Abstract
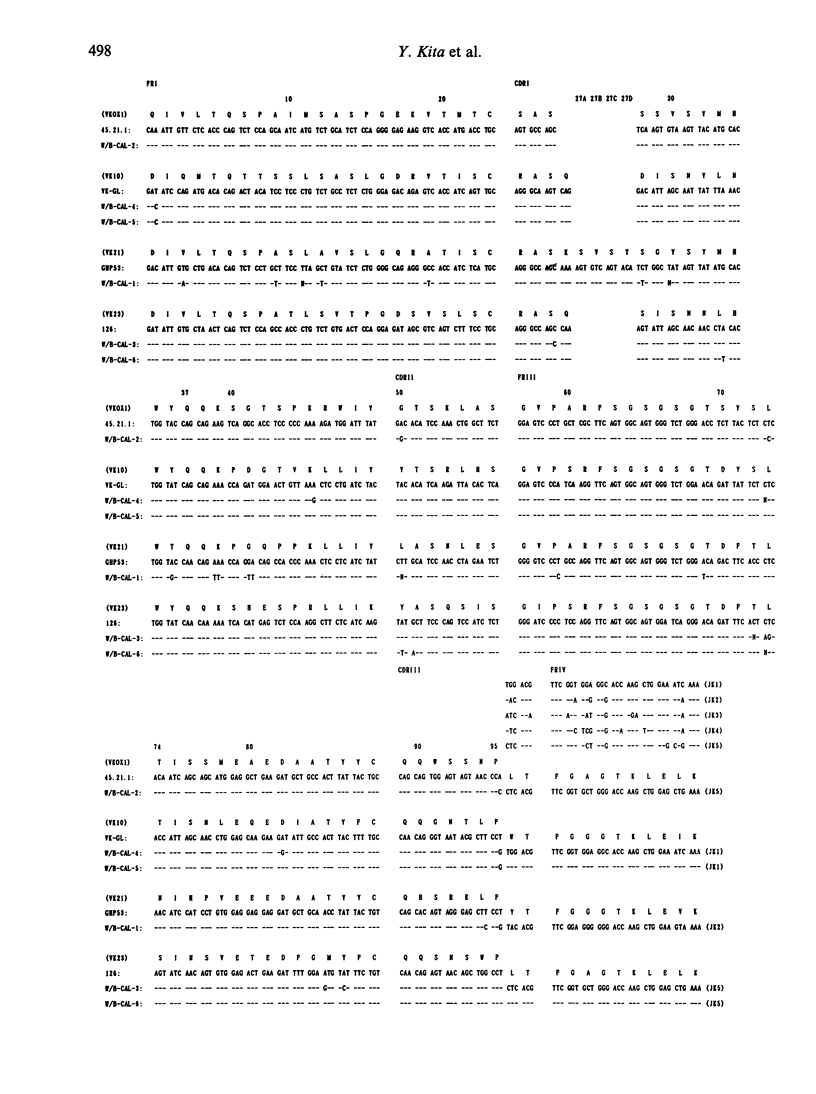
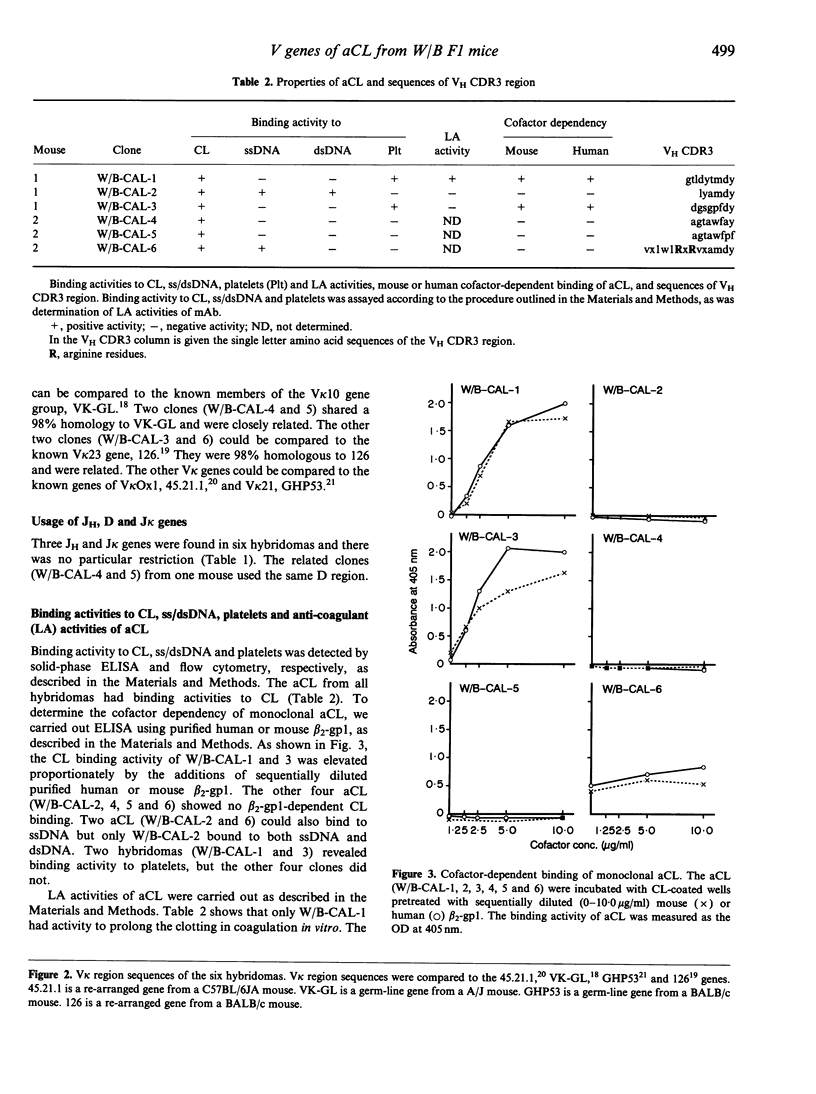
In (NZW x BXSB) F1 (W/B F1) male mice, systemic lupus-like disease, thrombocytopenia and coronary vascular disease with myocardial infarction occur, due to the presence of platelet-associated antibodies, anti-platelet antibodies and anti-cardiolipin antibodies (aCL). We developed monoclonal aCL and analysed the specificity of aCL. In the W/B F1 mice, there are aCL with pathogenic properties, which have an IgG isotype and reveal a cofactor-dependent binding to CL, binding activity to platelets, and lupus anti-coagulant (LA) activity. Here, we analysed the usage of VH and V kappa genes of six aCL, including two pathogenic aCL, from W/B F1 mice, in an attempt to address the question of whether or not aCL with pathogenic properties use restricted Ig V genes. Sequence analysis of VH and V kappa genes of aCL showed that the pathogenic aCL had VHJ558 and V kappa 21 or V kappa 23 genes, whereas the other aCL without pathogenic features used mainly the 7183 VH family and the random V kappa gene group. However, two pathogenic aCL showed a 86.6% homology with the IgV region, each other, indicating that they were not closely related clones. Thus, these findings suggest the possibility that usage of Ig VH genes in pathogenic aCL is not random, but that there may exist a few epitopes of antigen recognized by the pathogenic aCL.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bothwell A. L., Paskind M., Reth M., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K., Baltimore D. Heavy chain variable region contribution to the NPb family of antibodies: somatic mutation evident in a gamma 2a variable region. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur P. H., Riblet R. The immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Igh-V) locus in the mouse. I. One hundred Igh-V genes comprise seven families of homologous genes. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):922–930. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewulonu U. K., Nell L. J., Thomas J. W. VH and VL gene usage by murine IgG antibodies that bind autologous insulin. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3091–3098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exner T. Comparison of two simple tests for the lupus anticoagulant. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Feb;83(2):215–218. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exner T. Similar mechanism of various lupus anticoagulants. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Feb 18;53(1):15–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förster I., Gu H., Rajewsky K. Germline antibody V regions as determinants of clonal persistence and malignant growth in the B cell compartment. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3693–3703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03251.