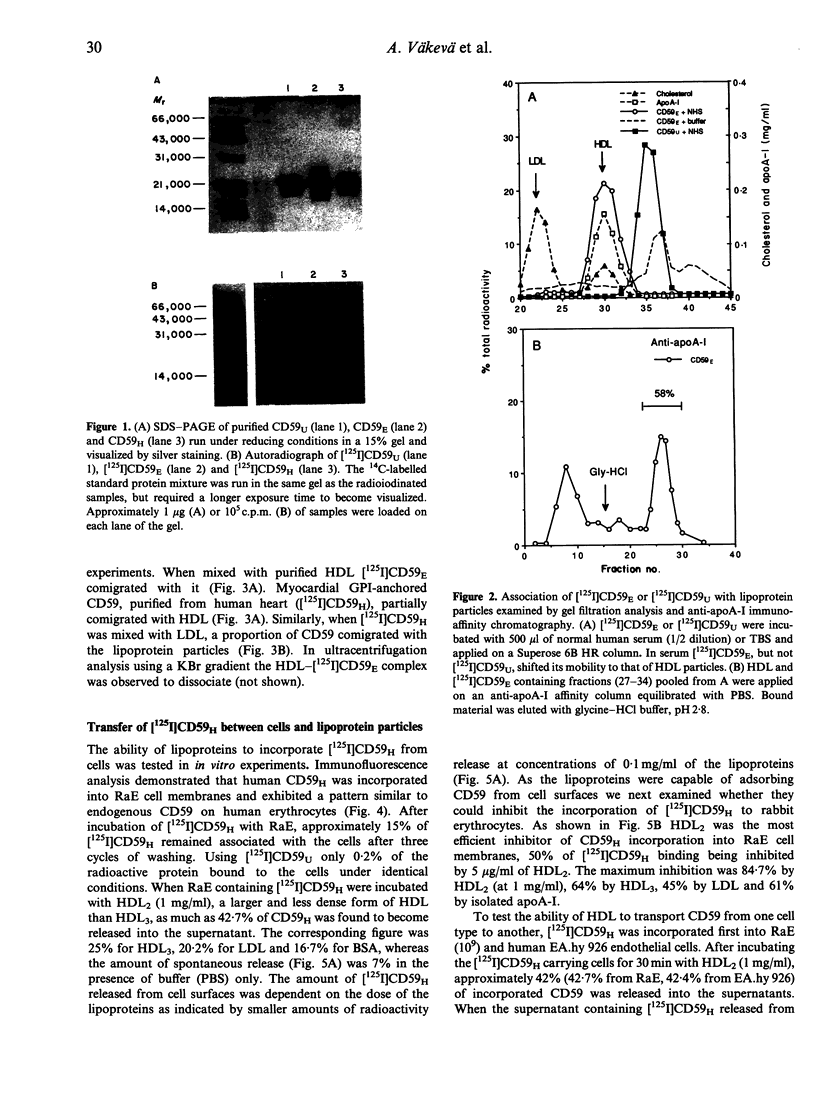
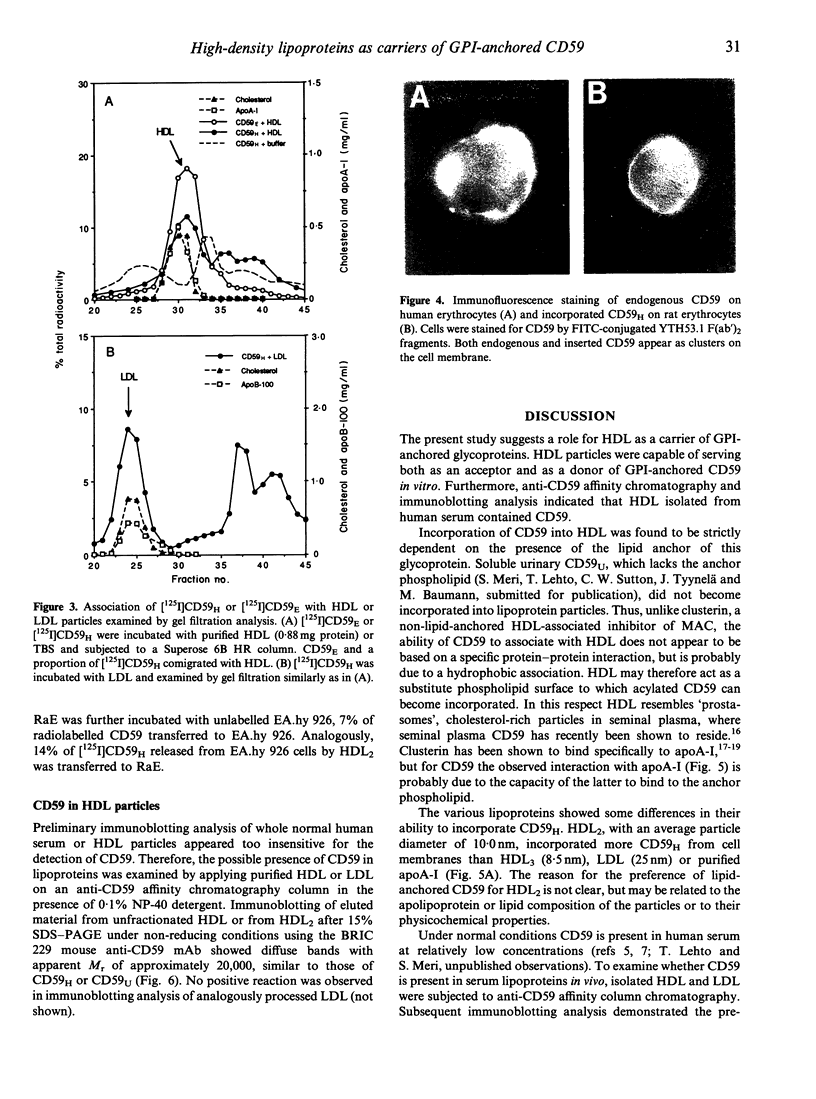
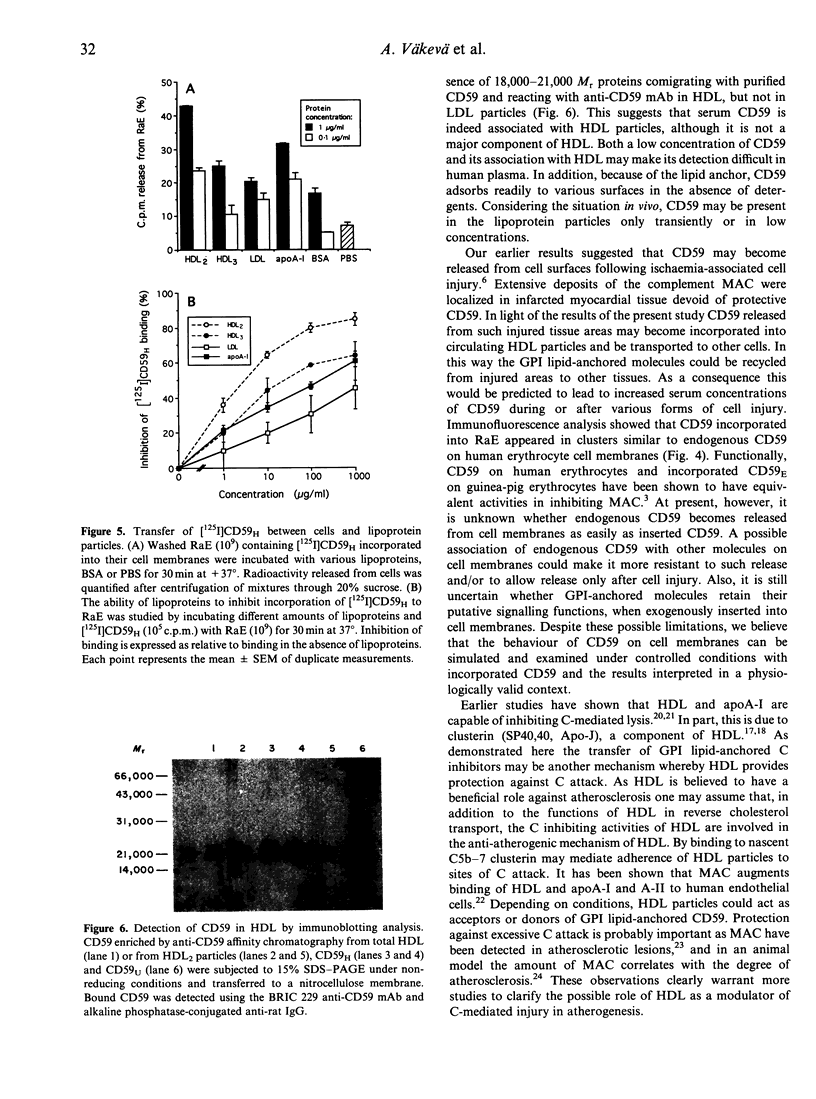
CD59 (protectin) is a glycophosphoinositol (GPI) lipid-anchored inhibitor of complement lysis that is expressed on the membranes of blood cells, endothelial cells, epithelial cells and cardiomyocytes. CD59 may be shed from cell surfaces, e.g. during cell injury, but when entering human plasma its fate is unknown. In this study we observed that radiolabelled lipid-anchored CD59, but not soluble urinary CD59 without anchor lipid, incorporated into high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles when mixed with human serum and analysed by high resolution gel filtration and anti-apoA-I affinity chromatography. Only a small proportion of CD59 entered the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) fraction. HDL particles were capable of incorporating 25-42% of [125I]CD that was preinserted into the membranes of rabbit erythrocytes (RaE) and transferred 7-14% of [125I]CD59 back to RaE or to cultured human endothelial cells (EA.hy 926). Immunoaffinity purification and immunoblotting analysis demonstrated that HDL isolated from normolipidemic human serum contained small amounts of CD59. These results suggest that HDL particles could be involved in the recycling of GPI lipid-anchored molecules released from cell surfaces.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanche P. J., Gong E. L., Forte T. M., Nichols A. V. Characterization of human high-density lipoproteins by gradient gel electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 24;665(3):408–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi-Miura N. H., Sakamoto T., Tobe T., Nakano Y., Tomita M. The role of HDL consisting of SP-40,40, apo A-I, and lipids in the formation of SMAC of complement. J Biochem. 1993 Apr;113(4):484–487. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Simmons D. L., Hale G., Harrison R. A., Tighe H., Lachmann P. J., Waldmann H. CD59, an LY-6-like protein expressed in human lymphoid cells, regulates the action of the complement membrane attack complex on homologous cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):637–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgell C. J., McDonald C. C., Graham J. B. Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Bozas S. E., Tenkanen H., Kirszbaum L., Metso J., Murphy B., Walker I. D. The apolipoprotein A-I binding protein of placenta and the SP-40,40 protein of human blood are different proteins which both bind to apolipoprotein A-I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 27;1086(3):255–260. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90167-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton K. K., Sims P. J. The terminal complement proteins C5b-9 augment binding of high density lipoprotein and its apolipoproteins A-I and A-II to human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1833–1840. doi: 10.1172/JCI115504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauhiainen M., Metso J., Pahlman R., Blomqvist S., van Tol A., Ehnholm C. Human plasma phospholipid transfer protein causes high density lipoprotein conversion. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4032–4036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Lowin B., Peitsch M. C., Böttcher A., Schmitz G., Tschopp J. Clusterin (complement lysis inhibitor) forms a high density lipoprotein complex with apolipoprotein A-I in human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11030–11036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Tolbert N. E., Bieber L. L. Protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples: manual and automated procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:296–303. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meri S., Morgan B. P., Davies A., Daniels R. H., Olavesen M. G., Waldmann H., Lachmann P. J. Human protectin (CD59), an 18,000-20,000 MW complement lysis restricting factor, inhibits C5b-8 catalysed insertion of C9 into lipid bilayers. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):1–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meri S., Waldmann H., Lachmann P. J. Distribution of protectin (CD59), a complement membrane attack inhibitor, in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1991 Nov;65(5):532–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman C. H., Rosenfeld S. I., Leddy J. P. High-density lipoprotein and its apolipoproteins inhibit cytolytic activity of complement. Studies on the nature of inhibitory moiety. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 10;812(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepponen P., Marniemi J., Rautaoja T. Immunoturbidimetric determination of apolipoproteins A-1 and B in serum. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1987 Nov;47(7):739–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins S. A., Sims P. J. The complement-inhibitory activity of CD59 resides in its capacity to block incorporation of C9 into membrane C5b-9. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3478–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney I. A., Atkinson J. P., Krul E. S., Schonfeld G., Polakoski K., Saffitz J. E., Morgan B. P. Physiologic relevance of the membrane attack complex inhibitory protein CD59 in human seminal plasma: CD59 is present on extracellular organelles (prostasomes), binds cell membranes, and inhibits complement-mediated lysis. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1409–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Packman C. H., Leddy J. P. Inhibition of the lytic action of cell-bound terminal complement components by human high density lipoproteins and apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):795–808. doi: 10.1172/JCI110833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert P. S., Hugo F., Hansson G. K., Bhakdi S. Prelesional complement activation in experimental atherosclerosis. Terminal C5b-9 complement deposition coincides with cholesterol accumulation in the aortic intima of hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):747–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Väkevä A., Laurila P., Meri S. Loss of expression of protectin (CD59) is associated with complement membrane attack complex deposition in myocardial infarction. Lab Invest. 1992 Nov;67(5):608–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]