Abstract
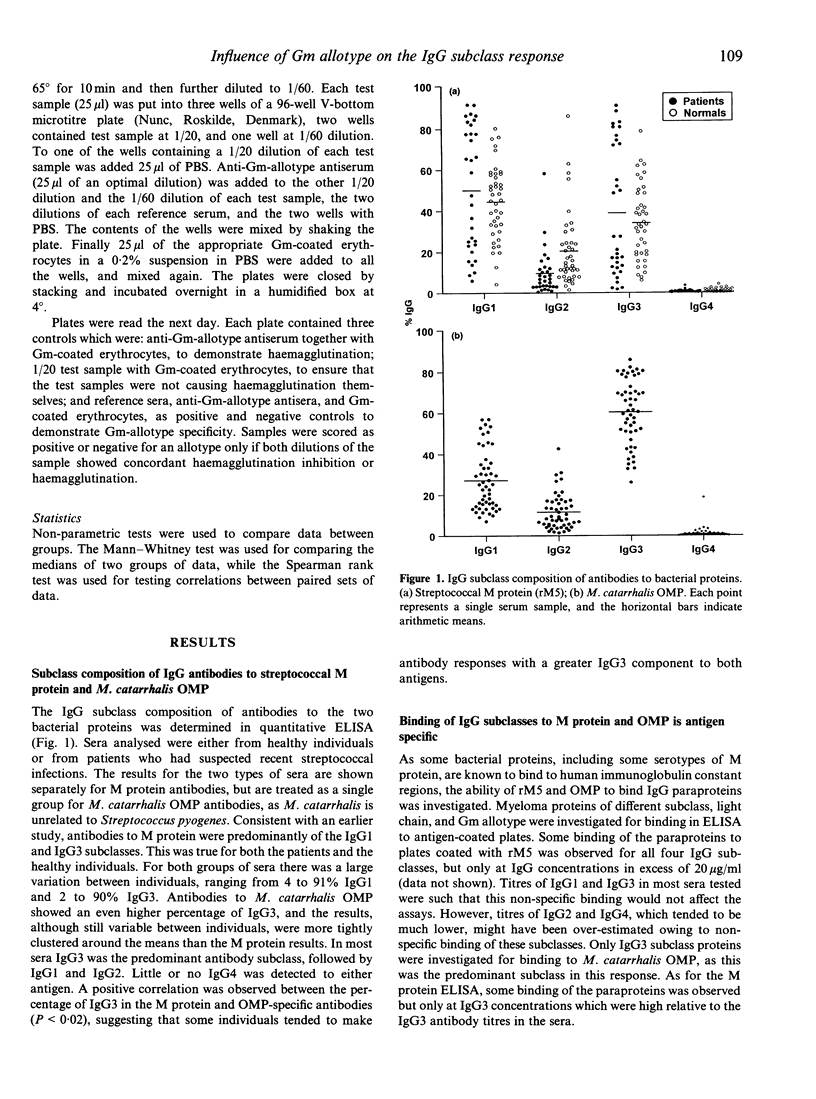
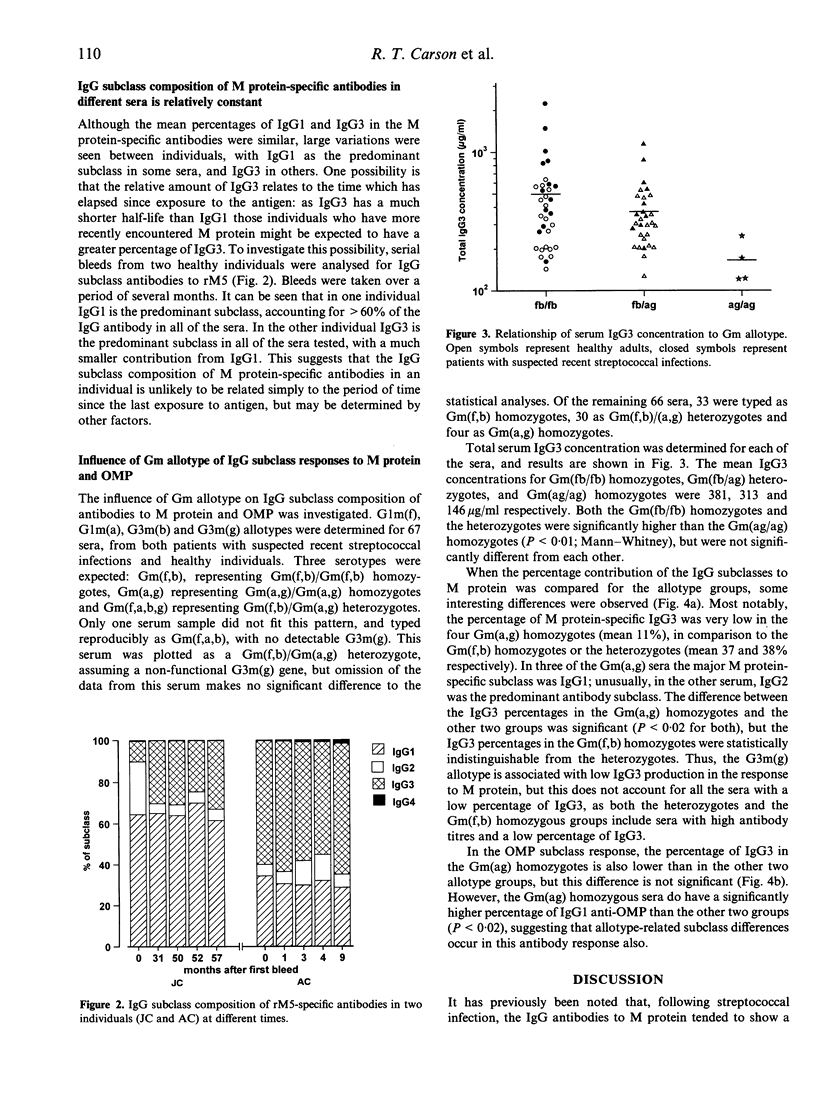
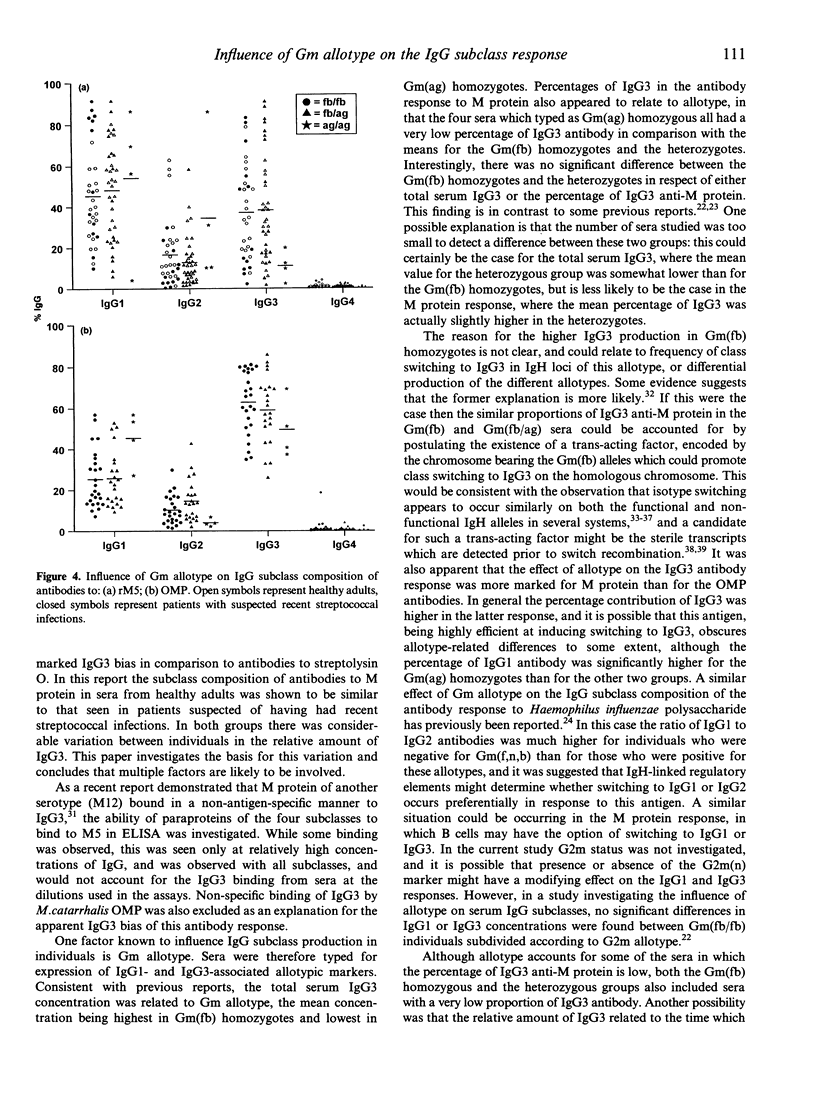
The IgG antibody response to streptococcal M protein is distributed between the IgG1 and IgG3 subclasses, however individual sera vary with respect to the relative amounts of these two subclasses. The basis of this variation was investigated. Sera were also analysed for IgG subclass antibodies to the outer membrane proteins (OMP) of Moraxella catarrhalis, as these have also been reported to have a major IgG3 component. The mean percentage of IgG3 was higher in the antibody response to OMP and there was less variability between sera for this antigen than was seen for M protein. Non-specific binding of IgG3 in ELISA, which has been reported for some bacterial proteins (including M protein of some serotypes) was excluded as an explanation for the apparent IgG3 bias of these antibodies. The relative amount of IgG3 antibody to the two antigens showed a positive correlation, suggesting that some individuals tended to make a greater IgG3 response to unrelated antigens. Serial bleeds from two individuals maintained a relatively constant subclass profile over several months, suggesting that time since infection did not play a major role in determining the proportion of IgG1 and IgG3. Gm allotypes for the sera were determined, and found to correlate with both total serum IgG3 concentrations and with IgG subclass composition of specific antibodies. Mean serum IgG3 concentrations were highest in sera typed as Gm(fb/fb) homozygous and lowest in sera typed as Gm(ag/ag) homozygous. Similarly, in the M protein-specific antibodies, the mean percentage of IgG3 was much lower in the Gm(ag/ag) sera than in the Gm(fb/fb) homozygous sera. Sera which typed as Gm(fb/ag) heterozygous were not significantly different from the Gm(fb/fb) homozygous sera for either total serum IgG3 or for M protein-specific IgG3. Moreover, both Gm(fb/fb) homozygous and Gm(fb/ag) heterozygous sera included samples in which IgG1 was the predominant antibody subclass and the percentage of IgG3 was very low. In contrast to the M protein-specific antibodies, for the OMP-specific antibodies there was no correlation between Gm phenotype and the proportion of IgG3. The data suggest that Gm allotype may influence the IgG subclass composition of antibody responses to bacterial surface protein, but that other factors are also likely to be involved.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalberse R. C., van der Gaag R., van Leeuwen J. Serologic aspects of IgG4 antibodies. I. Prolonged immunization results in an IgG4-restricted response. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):722–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amlot P. L., Hayes A. E., Gray D., Gordon-Smith E. C., Humphrey J. H. Human immune responses in vivo to protein (KLH) and polysaccharide (DNP-Ficoll) neoantigens: normal subjects compared with bone marrow transplant patients on cyclosporine. