Abstract
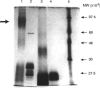
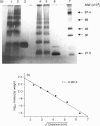
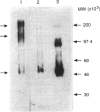
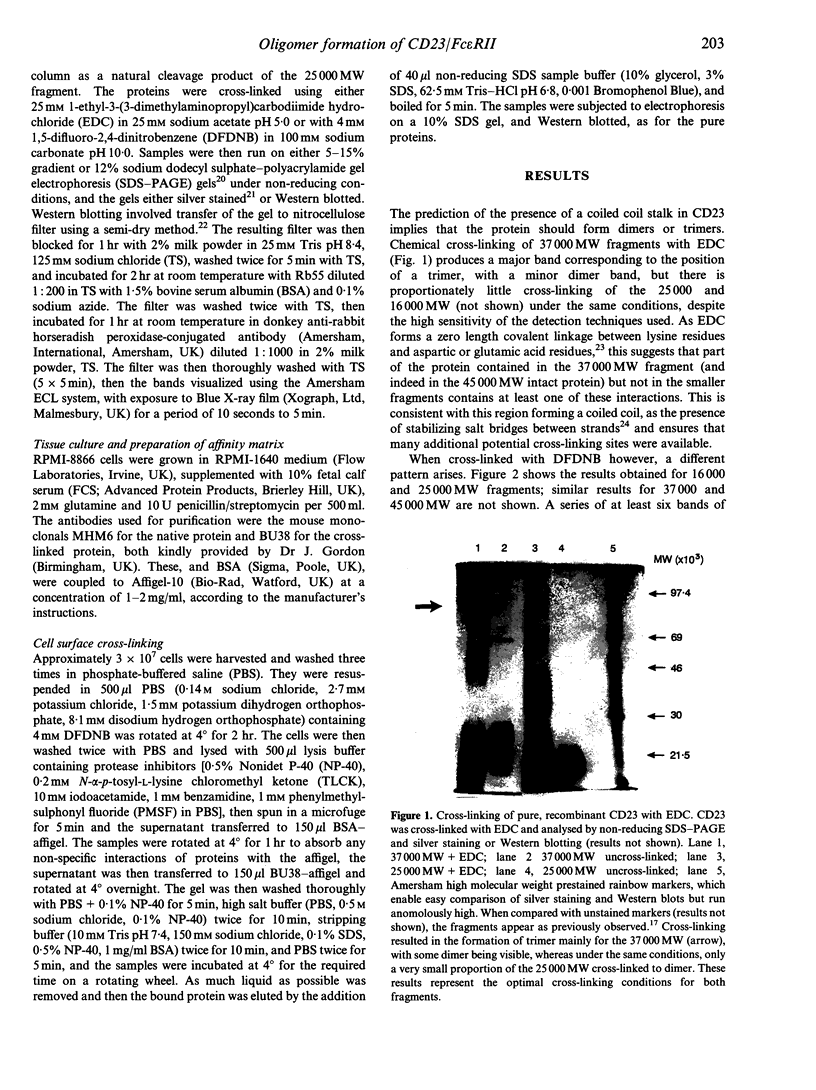
Human CD23 (also known as Fc epsilon RII) is a 45,000 MW glycoprotein with homology to C-type animal lectins. It is involved in B-cell differentiation and IgE regulation, and is naturally cleaved to give soluble products of 37,000, 33,000, 29,000, 25,000 and 16,000 MW. Previous work has suggested that the region between the transmembrane sequence and the extracellular lectin head is capable of forming an alpha-helical coiled coil, one of the main consequences of which would be formation of dimers or trimers. Here we present protein-protein cross-linking data showing that CD23 forms trimers on the cell surface and hexamers in solution, and we use several different fragments to determine the regions of the protein involved in this self-association. The region of the putative coiled coil is indeed responsible for trimerization, with additional interactions between the lectin heads resulting in the formation of hexamers observed in solution.
