Abstract
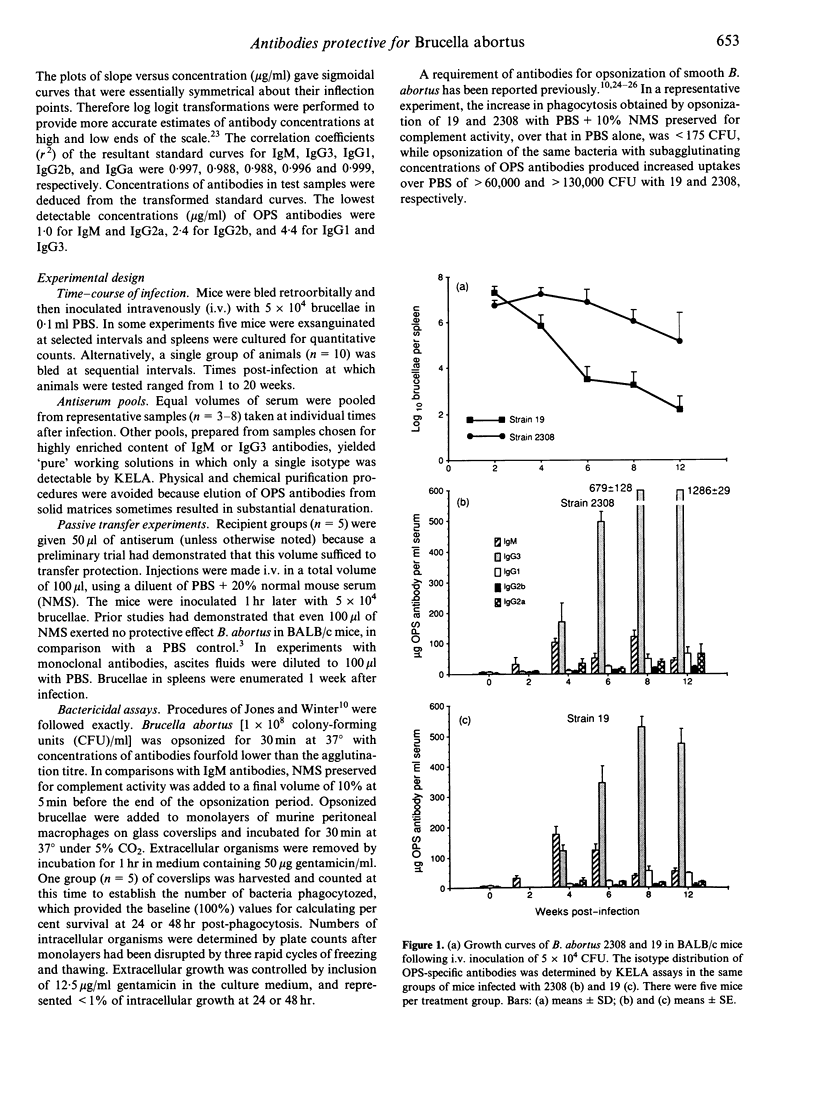
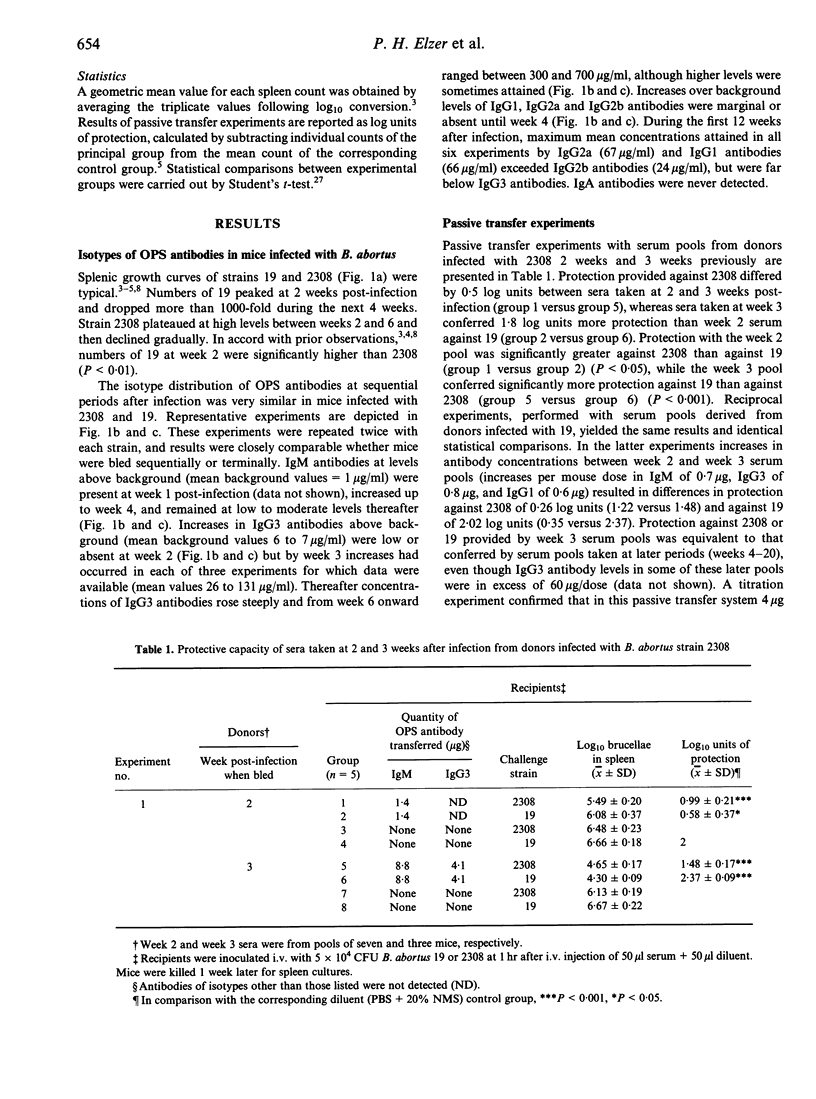
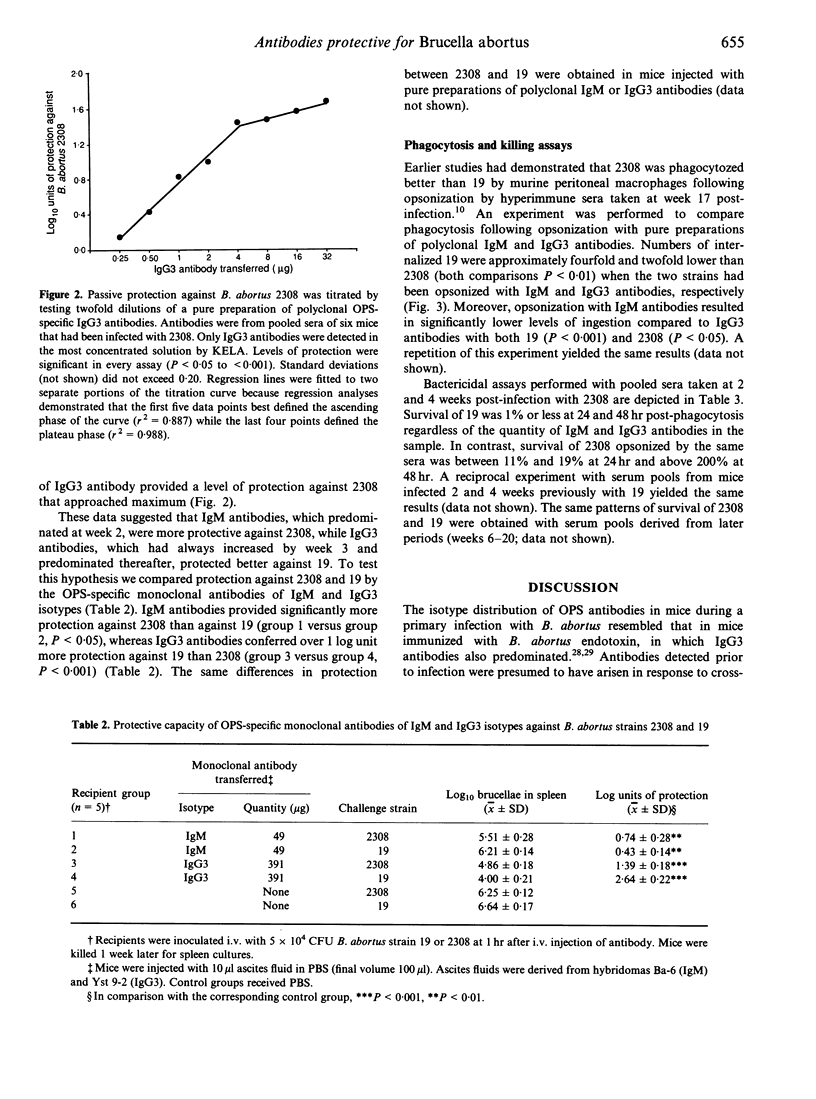
In BALB/c mice antibodies specific for the O polysaccharide (OPS) as well as T lymphocytes mediate protective immunity to Brucella abortus. We performed quantitative analyses of isotypes of OPS antibodies generated during primary infections, and tested the protective qualities of antisera at successive stages of infection against B. abortus strain 2308, representative of the wild type, and attenuated vaccine strain 19. IgM antibodies predominated during the first 3-4 weeks of infection. IgG3 antibodies increased slowly for the first 3 weeks but then rose rapidly and persisted at high levels (> 300 micrograms/ml). IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b antibodies had increased slightly by week 4 and then remained at low to moderate levels (< 70 micrograms/ml). Week 2 serum pools (IgM high, IgG3 low or undetectable) transferred substantial protection against 2308 (> or = 1 log unit) which increased relatively little (to 1.2-1.5 log units) with later sera that were high in IgG antibodies. In contrast, week 2 sera conferred low levels of protection against 19 (< 0.6 log units), but protection was dramatically increased (to > or = 2.3 log units) with sera obtained 1 week later that had slightly increased IgG antibodies. Monoclonal IgM antibodies also provided better protection against 2308 than 19, while monoclonal IgG3 antibodies protected much better against 19. Strain 19 opsonized with antibodies taken at any stage of infection was killed within normal macrophages, whereas comparably opsonized 2308 underwent intracellular replication. Phagocytosis of 2308 was better than of 19 when brucellae were opsonized with either polyclonal IgM or IgG3 antibodies, and the difference between strains was more extreme following IgM opsonization. The data suggest an explanation for differences in the growth curves of 2308 and 19 in spleens of BALB/c mice. Higher numbers achieved by 19 at week 2 could result from extracellular replication owing to ineffectual opsonization by IgM antibodies, while the precipitous decline of 19 beginning at week 3 could be caused by the increase in more effective IgG3 opsonins that facilitate its rapid intracellular destruction.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araya L. N., Elzer P. H., Rowe G. E., Enright F. M., Winter A. J. Temporal development of protective cell-mediated and humoral immunity in BALB/c mice infected with Brucella abortus. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3330–3337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. M. Role of macrophage complement and lectin-like receptors in binding Leishmania parasites to host macrophages. Immunol Lett. 1985;11(3-4):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundle D. R., Gidney M. A., Perry M. B., Duncan J. R., Cherwonogrodzky J. W. Serological confirmation of Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 O-antigens by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):389–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.389-393.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Duncan J. R. Antigenic S-type lipopolysaccharide of Brucella abortus 1119-3. