Abstract
More than 90% of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APC) have in their binding site a peptide derived from an extracellular protein ingested by the APC or from a protein of the APC itself. These self-peptides can be eluted from affinity-purified MHC class II molecules by acid elution, and have been studied with a variety of techniques. We show here that the self-peptides eluted from the mouse MHC class II molecules Ad, Ed and Ek bind specifically to MHC class II molecules of the allelic type from which they were derived. The pH optimum for binding is around 5.0, i.e. the same optimum at which synthetic peptides representing sequences of foreign antigens bind to MHC class II molecules. This suggests that the physiological compartment where MHC class II molecules bind self-peptides may be very late in the endocytic pathway. The chemical properties of the eluted and labelled MHC class II peptides were studied by isoelectric focusing. This method was able to separate the peptides very efficiently, and enabled a rapid comparison of peptides eluted from different MHC molecules. The 125I-labelled peptides displayed a broad range of isoelectric points with values predominantly below neutral. This suggests that such peptides bind to MHC in a predominantly non-charged state.
Full text
PDF

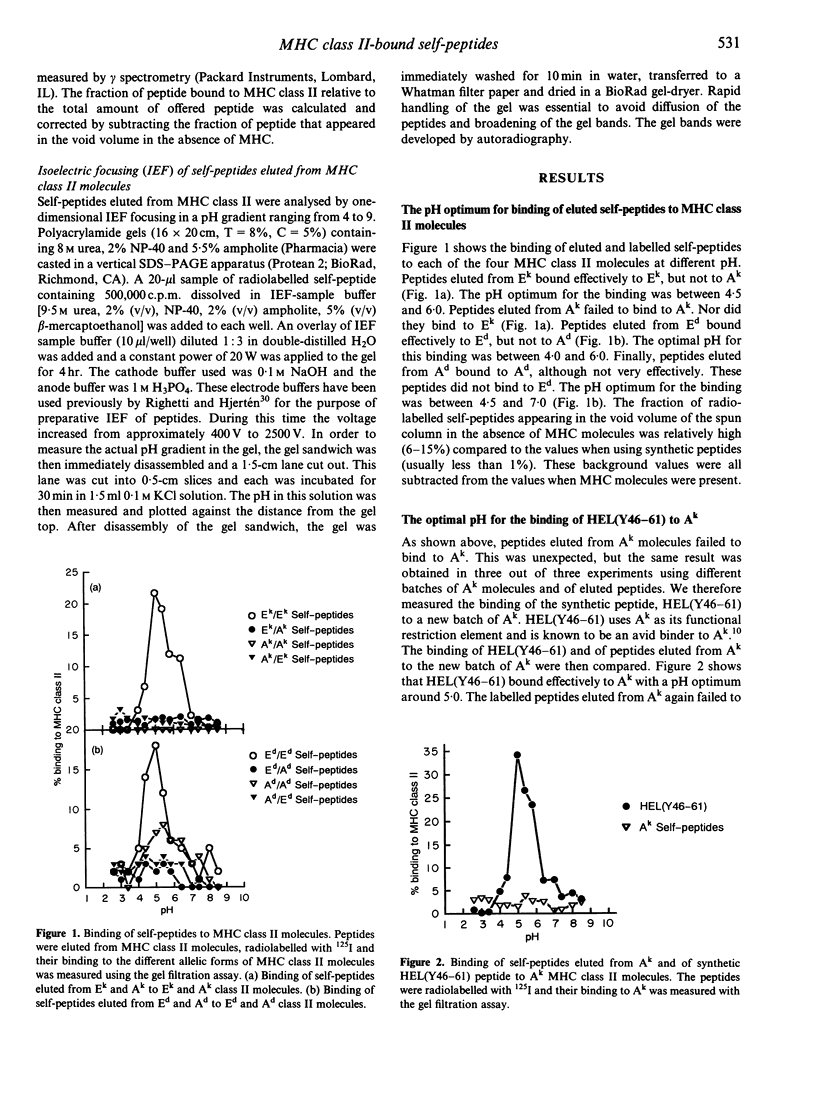
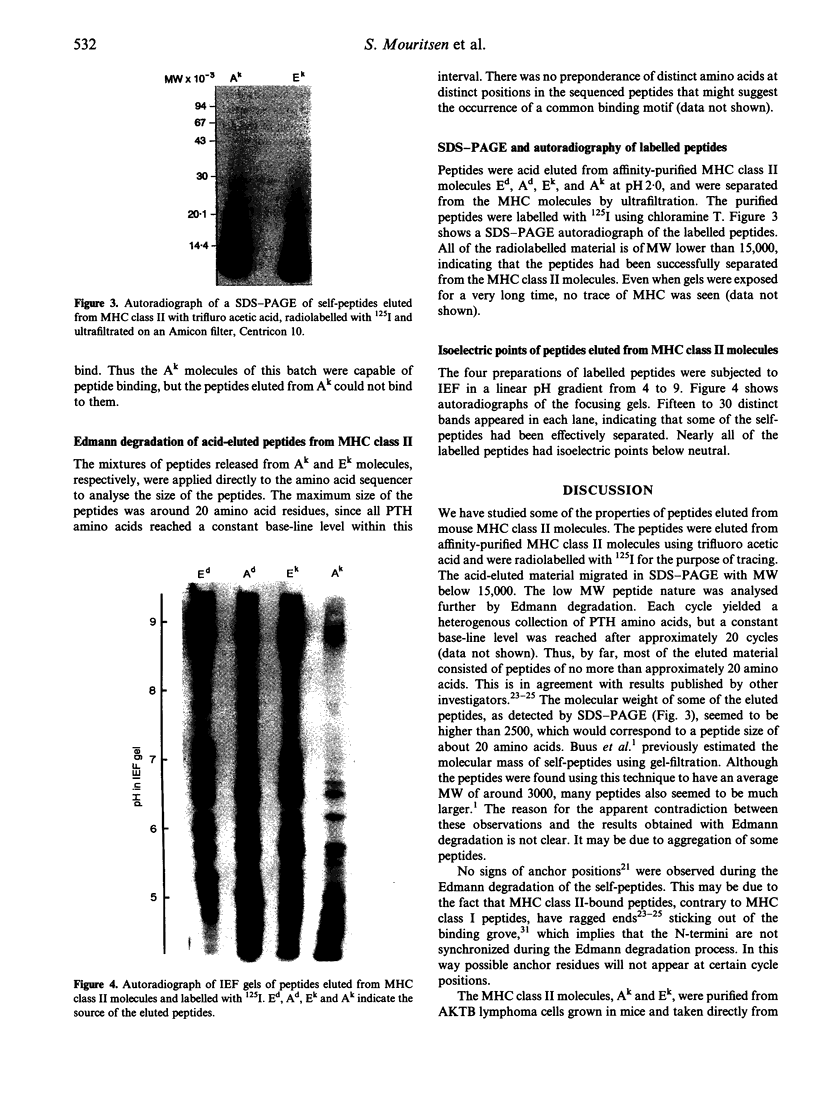


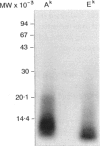
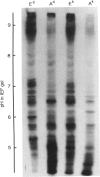
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T. S., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Urban R. G., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):33–39. doi: 10.1038/364033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Grey H. M. Autologous peptides constitutively occupy the antigen binding site on Ia. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1045–1047. doi: 10.1126/science.3194755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Jenis D. M., Grey H. M. Isolation and characterization of antigen-Ia complexes involved in T cell recognition. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1071–1077. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicz R. M., Urban R. G., Lane W. S., Gorga J. C., Stern L. J., Vignali D. A., Strominger J. L. Predominant naturally processed peptides bound to HLA-DR1 are derived from MHC-related molecules and are heterogeneous in size. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):764–768. doi: 10.1038/358764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demotz S., Grey H. M., Appella E., Sette A. Characterization of a naturally processed MHC class II-restricted T-cell determinant of hen egg lysozyme. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):682–684. doi: 10.1038/342682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donermeyer D. L., Allen P. M. Binding to Ia protects an immunogenic peptide from proteolytic degradation. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1063–1068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Stevanović S., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):290–296. doi: 10.1038/351290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremont D. H., Matsumura M., Stura E. A., Peterson P. A., Wilson I. A. Crystal structures of two viral peptides in complex with murine MHC class I H-2Kb. