Abstract
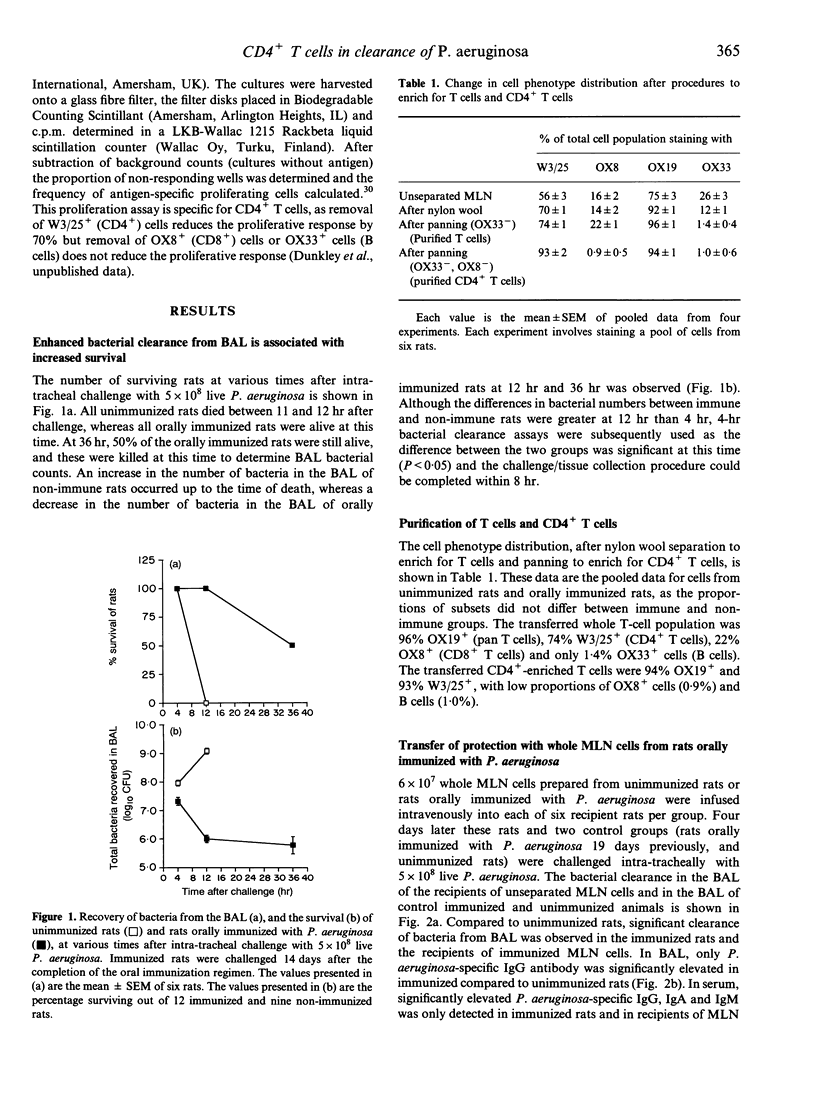
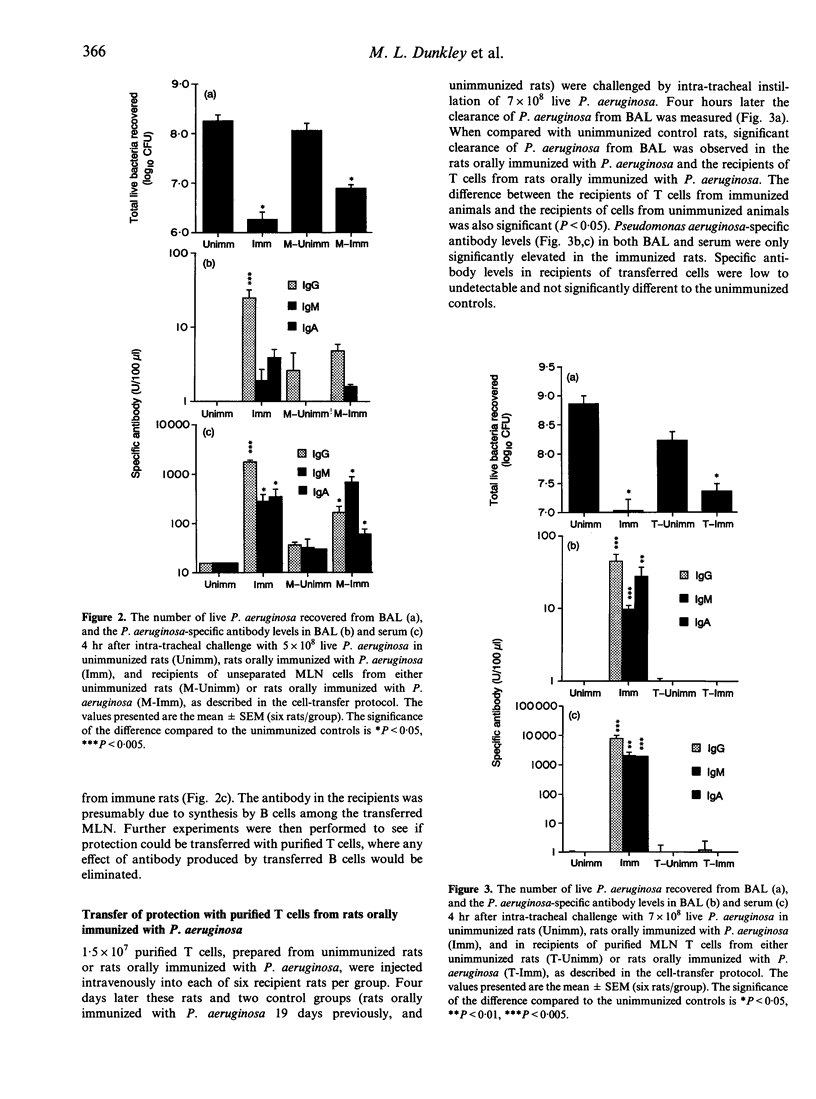
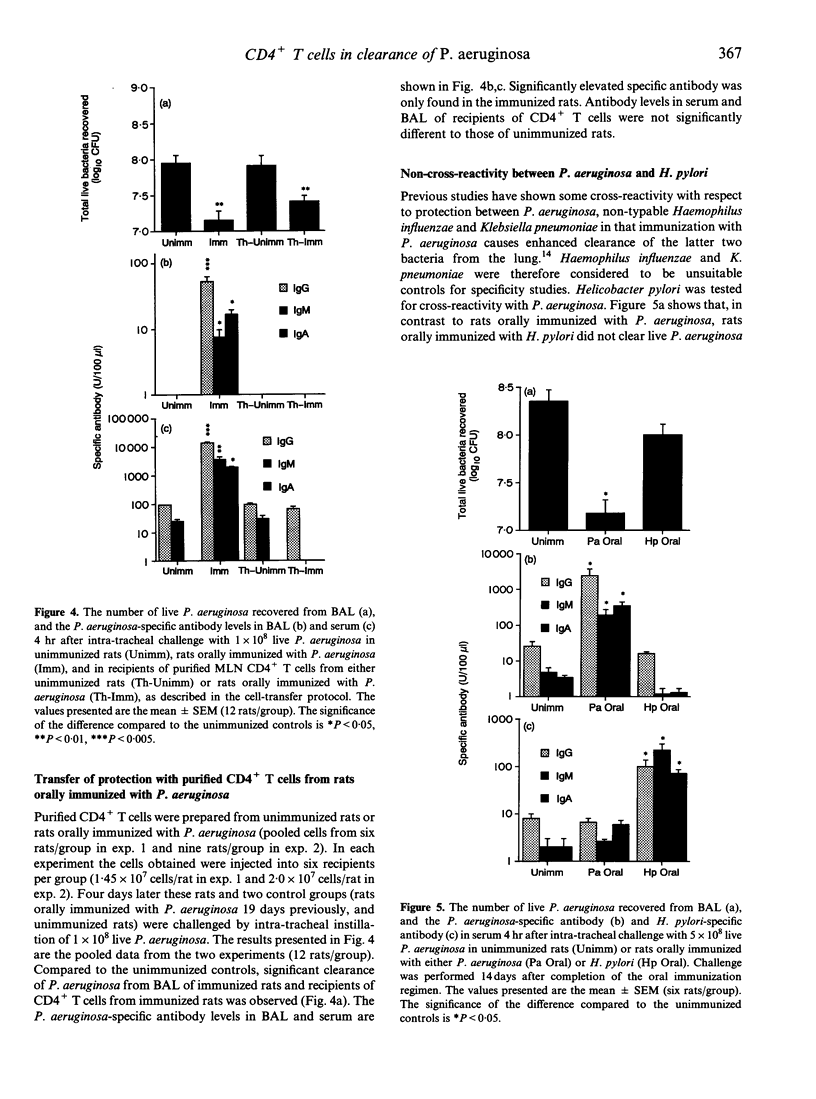
The role of gut-derived CD4+ T cells in clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the lung was studied by cell transfer experiments. Mesenteric lymph node cells from unimmunized rats, or rats orally immunized with either killed P. aeruginosa or Helicobacter pylori, were transferred to naive rats which were subsequently challenged intra-tracheally with live P. aeruginosa. Recipients of unseparated mesenteric lymph node cells, purifed T cells or CD4+ T cells, from P. aeruginosa-immunized donors, all exhibited enhanced bacterial clearance from the airways compared to recipients of cells from unimmunized donors. Enhanced clearance by T cells was antigen-specific as no enhanced clearance was observed by transfer of cells from donors immunized with H. pylori.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brett M. M., Ghoneim A. T., Littlewood J. M. Serum antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Nov;61(11):1114–1120. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.11.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buret A., Cripps A. W. The immunoevasive activities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Relevance for cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Sep;148(3):793–805. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.3.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buret A., Dunkley M., Clancy R. L., Cripps A. W. Effector mechanisms of intestinally induced immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the rat lung: role of neutrophils and leukotriene B4. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):671–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.671-679.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. A. The neutrophil, a professional killer of bacteria, may be controlled by T cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Feb;79(2):141–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps A. W., Dunkley M. L., Clancy R. L. Mucosal and systemic immunizations with killed Pseudomonas aeruginosa protect against acute respiratory infection in rats. Infect Immun. 1994 Apr;62(4):1427–1436. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.4.1427-1436.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley M. L., Husband A. J. Distribution and functional characteristics of antigen-specific helper T cells arising after Peyer's patch immunization. Immunology. 1987 Aug;61(4):475–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley M. L., Husband A. J. The induction and migration of antigen-specific helper cells for IgA responses in the intestine. Immunology. 