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):384–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.384-388.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B. Structure of the O-chain of the phenol-phase soluble cellular lipopolysaccharide of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 15;139(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. T., Palmer D. A. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify the distribution of A and M epitopes on smooth Brucella species. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1353–1356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1353-1356.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzer P. H., Rowe G. E., Enright F. M., Winter A. J. Effects of gamma radiation and azathioprine on Brucella abortus infection in BALB/c mice. Am J Vet Res. 1991 Jun;52(6):838–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enright F. M., Araya L. N., Elzer P. H., Rowe G. E., Winter A. J. Comparative histopathology in BALB/c mice infected with virulent and attenuated strains of Brucella abortus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Oct;26(2):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(90)90065-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon B. G., Adams L. G., Frey M. Survival of rough and smooth strains of Brucella abortus in bovine mammary gland macrophages. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;49(7):1092–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Immunochemical studies on phenol-water extracted lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica type IX. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Baldwin C. L. Effects of cytokines on intracellular growth of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):124–134. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.124-134.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Baldwin C. L. Iron augments macrophage-mediated killing of Brucella abortus alone and in conjunction with interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1993 May;148(2):397–407. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. M., Winter A. J. Survival of virulent and attenuated strains of Brucella abortus in normal and gamma interferon-activated murine peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):3011–3014. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.3011-3014.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz R. S., Berman D. T. Influence of endotoxin-protein in immunoglobulin G isotype responses of mice to Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):728–734. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.728-734.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limet J., Plommet A. M., Dubray G., Plommet M. Immunity conferred upon mice by anti-LPS monoclonal antibodies in murine brucellosis. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 May-Jun;138(3):417–424. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaraz J. A., Winter A. J. Comparison of living and nonliving vaccines for Brucella abortus in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):245–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.245-251.