Abstract
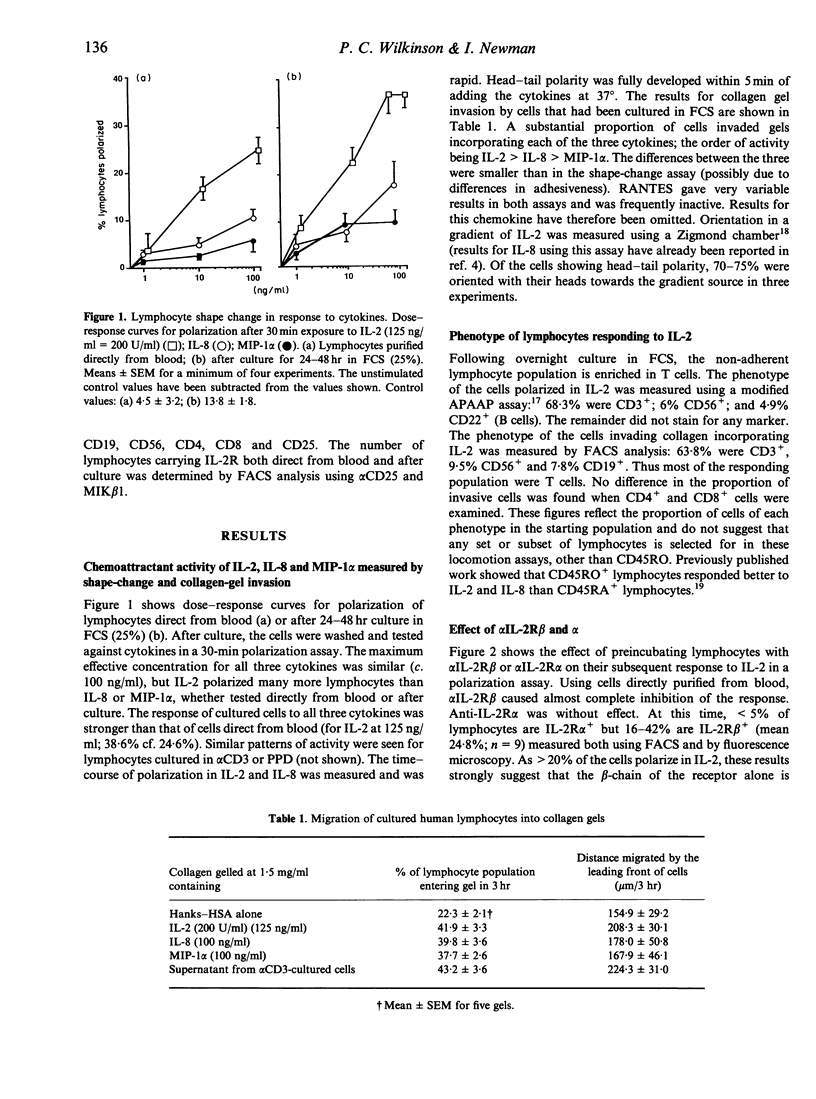
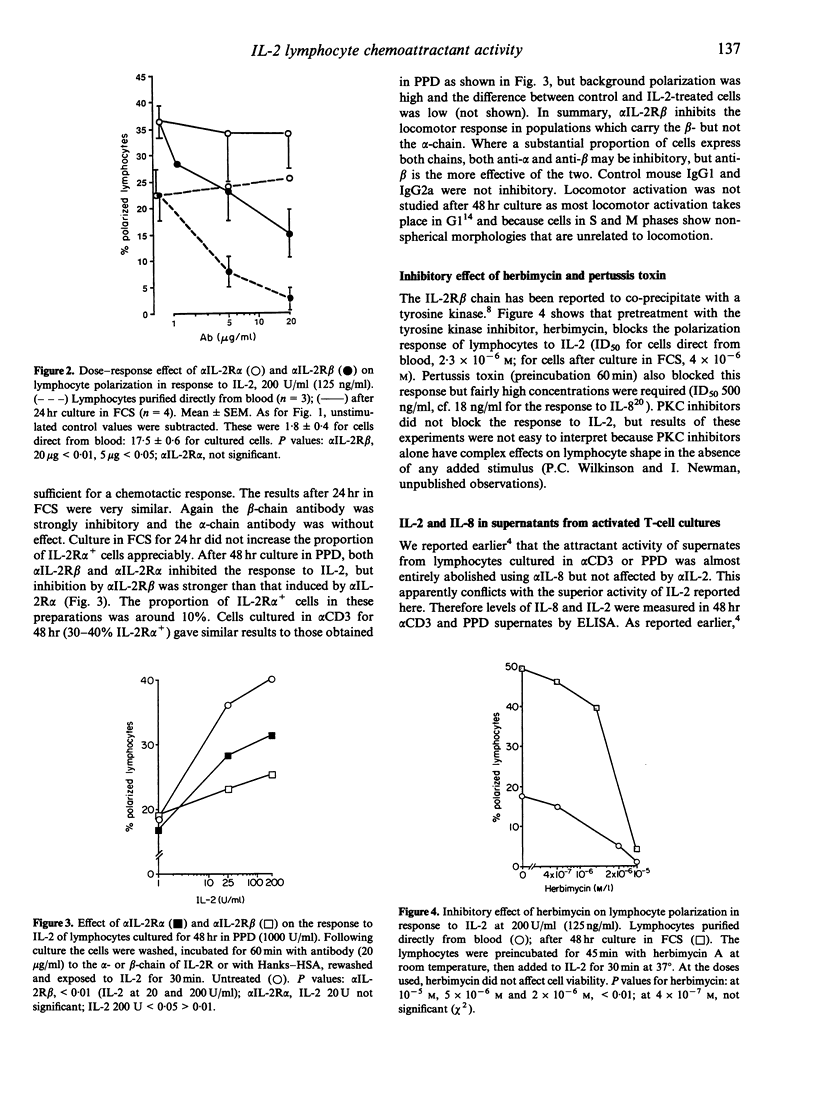
Recombinant human interleukin-2 (IL-2) stimulated locomotion and chemotaxis of human blood lymphocytes as measured by shape change to a polar morphology, by orientation in a chemotactic gradient, and by a collagen gel invasion assays. IL-2 stimulated locomotion of a larger number of lymphocytes than IL-8 or macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1 alpha, but the maximally effective concentration of all three was similar (around 100 ng/ml). Activation of the lymphocytes by culture for 24-48 hr in fetal calf serum (FCS), anti-CD3, or purified protein derivative (PPD) increased the proportion of responsive cells, though even direct from blood, > 20% of lymphocytes showed locomotor responses to IL-2, a figure which was similar to the number of IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) beta+ lymphocytes but higher than the number of IL-2R alpha+ cells. The effect of antibodies to IL-2R alpha and IL-2R beta as inhibitors of these responses was therefore tested. Anti-IL-2R beta (alpha IL-2R beta) completely inhibited the response of both resting and activated cells: alpha IL-2R alpha had no inhibitory effect on the locomotion of lymphocytes direct from blood, and only partially inhibited locomotion after culture for 48 hr in alpha CD3 or PPD. The locomotor response to IL-2 was inhibited by pretreatment of the cells with herbimycin, a protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) inhibitor, an observation consistent with PTK control of cytoskeletal activity following binding of IL-2 to IL-2R beta. These results suggest that the beta-chain of the IL-2R is required for activation of lymphocyte locomotion by IL-2 and that binding of IL-2 to this chain alone is sufficient for a response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elsdale T., Bard J. Collagen substrata for studies on cell behavior. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):626–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Scearce R. M., Hoffman J. A., Peffer N. J., Hammes S. R., Hosking J. B., Schmandt R., Kuziel W. A., Haynes B. F., Mills G. B. A tyrosine kinase physically associates with the beta-subunit of the human IL-2 receptor. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1253–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddox J. L., Pfister R. R. Evaluation of the methodology of polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotaxis. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Aug 9;163(2):273–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90132-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haston W. S., Shields J. M. Neutrophil leucocyte chemotaxis: a simplified assay for measuring polarizing responses to chemotactic factors. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Aug 2;81(2):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haston W. S., Wilkinson P. C. Visual methods for measuring leukocyte locomotion. Methods Enzymol. 1988;162:17–38. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)62060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo M., Cantrell D. A. Protein tyrosine kinases couple the interleukin-2 receptor to p21ras. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jan;23(1):131–135. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Berman J. S., Beer D. J., Center D. M. Induction of human T lymphocyte motility by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3887–3890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. G., Anderson A. O., Appella E., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. The neutrophil-activating protein (NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1464–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.2648569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed I., Wang G., Roifman C. M. Antigen receptor-mediated protein tyrosine kinase activity is regulated by a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Wieland D., White M. F., Behnke B., Gebhardt A., Neumann S., Krone W., Kahn C. R. Pertussis toxin inhibits autophosphorylation and activation of the insulin receptor kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1479–1485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92106-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman I., Wilkinson P. C. Locomotor responses of human CD45 lymphocyte subsets: preferential locomotion of CD45RO+ lymphocytes in response to attractants and mitogens. Immunology. 