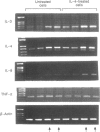
Abstract
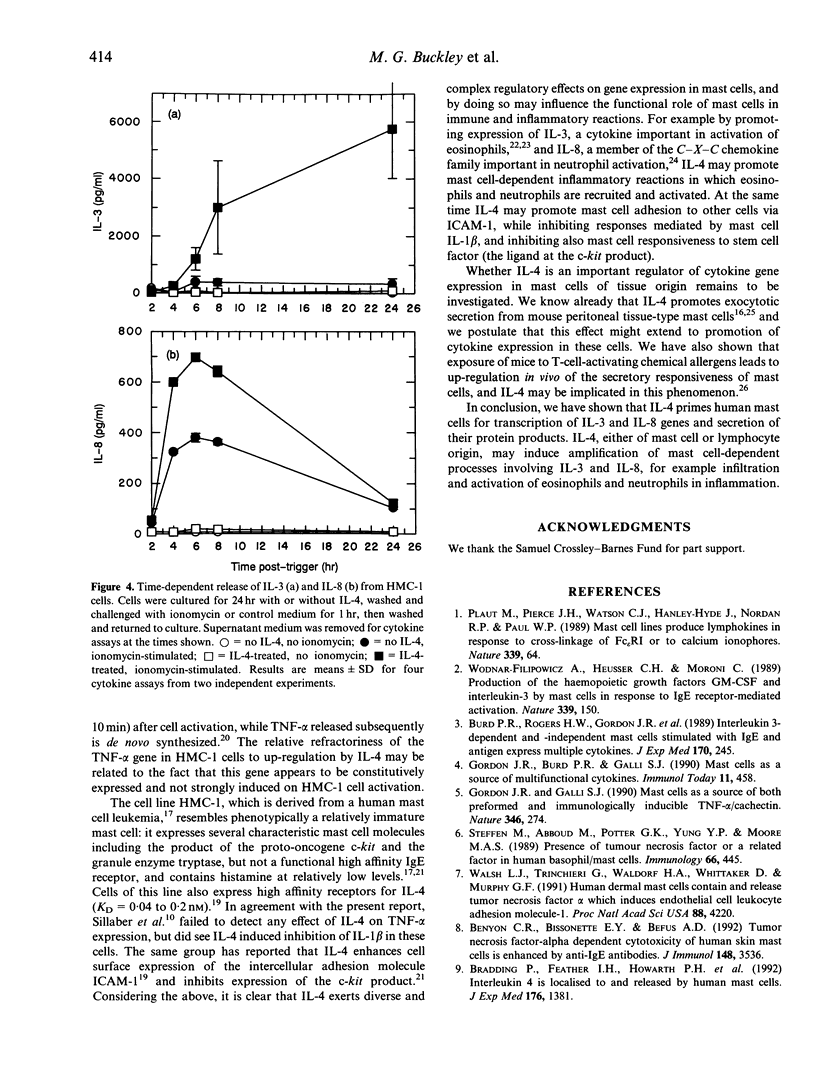
We examined the capacity of interleukin (IL)-4 to induce or enhance the expression of certain cytokines in resting and activated cells of the HMC-1 human leukemic mast cell line. The HMC-1 mast cells were cultured with or without recombinant human IL-4 and then activated with the calcium ionophore ionomycin. Stimulation of non-IL-4-treated cells with ionomycin (10 microM) for periods of 30 min to 8 hr induced expression of mRNA encoding IL-3, IL-4 and IL-8 but was without effect on levels of mRNA for tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha or beta-actin. Culture of the cells with IL-4 (100 ng/ml) for 24 hr led to a small increase in resting levels of mRNA for IL-3 and IL-8 but not for IL-4, TNF-alpha or beta-actin. More notably, the IL-4 treatment produced a pronounced elevation of mRNA for IL-3 and IL-8 when the cells were subsequently activated with ionomycin. The IL-4 treatment produced a negligible effect on IL-4 mRNA, and no effect on TNF-alpha or beta-actin mRNA levels in ionomycin-activated cells. Quantitation of cDNA by competitive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) revealed that the IL-4 treatment produced a sixfold increase in ionomycin-induced levels of cellular IL-3 mRNA, a fourfold increase in induced IL-8 mRNA and less than a twofold increase in induced IL-4 mRNA. The IL-4 treatment led to a 15- to 20-fold increase in ionomycin-induced secretion of IL-3 product and a doubling of induced IL-8 product. These effects of IL-4 were not associated with increased mast cell numbers. We conclude that IL-4 alone is a weak activator of IL-3 and IL-8 gene expression in mast cells, but is able to enhance activation signals in stimulated mast cells leading to transcription and secretion of these two cytokines.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradding P., Feather I. H., Howarth P. H., Mueller R., Roberts J. A., Britten K., Bews J. P., Hunt T. C., Okayama Y., Heusser C. H. Interleukin 4 is localized to and released by human mast cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1381–1386. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd P. R., Rogers H. W., Gordon J. R., Martin C. A., Jayaraman S., Wilson S. D., Dvorak A. M., Galli S. J., Dorf M. E. Interleukin 3-dependent and -independent mast cells stimulated with IgE and antigen express multiple cytokines. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):245–257. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterfield J. H., Weiler D., Dewald G., Gleich G. J. Establishment of an immature mast cell line from a patient with mast cell leukemia. Leuk Res. 1988;12(4):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(88)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. W., Holliday M. R., Kimber I., Zsebo K. M., Galli S. J. Regulation of mouse peritoneal mast cell secretory function by stem cell factor, IL-3 or IL-4. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):556–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian I., Kletter Y., Mor S., Geller-Bernstein C., Ben-Yaakov M., Volovitz B., Golde D. W. Activation of human eosinophil and neutrophil functions by haematopoietic growth factors: comparisons of IL-1, IL-3, IL-5 and GM-CSF. Br J Haematol. 1992 Feb;80(2):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb08890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Burd P. R., Galli S. J. Mast cells as a source of multifunctional cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90176-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Galli S. J. Mast cells as a source of both preformed and immunologically inducible TNF-alpha/cachectin. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):274–276. doi: 10.1038/346274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Galli S. J. Release of both preformed and newly synthesized tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)/cachectin by mouse mast cells stimulated via the Fc epsilon RI. A mechanism for the sustained action of mast cell-derived TNF-alpha during IgE-dependent biological responses. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):103–107. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi Y., Kanakura Y., Fujita J., Takeda S., Nakano T., Tarui S., Honjo T., Kitamura Y. Interleukin 4 as an essential factor for in vitro clonal growth of murine connective tissue-type mast cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):268–273. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday M. R., Banks E. M., Dearman R. J., Kimber I., Coleman J. W. Interactions of IFN-gamma with IL-3 and IL-4 in the regulation of serotonin and arachidonate release from mouse peritoneal mast cells. Immunology. 1994 May;82(1):70–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday M. R., Dearman R. J., Kimber I., Coleman J. W. Sensitization of mice to chemical allergens modulates the responsiveness of isolated mast cells to IgE-dependent activation. Immunology. 1993 Mar;78(3):508–510. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., To L. B., Yang Y. C., Gamble J. R., Shannon M. F., Burns G. F., Dyson P. G., Juttner C. A., Clark S., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of proliferation, differentiation, and function of human cells by primate interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2761–2765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. Heterogeneity of cytokine secretion patterns and functions of helper T cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:111–147. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60652-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller A., Lippert U., Lessmann D., Kolde G., Hamann K., Welker P., Schadendorf D., Rosenbach T., Luger T., Czarnetzki B. M. Human mast cells produce IL-8. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 15;151(6):3261–3266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Interleukin-4: a prototypic immunoregulatory lymphokine. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):1859–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raible D. G., Schulman E. S., DiMuzio J., Cardillo R., Post T. J. Mast cell mediators prostaglandin-D2 and histamine activate human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3536–3542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvan R. S., Butterfield J. H., Krangel M. S. Expression of multiple chemokine genes by a human mast cell leukemia. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13893–13898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert P. D., Larrick J. W. Competitive PCR. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):557–558. doi: 10.1038/359557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillaber C., Bevec D., Butterfield J. H., Heppner C., Valenta R., Scheiner O., Kraft D., Lechner K., Bettelheim P., Valent P. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta mRNA expression in HMC-1 cells: differential regulation of gene product expression by recombinant interleukin-4. Exp Hematol. 1993 Aug;21(9):1271–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillaber C., Strobl H., Bevec D., Ashman L. K., Butterfield J. H., Lechner K., Maurer D., Bettelheim P., Valent P. IL-4 regulates c-kit proto-oncogene product expression in human mast and myeloid progenitor cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4224–4228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen M., Abboud M., Potter G. K., Yung Y. P., Moore M. A. Presence of tumour necrosis factor or a related factor in human basophil/mast cells. Immunology. 1989 Mar;66(3):445–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Bevec D., Maurer D., Besemer J., Di Padova F., Butterfield J. H., Speiser W., Majdic O., Lechner K., Bettelheim P. Interleukin 4 promotes expression of mast cell ICAM-1 antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3339–3342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh L. J., Trinchieri G., Waldorf H. A., Whitaker D., Murphy G. F. Human dermal mast cells contain and release tumor necrosis factor alpha, which induces endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4220–4224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Heusser C. H., Moroni C. Production of the haemopoietic growth factors GM-CSF and interleukin-3 by mast cells in response to IgE receptor-mediated activation. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):150–152. doi: 10.1038/339150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]