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaraz J. A., Winter A. J., Hunter D. M., Sowa B. A., Wu A. M., Adams L. G. Protection against Brucella abortus in mice with O-polysaccharide-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):961–963. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.961-963.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Immunochemical characterization of rough Brucella lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):779–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.779-782.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Kurtz R. S., Berman D. T. Induction of immune and adjuvant immunoglobulin G responses in mice by Brucella lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):74–80. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.74-80.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Pitt M. W., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Purification and characterization of smooth and rough lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.361-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller J. M., Nielsen K. H. Affinity purification of bovine antibodies to Brucella abortus Lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):323–326. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.323-326.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Wilson B. C., Maddison S. E. Kinetic studies of a quantitative single-tube enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Chem. 1980 Aug;26(9):1255–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstreate D. R., Creasy M. T., Caveney N. T., Baldwin C. L., Blab M. W., Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins of Brucella abortus: isolation and characterization. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):979–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.979-989.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstreate D. R., Winter A. J. Comparison of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles and antigenic relatedness among outer membrane proteins of 49 Brucella abortus strains. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):182–187. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.182-187.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J., Duncan J. R., Santisteban C. G., Douglas J. T., Adams L. G. Capacity of passively administered antibody to prevent establishment of Brucella abortus infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3438–3444. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3438-3444.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J., Rowe G. E., Duncan J. R., Eis M. J., Widom J., Ganem B., Morein B. Effectiveness of natural and synthetic complexes of porin and O polysaccharide as vaccines against Brucella abortus in mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2808–2817. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2808-2817.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. J., Borchert M., Kretzer F. L., Musher D. M. Phagocytosis and killing of Brucella by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):682–690. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