1986 Mar;57(3):379–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Høiby N. Longitudinal study of immune response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa antigens in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):197–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.197-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finke M., Muth G., Reichhelm T., Thoma M., Duchêne M., Hungerer K. D., Domdey H., von Specht B. U. Protection of immunosuppressed mice against infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa by recombinant P. aeruginosa lipoprotein I and lipoprotein I-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1251–1254. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1251-1254.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hector R. F., Collins M. S., Pennington J. E. Treatment of experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia with a human IgM monoclonal antibody. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):483–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry R. L., Mellis C. M., Petrovic L. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a marker of poor survival in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1992 Mar;12(3):158–161. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950120306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaratilake L. M., Ferrante A., Rzepczyk C. The role of T lymphocytes in immunity to Plasmodium falciparum. Enhancement of neutrophil-mediated parasite killing by lymphotoxin and IFN-gamma: comparisons with tumor necrosis factor effects. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):762–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham R. B., Goellner J., Pier G. B. In vitro T cell-mediated killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Evidence that a lymphokine mediates killing. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):962–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham R. B., Pier G. B., Goellner J. J., Mizel S. B. In vitro T cell-mediated killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. II. The role of macrophages and T cell subsets in T cell killing. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4112–4117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham R. B., Powderly W. G. Exposure of mice to live Pseudomonas aeruginosa generates protective cell-mediated immunity in the absence of an antibody response. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2039–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Arthur R. P., Dallman M. J., Green J. R., Spickett G. P., Thomas M. L. Functions of rat T-lymphocyte subsets isolated by means of monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:57–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. S., Espersen F., Høiby N., Jensen T. Immunoglobulin A and immunoglobulin G antibody responses to alginates from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):747–755. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.747-755.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Markham R. B. Induction in mice of cell-mediated immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa by high molecular weight polysaccharide and vinblastine. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2121–2125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Saunders J. M., Ames P., Edwards M. S., Auerbach H., Goldfarb J., Speert D. P., Hurwitch S. Opsonophagocytic killing antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide in older noncolonized patients with cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 24;317(13):793–798. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709243171303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Small G. J., Warren H. B. Protection against mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in rodent models of endobronchial infections. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):537–540. doi: 10.1126/science.2116663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powderly W. G., Pier G. B., Markham R. B. T lymphocyte-mediated protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in granulocytopenic mice. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):375–380. doi: 10.1172/JCI112587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosok M. J., Stebbins M. R., Connelly K., Lostrom M. E., Siadak A. W. Generation and characterization of murine antiflagellum monoclonal antibodies that are protective against lethal challenge with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3819–3828. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3819-3828.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen R. U., Stern R. C., Polmar S. H. Cellular immunity to bacteria: impairment of in vitro lymphocyte responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):735–740. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.735-740.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. A., Mason D. W., Williams A. F., Galfre G., Milstein C. T-lymphocyte heterogeneity in the rat: separation of functional subpopulations using a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):664–673. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woollett G. R., Barclay A. N., Puklavec M., Williams A. F. Molecular and antigenic heterogeneity of the rat leukocyte-common antigen from thymocytes and T and B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Feb;15(2):168–173. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