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):919–927. doi: 10.1126/science.1323877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansch C., Leo A., Unger S. H., Kim K. H., Nikaitani D., Lien E. J. "Aromatic" substituent constants for structure-activity correlations. J Med Chem. 1973 Nov;16(11):1207–1216. doi: 10.1021/jm00269a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Collins D. S., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Unanue E. R. Liposome-encapsulated antigens are processed in lysosomes, recycled, and presented to T cells. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90647-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Geuze H. J. Immunogenic peptides bind to class II MHC molecules in an early lysosomal compartment. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):3988–3998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Henderson R. A., Shabanowitz J., Sakaguchi K., Michel H., Sevilir N., Cox A. L., Appella E., Engelhard V. H. Characterization of peptides bound to the class I MHC molecule HLA-A2.1 by mass spectrometry. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1261–1263. doi: 10.1126/science.1546328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Michel H., Dickinson T. A., Shabanowitz J., Cox A. L., Sakaguchi K., Appella E., Grey H. M., Sette A. Peptides presented to the immune system by the murine class II major histocompatibility complex molecule I-Ad. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1817–1820. doi: 10.1126/science.1319610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Lane W. S., Robinson R. A., Madden D. R., Wiley D. C. Identification of self peptides bound to purified HLA-B27. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):326–329. doi: 10.1038/353326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. E. Long-lived complexes between peptide and class II major histocompatibility complex are formed at low pH with no requirement for pH neutralization. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):793–798. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. E. Regulation of antigen presentation by acidic pH. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1779–1784. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden D. R., Gorga J. C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The three-dimensional structure of HLA-B27 at 2.1 A resolution suggests a general mechanism for tight peptide binding to MHC. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen S., Hansen A. S., Petersen B. L., Buus S. pH dependence of the interaction between immunogenic peptides and MHC class II molecules. Evidence for an acidic intracellular compartment being the organelle of interaction. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1438–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen S., Meldal M., Ruud-Hansen J., Werdelin O. T-helper-cell determinants in protein antigens are preferentially located in cysteine-rich antigen segments resistant to proteolytic cleavage by cathepsin B, L, and D. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Oct;34(4):421–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb01565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen S., Meldal M., Werdelin O., Hansen A. S., Buus S. MHC molecules protect T cell epitopes against proteolytic destruction. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):1987–1993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb J. R., Cresswell P. Characterization of endogenous peptides bound to purified HLA-DR molecules and their absence from invariant chain-associated alpha beta dimers. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):499–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. J., Neefjes J. J., Oorschot V., Ploegh H. L., Geuze H. J. Segregation of MHC class II molecules from MHC class I molecules in the Golgi complex for transport to lysosomal compartments. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):669–676. doi: 10.1038/349669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righetti P. G., Hjertén S. High-molecular-weight carrier ampholytes for isoelectric focusing of peptides. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1981 Dec;5(5):259–272. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(81)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudensky AYu, Preston-Hurlburt P., al-Ramadi B. K., Rothbard J., Janeway C. A., Jr Truncation variants of peptides isolated from MHC class II molecules suggest sequence motifs. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):429–431. doi: 10.1038/359429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudensky AYu, Rath S., Preston-Hurlburt P., Murphy D. B., Janeway C. A., Jr On the complexity of self. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):660–662. doi: 10.1038/353660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rötzschke O., Falk K., Deres K., Schild H., Norda M., Metzger J., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Isolation and analysis of naturally processed viral peptides as recognized by cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):252–254. doi: 10.1038/348252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Southwood S., O'Sullivan D., Gaeta F. C., Sidney J., Grey H. M. Effect of pH on MHC class II-peptide interactions. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):844–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L. J., Brown J. H., Jardetzky T. S., Gorga J. C., Urban R. G., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Crystal structure of the human class II MHC protein HLA-DR1 complexed with an influenza virus peptide. Nature. 1994 Mar 17;368(6468):215–221. doi: 10.1038/368215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettstein D. A., Boniface J. J., Reay P. A., Schild H., Davis M. M. Expression of a class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) heterodimer in a lipid-linked form with enhanced peptide/soluble MHC complex formation at low pH. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):219–228. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bleek G. M., Nathenson S. G. The structure of the antigen-binding groove of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules determines specific selection of self-peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11032–11036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]