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird P., Calvert J. E., Amlot P. L. Distinctive development of IgG4 subclass antibodies in the primary and secondary responses to keyhole limpet haemocyanin in man. Immunology. 1990 Mar;69(3):355–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird P., Lowe J., Stokes R. P., Bird A. G., Ling N. R., Jefferis R. The separation of human serum IgG into subclass fractions by immunoaffinity chromatography and assessment of specific antibody activity. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Jun 8;71(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M., Williams G. T., Bindon C. I., Clark M. R., Walker M. R., Jefferis R., Waldmann H., Neuberger M. S. Comparison of the effector functions of human immunoglobulins using a matched set of chimeric antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1351–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R., Gregory L., Jefferis R. Aspects of the molecular structure of IgG subclasses. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:7–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Voak D. A critical study of the IgG subclasses of Rh anti-D antibodies formed in pregnancy and in immunized volunteers. Immunology. 1974 Dec;27(6):1073–1079. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Wilson D. V., Wheeler A. W. The IgG subclasses of antibodies to grass pollen allergens produced in hay fever patients during hyposensitization. Clin Allergy. 1976 May;6(3):227–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconer A. E., Carson R., Johnstone R., Bird P., Kehoe M., Calvert J. E. Distinct IgG1 and IgG3 subclass responses to two streptococcal protein antigens in man: analysis of antibodies to streptolysin O and M protein using standardized subclass-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Immunology. 1993 May;79(1):89–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconer A. E., Friedmann P. S., Bird P., Calvert J. E. Abnormal immunoglobulin G subclass production in response to keyhole limpet haemocyanin in atopic patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Sep;89(3):495–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt D., Turner M. W., Levinsky R. J. Branhamella catarrhalis: antigenic determinants and the development of the IgG subclass response in childhood. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1128–1135. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Suarez B. K., Pandey J. P., Shackelford P. G. Genes associated with the G2m(23) immunoglobulin allotype regulate the IgG subclass responses to Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1142–1149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Smith C. I. IgG subclasses in bacterial infections. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:122–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irsch J., Hendriks R., Tesch H., Schuurman R., Radbruch A. Evidence for a human IgG1 class switch program. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Feb;23(2):481–486. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jertborn M., Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. IgG and IgA subclass distribution of antitoxin antibody responses after oral cholera vaccination or cholera disease. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;85(3):358–363. doi: 10.1159/000234532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Weiss J. B., Brown R. J., Lee T., Schanfield M. S. Immunoglobulin allotype markers in gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Lancet. 1983 Apr 30;1(8331):952–953. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., Steinberg A. G., Van Loghem E., Terry W. D. Correlations between the concentrations of the four sub-classes of IgG and Gm Allotypes in normal human sera. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Vassalli G., DeLange G. G., Skvaril F., Ambrosino D. M., Siber G. R. Ig allotype-linked regulation of class and subclass composition of natural antibodies to group A streptococcal carbohydrate. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2495–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Loeb M. R. Isolation of the outer membrane of Branhamella catarrhalis. Microb Pathog. 1989 Mar;6(3):159–174. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A., Carlsson A. M. Quantitation of Gm allotypes. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Feb;37(2):143–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A. Gm allotype genes and gene dosage affecting both IgG subclass and IgE levels in atopic patients. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;91(1):58–61. doi: 10.1159/000235090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A. Serum IgG and IgG subclass contents in different Gm phenotypes. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Feb;37(2):149–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Müller W., Rajewsky K. Class switch recombination is IgG1 specific on active and inactive IgH loci of IgG1-secreting B-cell blasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3954–3957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Sablitzky F. Deletion of Cmu genes in mouse B lymphocytes upon stimulation with LPS. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1929–1935. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautonen N., Sarvas H., Julkunen I., Pyhälä R., Mäkelä O. Gm allotypes influence the production of IgG3 but the effect is age-dependent. Hum Immunol. 1991 Sep;32(1):72–77. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(91)90119-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaban M. E., Griffin J. A. Induction of RNA-stabilized DNA conformers by transcription of an immunoglobulin switch region. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):342–344. doi: 10.1038/348342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retnoningrum D. S., Podbielski A., Cleary P. P. Type M12 protein from Streptococcus pyogenes is a receptor for IgG3. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2332–2340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. H., Atherton M. C., Goodacre J. A., Pinkney M., Weightman H., Kehoe M. A. Mapping T-cell epitopes in group A streptococcal type 5 M protein. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4324–4331. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4324-4331.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas H., Rautonen N., Sipinen S., Mäkelä O. IgG subclasses of pneumococcal antibodies--effect of allotype G2m(n). Scand J Immunol. 1989 Feb;29(2):229–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz C., Petrini J., Collins J., Claflin J. L., Denis K. A., Gearhart P., Gritzmacher C., Manser T., Shulman M., Dunnick W. Patterns and extent of isotype-specificity in the murine H chain switch DNA rearrangement. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):363–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä I. J., Routonen N., Sarnesto A., Mattila P. A., Mäkelä O. The percentages of six immunoglobulin isotypes in human antibodies to tetanus toxoid: standardization of isotype-specific second antibodies in solid-phase assay. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Sep;14(9):868–875. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä I. J., Sarvas H., Mäkelä O. Low concentrations of Gm allotypic subsets G3 mg and G1 mf in homozygotes and heterozygotes. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2529–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvaril F. IgG subclasses in viral infections. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:134–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. G., Morell A., Skvaril F., van Loghem E. The effect of Gm(23) on the concentration of IgG2 and IgG4 in normal human serum. J Immunol. 1973 Jun;110(6):1642–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakatsuki Y., Strober W. Effect of downregulation of germline transcripts on immunoglobulin A isotype differentiation. J Exp Med. 1993 Jul 1;178(1):129–138. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Austin R. K., Schanfield M. S., Kagnoff M. F. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Immunoglobulin G heavy-chain (Gm) allotypes and the immune response to wheat gliadin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):96–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI110988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Mathews J. D., Schanfield M. S., Tait B. D., Mackay I. R. Interaction of HLA and Gm in autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Jan;43(1):80–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Krawinkel U., Radbruch A. Directed Ig class switch recombination in activated murine B cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1663–1671. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G., Litwin S. D. Studies of the Vi (gamma-2c) subgroup of gamma-globulin. A relationship between concentration and genetic type among normal individuals. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):177–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