Full text
PDF
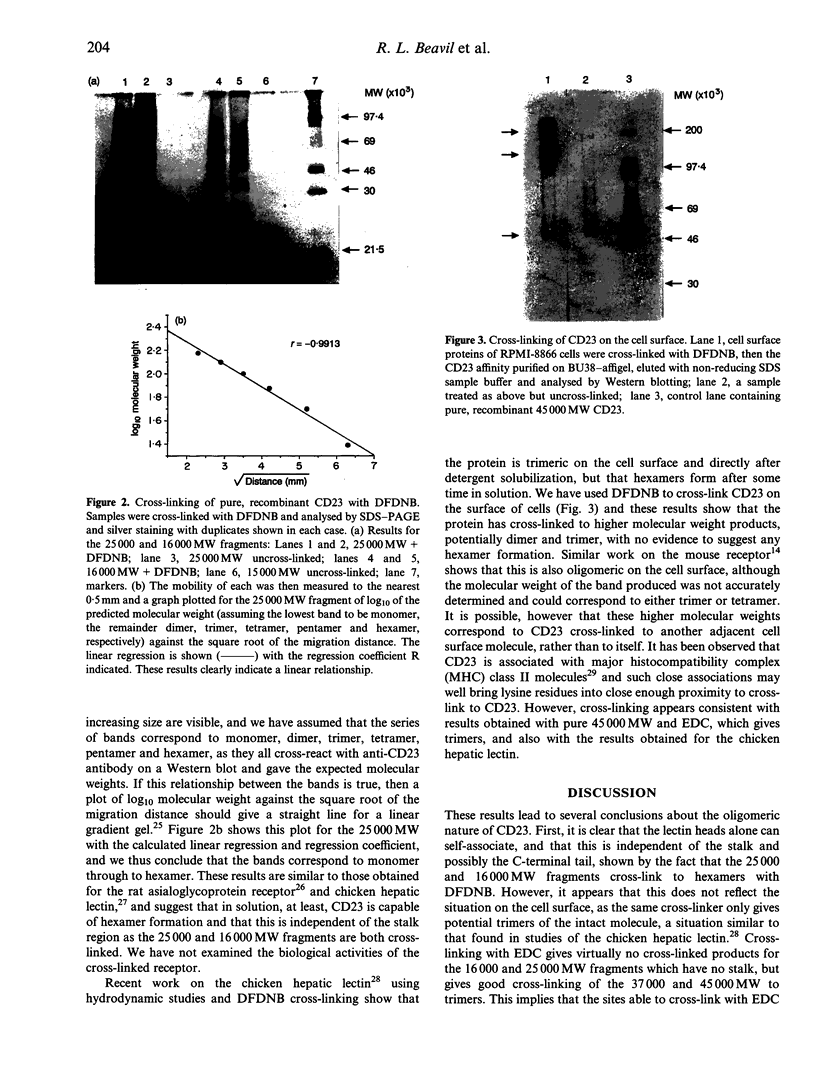


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubry J. P., Pochon S., Gauchat J. F., Nueda-Marin A., Holers V. M., Graber P., Siegfried C., Bonnefoy J. Y. CD23 interacts with a new functional extracytoplasmic domain involving N-linked oligosaccharides on CD21. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):5806–5813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubry J. P., Pochon S., Graber P., Jansen K. U., Bonnefoy J. Y. CD21 is a ligand for CD23 and regulates IgE production. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):505–507. doi: 10.1038/358505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavil A. J., Edmeades R. L., Gould H. J., Sutton B. J. Alpha-helical coiled-coil stalks in the low-affinity receptor for IgE (Fc epsilon RII/CD23) and related C-type lectins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):753–757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy J. Y., Guillot O., Spits H., Blanchard D., Ishizaka K., Banchereau J. The low-affinity receptor for IgE (CD23) on B lymphocytes is spatially associated with HLA-DR antigens. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):57–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. A., Lees A., Finkelman F. D., Conrad D. H. Co-crosslinking Fc epsilon RII/CD23 and B cell surface immunoglobulin modulates B cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Aug;22(8):2107–2112. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Suter U., Mossalayi D., Bettler B., Sarfati M., Hofstetter H., Kilcherr E., Debre P., Dalloul A. Expression, structure, and function of the CD23 antigen. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:149–191. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks S. E., Bartlett W. C., Edmeades R. L., Gould H. J., Rao M., Conrad D. H. The oligomeric nature of the murine Fc epsilon RII/CD23. Implications for function. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2372–2382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber P., Jansen K., Pochon S., Shields J., Aubonney N., Turcatti G., Bonnefoy J. Y. Purification and characterization of biologically active human recombinant 37 kDa soluble CD23 (sFc epsilon RII) expressed in insect cells. J Immunol Methods. 1992 May 18;149(2):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90253-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halberg D. F., Wager R. E., Farrell D. C., Hildreth J., 4th, Quesenberry M. S., Loeb J. A., Holland E. C., Drickamer K. Major and minor forms of the rat liver asialoglycoprotein receptor are independent galactose-binding proteins. Primary structure and glycosylation heterogeneity of minor receptor forms. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9828–9838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henis Y. I., Katzir Z., Shia M. A., Lodish H. F. Oligomeric structure of the human asialoglycoprotein receptor: nature and stoichiometry of mutual complexes containing H1 and H2 polypeptides assessed by fluorescence photobleaching recovery. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta K., Takami M., Kim C. W., Honjo T., Miyoshi T., Tagaya Y., Kawabe T., Yodoi J. Human lymphocyte Fc receptor for IgE: sequence homology of its cloned cDNA with animal lectins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):819–823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen K. U., Shields J., Gordon J., Cairns J., Graber P., Bonnefoy J. Y. Expression of human recombinant CD23 in insect cells. J Recept Res. 1991;11(1-4):507–520. doi: 10.3109/10799899109066424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikutani H., Inui S., Sato R., Barsumian E. L., Owaki H., Yamasaki K., Kaisho T., Uchibayashi N., Hardy R. R., Hirano T. Molecular structure of human lymphocyte receptor for immunoglobulin E. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):657–665. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. T., Conrad D. H. The murine lymphocyte receptor for IgE. II. Characterization of the multivalent nature of the B lymphocyte receptor for IgE. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1790–1795. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letellier M., Sarfati M., Delespesse G. Mechanisms of formation of IgE-binding factors (soluble CD23)--I. Fc epsilon R II bearing B cells generate IgE-binding factors of different molecular weights. Mol Immunol. 1989 Dec;26(12):1105–1112. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Frigeri L. G., Gritzmacher C. A., Hsu D. K., Robertson M. W., Zuberi R. I. Expression and function of an IgE-binding animal lectin (epsilon BP) in mast cells. Immunopharmacology. 1993 Nov-Dec;26(3):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(93)90034-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. A., Drickamer K. The chicken receptor for endocytosis of glycoproteins contains a cluster of N-acetylglucosamine-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3022–3029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüdin C., Hofstetter H., Sarfati M., Levy C. A., Suter U., Alaimo D., Kilchherr E., Frost H., Delespesse G. Cloning and expression of the cDNA coding for a human lymphocyte IgE receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):109–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04726.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. H., Conrad D. H. Fine specificity, structure, and proteolytic susceptibility of the human lymphocyte receptor for IgE. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2654–2660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K., Turcatti G., Graber P., Pochon S., Regamey P. O., Jansen K. U., Magnenat E., Aubonney N., Bonnefoy J. Y. Partial characterization of natural and recombinant human soluble CD23. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj2860819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfati M., Bettler B., Letellier M., Fournier S., Rubio-Trujillo M., Hofstetter H., Delespesse G. Native and recombinant soluble CD23 fragments with IgE suppressive activity. Immunology. 1992 Aug;76(4):662–667. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr E., Macy E., Kimata H., Gilly M., Saxon A. Binding the low affinity Fc epsilon R on B cells suppresses ongoing human IgE synthesis. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):481–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Texido G., Eibel H., Le Gros G., van der Putten H. Transgene CD23 expression on lymphoid cells modulates IgE and IgG1 responses. J Immunol. 1994 Oct 1;153(7):3028–3042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Helm B., Marsh P., Padlan E., Geha R. S., Gould H. The B-cell binding site on human immunoglobulin E. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):649–651. doi: 10.1038/338649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrey F., Drickamer K. Determinants of oligomeric structure in the chicken liver glycoprotein receptor. Biochem J. 1993 May 15;292(Pt 1):149–155. doi: 10.1042/bj2920149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Imoto T., Fujita K., Okazaki K., Motomura M. Selective modification of aspartic acid-101 in lysozyme by carbodiimide reaction. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4836–4842. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota A., Kikutani H., Tanaka T., Sato R., Barsumian E. L., Suemura M., Kishimoto T. Two species of human Fc epsilon receptor II (Fc epsilon RII/CD23): tissue-specific and IL-4-specific regulation of gene expression. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu P., Kosco-Vilbois M., Richards M., Köhler G., Lamers M. C. Negative feedback regulation of IgE synthesis by murine CD23. Nature. 1994 Jun 30;369(6483):753–756. doi: 10.1038/369753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]