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hang L. M., Izui S., Dixon F. J. (NZW x BXSB)F1 hybrid. A model of acute lupus and coronary vascular disease with myocardial infarction. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):216–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Kawamura M., Ichikawa K., Suzuki T., Sumida T., Yoshida S., Matsuura E., Ikehara S., Koike T. Anticardiolipin antibodies in NZW x BXSB F1 mice. A model of antiphospholipid syndrome. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):1063–1068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Traunecker A., Tonegawa S. Somatic mutation creates diversity in the major group of mouse immunoglobulin kappa light chains. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):417–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita Y., Sumida T., Ichikawa K., Maeda T., Yonaha F., Iwamoto I., Yoshida S., Koike T. V gene analysis of anticardiolipin antibodies from MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 15;151(2):849–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Maruyama N., Funaki H., Tomioka H., Yoshida S. Specificity of mouse hybridoma antibodies to DNA. II. Phospholipid reactivity and biological false positive serological test for syphilis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):345–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike T., Matsuura E. What is the "true" antigen for anticardiolipin antibodies? Lancet. 1991 Mar 16;337(8742):671–672. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92482-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura E., Igarashi Y., Fujimoto M., Ichikawa K., Koike T. Anticardiolipin cofactor(s) and differential diagnosis of autoimmune disease. Lancet. 1990 Jul 21;336(8708):177–178. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91697-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Immunology and clinical importance of antiphospholipid antibodies. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:193–280. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60777-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Simpson R. J., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anti-phospholipid antibodies are directed against a complex antigen that includes a lipid-binding inhibitor of coagulation: beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek K., Sanz I., Rathbun G., Nisonoff A., Capra J. D. Identity of the V kappa 10-Ars-A gene segments of the A/J and BALB/c strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6244–6248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollo R., Sikorav J. L., Rougeon F. Structural relationships among mouse and human immunoglobulin VH genes in the subgroup III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7887–7897. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyaizu N., Yasumizu R., Miyama-Inaba M., Nomura S., Yoshida H., Miyawaki S., Shibata Y., Mitsuoka S., Yasunaga K., Morii S. (NZW x BXSB)F1 mouse. A new animal model of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):2017–2022. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Newell J. B., Rudikoff S., Haber E. Classification of mouse VK groups based on the partial amino acid sequence to the first invariant tryptophan: impact of 14 new sequences from IgG myeloma proteins. Mol Immunol. 1982 Dec;19(12):1619–1630. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajewsky K., Förster I., Cumano A. Evolutionary and somatic selection of the antibody repertoire in the mouse. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1088–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.3317826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathbun G. A., Otani F., Milner E. C., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Molecular characterization of the A/J J558 family of heavy chain variable region gene segments. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M. J., Aucoin A. H., Pisetsky D. S., Weigert M. G. Structure and function of anti-DNA autoantibodies derived from a single autoimmune mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9150–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M., Mascelli M., Shan H., Radic M. Z., Pisetsky D., Marshak-Rothstein A., Weigert M. Anti-DNA antibodies from autoimmune mice arise by clonal expansion and somatic mutation. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):265–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikder S. K., Akolkar P. N., Kaladas P. M., Morrison S. L., Kabat E. A. Sequences of variable regions of hybridoma antibodies to alpha (1----6) dextran in BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4215–4221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taki S., Hirose S., Kinoshita K., Nishimura H., Shimamura T., Hamuro J., Shirai T. Somatically mutated IgG anti-DNA antibody clonally related to germ-line encoded IgM anti-DNA antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Apr;22(4):987–992. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Es J. H., Aanstoot H., Gmelig-Meyling F. H., Derksen R. H., Logtenberg T. A human systemic lupus erythematosus-related anti-cardiolipin/single-stranded DNA autoantibody is encoded by a somatically mutated variant of the developmentally restricted 51P1 VH gene. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):2234–2240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Es J. H., Gmelig Meyling F. H., van de Akker W. R., Aanstoot H., Derksen R. H., Logtenberg T. Somatic mutations in the variable regions of a human IgG anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibody suggest a role for antigen in the induction of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):461–470. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