1993 Jan;78(1):92–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman I., Wilkinson P. C. Methods for phenotyping polarized and locomotor human lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Feb 14;147(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(12)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. W., Van Epps D. E. Separation and purification of lymphocyte chemotactic factor (LCF) and interleukin 2 produced by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cell Immunol. 1987 Mar;105(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Bacon K., Camp R. D., Kaspari J. W., Goeddel D. V. Human macrophage inflammatory protein alpha (MIP-1 alpha) and MIP-1 beta chemokines attract distinct populations of lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1821–1826. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields J. M., Haston W., Wilkinson P. C. Invasion of collagen gels by mouse lymphoid cells. Immunology. 1984 Feb;51(2):259–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita T., Asao H., Ohtani K., Ishii N., Kumaki S., Tanaka N., Munakata H., Nakamura M., Sugamura K. Cloning of the gamma chain of the human IL-2 receptor. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.1631559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub D. D., Conlon K., Lloyd A. R., Oppenheim J. J., Kelvin D. J. Preferential migration of activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in response to MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):355–358. doi: 10.1126/science.7682337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Kitamura F., Miyasaka M. Characterization of the interleukin 2 receptor beta chain using three distinct monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1982–1986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Wakefield L. M., McCartney-Francis N., Wahl L. M., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor type beta induces monocyte chemotaxis and growth factor production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5788–5792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A. The interleukin-2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2681–2684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. M., Griffin J. D., Rambaldi A., Chen Z. G., Mantovani A. Induction of monocyte migration by recombinant macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):575–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., Newman I. Identification of IL-8 as a locomotor attractant for activated human lymphocytes in mononuclear cell cultures with anti-CD3 or purified protein derivative of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 15;149(8):2689–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. The locomotor capacity of human lymphocytes and its enhancement by cell growth. Immunology. 1986 Feb;57(2):281–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., Watson E. A. FK506 and pertussis toxin distinguish growth-induced locomotor activation from attractant-stimulated locomotion in human blood lymphocytes. Immunology. 1990 Nov;71(3):417–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H. Ability of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to orient in gradients of chemotactic factors. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):606–616. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


