Abstract
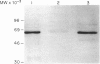
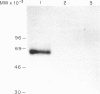
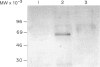
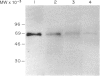
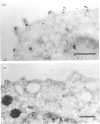
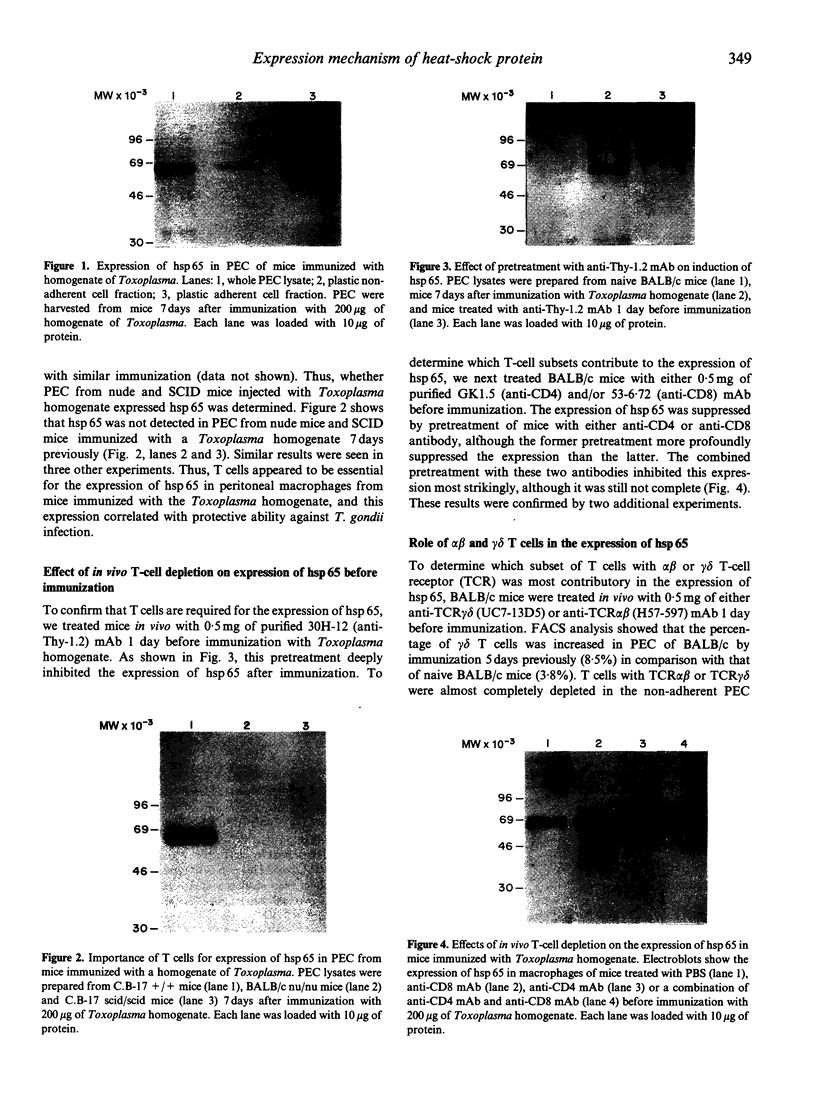
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite and cellular immunity plays a crucial role in protection against infection with this pathogen. When mice are immunized with Toxoplasma homogenate, they readily acquire resistance against infection with a lethal dose of a low virulence Beverley strain of T. gondii. We have reported previously that expression of 65,000 MW heat-shock protein (hsp 65) in host macrophages closely correlates with protective potentials of hosts, while this protein is not expressed in Toxoplasma themselves. In this study, we examined the mechanism of expression of hsp 65 in mice immunized with Toxoplasma homogenate. Heat-shock protein was detected in peritoneal macrophages of BALB/c mice immunized 7 days previously by electroblot assay with a specific monoclonal antibody (mAb) for microbial hsp 65. Furthermore, an immunogold ultracytochemistry assay demonstrated that this protein was expressed on the cell surface of peritoneal macrophages in immune mice. This expression was not induced in those of immune athymic nude mice and SCID mice. Treatment of BALB/c mice with anti-Thy-1.2 mAb 1 day before immunization led to an almost complete loss of the expression of hsp 65. To determine the subsets of T cells responsible for induction of this protein, mice were depleted of gamma delta T cells, alpha beta T cells, CD4+ T cells or CD8+ T cells by treating with corresponding antibodies before immunization. From these experiments, gamma delta T cells were shown to be essential for the expression of hsp 65, although CD4+ alpha beta T cells also contributed to some extent. Thus, gamma delta T cells appear to play an important role in protective immunity against infection with T. gondii through mediating the expression of hsp 65 in host macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchmeier N. A., Heffron F. Induction of Salmonella stress proteins upon infection of macrophages. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):730–732. doi: 10.1126/science.1970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emoto M., Danbara H., Yoshikai Y. Induction of gamma/delta T cells in murine salmonellosis by an avirulent but not by a virulent strain of Salmonella choleraesuis. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):363–372. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferm M. T., Söderström K., Jindal S., Grönberg A., Ivanyi J., Young R., Kiessling R. Induction of human hsp60 expression in monocytic cell lines. Int Immunol. 1992 Mar;4(3):305–311. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.3.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris D. K., Harel-Bellan A., Morimoto R. I., Welch W. J., Farrar W. L. Mitogen and lymphokine stimulation of heat shock proteins in T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3850–3854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsdyke D. R. Heat shock proteins defend against intracellular pathogens: a non-immunological basis for self/non-self discrimination? J Theor Biol. 1985 Aug 7;115(3):471–473. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(85)80205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Soman G., Hom R. C., Finberg R. W. Human gamma delta+ T cells respond to mycobacterial heat-shock protein. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):309–312. doi: 10.1038/340309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromatsu K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Ohga S., Muramori K., Matsumoto K., Bluestone J. A., Nomoto K. A protective role of gamma/delta T cells in primary infection with Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):49–56. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Koning F., Coligan J. E., De Bruyn J., Strober S. Isolation of CD4- CD8- mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):226–229. doi: 10.1038/339226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jindal S., Dudani A. K., Singh B., Harley C. B., Gupta R. S. Primary structure of a human mitochondrial protein homologous to the bacterial and plant chaperonins and to the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Heat shock proteins and the immune response. Immunol Today. 1990 Apr;11(4):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90050-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Wand-Württenberger A., DeBruyn J., Munk M. E., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. T cells against a bacterial heat shock protein recognize stressed macrophages. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1112–1115. doi: 10.1126/science.2788923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Manabe T., Maekawa Y., Oka M., Himeno K. Role of L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ T cell subsets in protective immune responses of mice against infection with a low or high virulent strain of Toxoplasma gondii. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(3):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa H., Oka M., Maeda K., Jian-Guo C., Hisaeda H., Ito Y., Good R. A., Himeno K. Induction of heat shock protein closely correlates with protection against Toxoplasma gondii infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3155–3158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Palmer E., Kubo R., Born W. K. Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor gamma delta by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Ab B. K., Van Embden J. D., Thole J. E., Kiessling R. The recombinant 65-kD heat shock protein of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin/M. tuberculosis is a target molecule for CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes that lyse human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1947–1952. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. Heat-shock proteins. Coming in from the cold. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):776–777. doi: 10.1038/332776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J. Heat shock proteins: the search for functions. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):321–325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smejkal R. M., Wolff R., Olenick J. G. Leishmania braziliensis panamensis: increased infectivity resulting from heat shock. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Feb;65(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanbuskirk A., Crump B. L., Margoliash E., Pierce S. K. A peptide binding protein having a role in antigen presentation is a member of the HSP70 heat shock family. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1799–1809. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wand-Württenberger A., Schoel B., Ivanyi J., Kaufmann S. H. Surface expression by mononuclear phagocytes of an epitope shared with mycobacterial heat shock protein 60. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1089–1092. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Russ F., Teixeira H. C., Conradt P., Kaufmann S. H. Listeria monocytogenes-induced gamma interferon secretion by intestinal intraepithelial gamma/delta T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2154–2161. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2154-2161.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]