Abstract
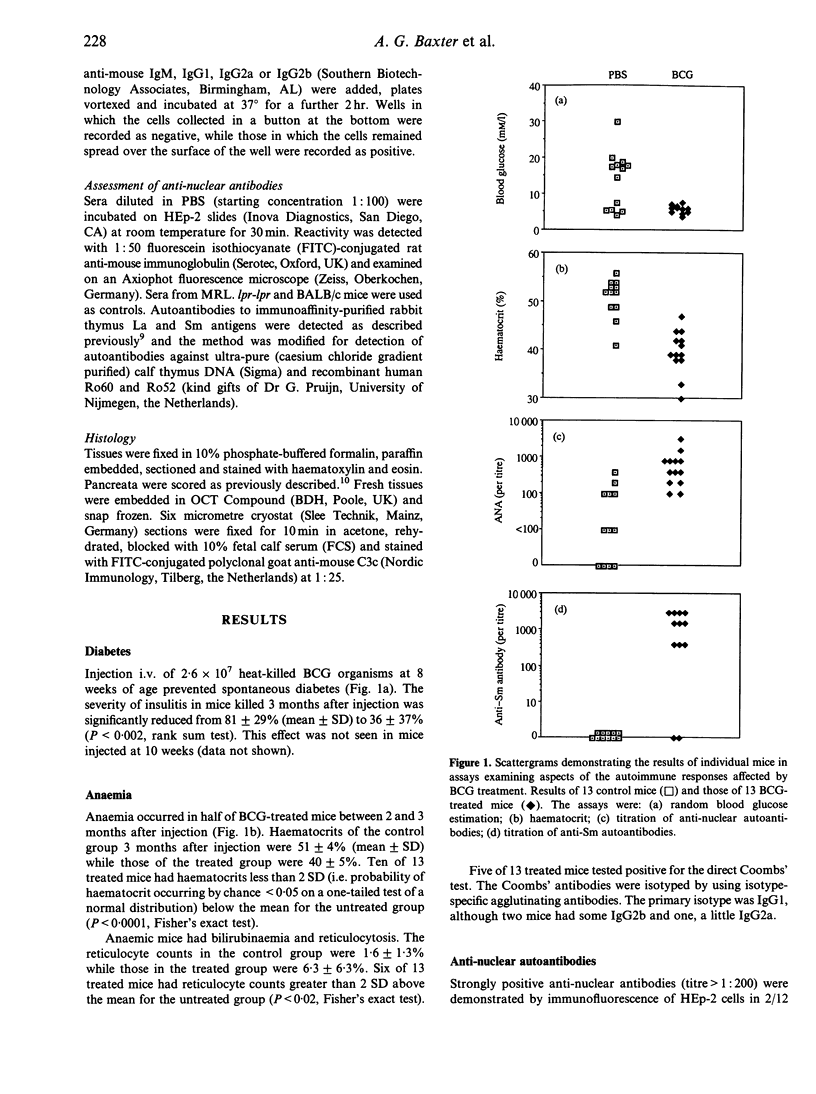
Non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice spontaneously develop organ-specific autoimmunity and are widely used as a model for diabetes. Aged NOD mice also exhibit some features of non-organ-specific autoimmune rheumatic disease such as anti-nuclear antibodies and late-onset haemolytic anaemia. Here, we report that a single dose of 2.6 x 10(7) heat-killed bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) i.v. in 8-week-old NOD mice prevented diabetes but precipitated a syndrome similar to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Treated mice developed haemolytic anaemia, anti-DNA and anti-Sm anti-nuclear autoantibodies and an increased severity of sialadenitis. Perivascular lymphocytic infiltration in the kidneys and glomerular immune complex deposition were also found. The action of BCG appeared to be mediated by an adjuvant-like activity as treated mice showed a substantial increase in reticuloendothelial cell function and enhanced antigen presentation capacity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter A. G., Adams M. A., Mandel T. E. Comparison of high- and low-diabetes-incidence NOD mouse strains. Diabetes. 1989 Oct;38(10):1296–1300. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.10.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter A. G., Mandel T. E. Hemolytic anemia in non-obese diabetic mice. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2051–2055. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callis A. H., Schrier D. J., David C. S., Moore V. L. Immunogenetics of BCG-induced anergy in mice. Control by Igh- and H-2-linked genes. Immunology. 1983 Aug;49(4):609–616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornall R. J., Prins J. B., Todd J. A., Pressey A., DeLarato N. H., Wicker L. S., Peterson L. B. Type 1 diabetes in mice is linked to the interleukin-1 receptor and Lsh/Ity/Bcg genes on chromosome 1. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):262–265. doi: 10.1038/353262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Williams D. G., Charles P., Maini R. N. Specificity of anti-Sm antibodies by ELISA for systemic lupus erythematosus: increased sensitivity of detection using purified peptide antigens. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Oct;47(10):820–825. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.10.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Skamene E., Forget A. Cellular mechanisms of genetically controlled host resistance to Mycobacterium bovis (BCG). J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1966–1972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada M., Kishimoto Y., Makino S. Prevention of overt diabetes and insulitis in NOD mice by a single BCG vaccination. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1990 Jan;8(2):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(90)90017-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Buse J. B., Jackson R. A., Glimcher L., Dorf M. E., Minami M., Makino S., Moriwaki K., Kuzuya H., Imura H. The NOD mouse: recessive diabetogenic gene in the major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):733–735. doi: 10.1126/science.3003909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys-Beher M. G., Brinkley L., Purushotham K. R., Wang P. L., Nakagawa Y., Dusek D., Kerr M., Chegini N., Chan E. K. Characterization of antinuclear autoantibodies present in the serum from nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Sep;68(3):350–356. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings P., Rosen H., O'Reilly L., Simpson E., Gordon S., Cooke A. Transfer of diabetes in mice prevented by blockade of adhesion-promoting receptor on macrophages. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):639–642. doi: 10.1038/348639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehuen A., Bendelac A., Bach J. F., Carnaud C. The nonobese diabetic mouse model. Independent expression of humoral and cell-mediated autoimmune features. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2147–2151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi P. S., Oehen S., Buerki K., Pircher H., Ohashi C. T., Odermatt B., Malissen B., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. Ablation of "tolerance" and induction of diabetes by virus infection in viral antigen transgenic mice. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90164-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadelain M. W., Qin H. Y., Lauzon J., Singh B. Prevention of type I diabetes in NOD mice by adjuvant immunotherapy. Diabetes. 1990 May;39(5):583–589. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.5.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Patel P. J., Nesbitt M. N. Regulation of resistance to leprosy by chromosome 1 locus in the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(2):117–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00387854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Paul W. E. Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science. 1987 May 22;236(4804):944–947. doi: 10.1126/science.3107127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocks M. R., Williams D. G., Maini R. N. Analysis of a positive feedback mechanism in the anti-Sm autoantibody response of MRL/MPJ-lpr/lpr mice. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):267–272. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal S. M., Malo D., Vogan K., Skamene E., Gros P. Natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites: isolation of a candidate for Bcg. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):469–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90135-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi H., Matsumoto M., Suzuki S., Misaki R., Suzuki R., Makino S., Harada M. Possible mechanism of the preventive effect of BCG against diabetes mellitus in NOD mouse. I. Generation of suppressor macrophages in spleen cells of BCG-vaccinated mice. Cell Immunol. 1991 Nov;138(1):130–141. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]