Abstract
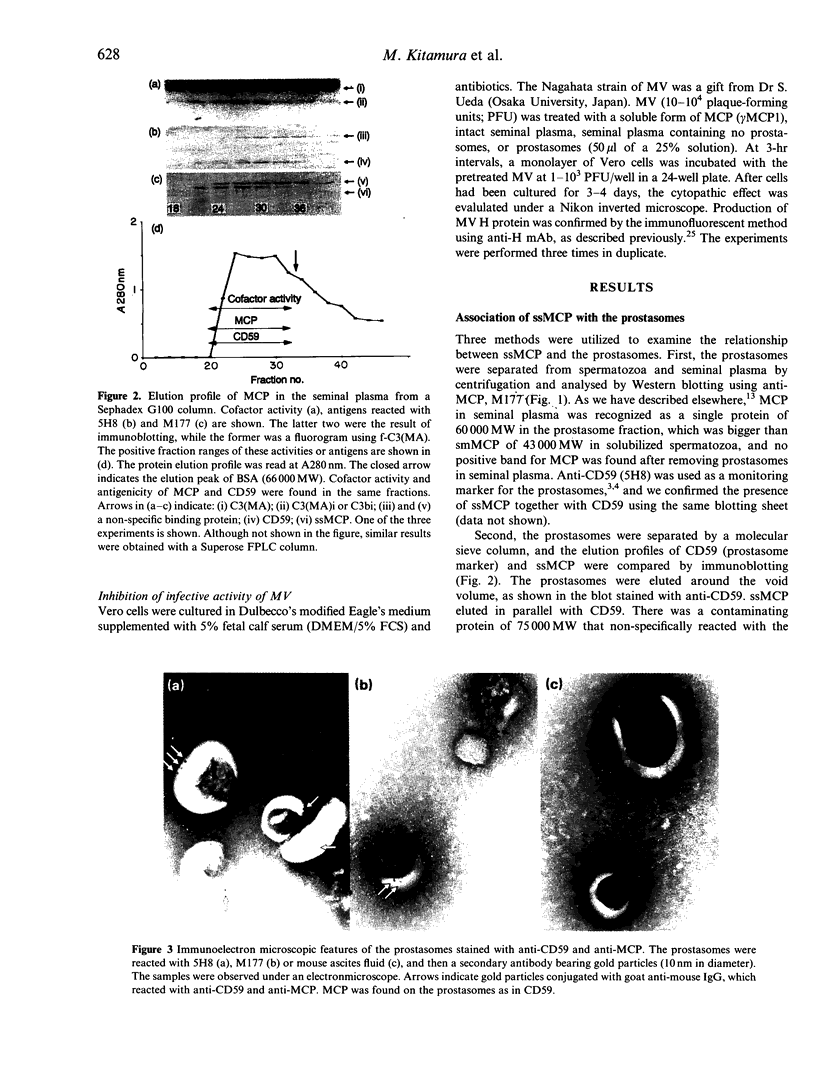
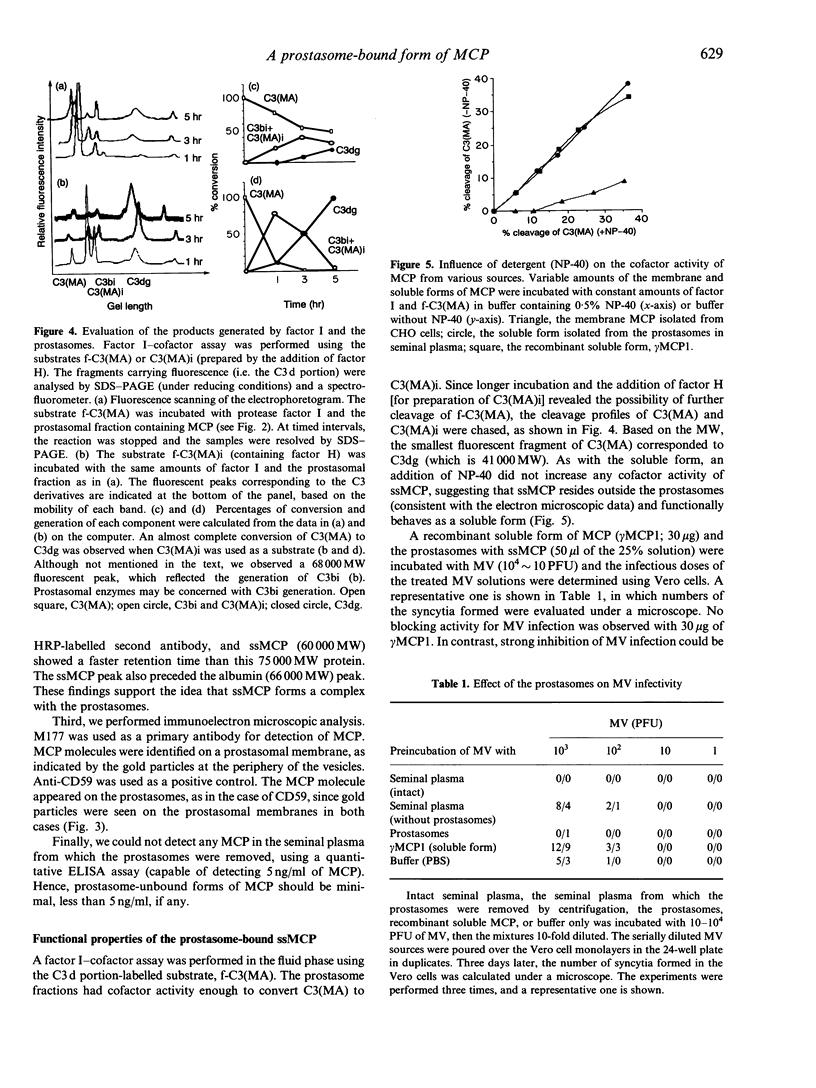
Human seminal plasma contains 0.55 microgram/ml of membrane cofactor protein (MCP; CD46) of 60,000 MW. By ultracentrifugation, gel filtration and immunoelectron microscope methods, we found that the MCP in seminal plasma was associated with prostasomes. The functional properties of the prostasome-bound MCP were assessed in comparison with a recombinant soluble form, gamma MCP1, which is composed of four short consensus repeats (SCR), type C of the serine/threonine-rich domain (STC), and unknown significance (UK). The MCP in seminal plasma, although demonstrably bound to prostasomes, behaved more like the soluble form of MCP. In the absence of detergent it, together with factor I, degraded the fluid-phase ligand, methylamine-treated C3 [C3(MA)], which is insensitive under no-detergent conditions to the membrane form of MCP and factor I. Moreover, C3dg fragment was generated as a final product instead of C3bi during the incubation, indicating that the prostasomal MCP and proteases may be responsible for the C3dg generation. The prostasomes neutralized measles virus (MV) infectivity, while gamma MCP1, for the most part, did not. These results, taken together with the CD59 concentration on the prostasomes, suggest that the prostasomes are potential immunomodulators for complement activation, providing the C3- and C9-step inhibitors. The present report also reinforces the idea that there are two different forms of MCP in semen. One is located in the inner acrosomal membrane of spermatozoa, which appears through acrosomal reaction and spermatoon-egg interaction. The other is a prostasome-bound form maintaining activities sufficient to regulate complement activation and, probably, MV infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Fearon D. T. Structure and function of the complement receptors, CR1 (CD35) and CR2 (CD21). Adv Immunol. 1989;46:183–219. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Abbott A. F., Jack R. M. The role of complement component C3b and its receptors in sperm-oocyte interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10051–10055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Michaelson J. S., Johnson P. M. Trophoblast/leukocyte-common antigen is expressed by human testicular germ cells and appears on the surface of acrosome-reacted sperm. Biol Reprod. 1989 Aug;41(2):285–293. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod41.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervoni F., Fenichel P., Akhoundi C., Hsi B. L., Rossi B. Characterization of a cDNA clone coding for human testis membrane cofactor protein (MCP, CD46). Mol Reprod Dev. 1993 Jan;34(1):107–113. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080340117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervoni F., Oglesby T. J., Adams E. M., Milesifluet C., Nickells M., Fenichel P., Atkinson J. P., Hsi B. L. Identification and characterization of membrane cofactor protein of human spermatozoa. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1431–1437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. L., Housley G. A., Jr, Dykman T. R., MacDermott R. P., Atkinson J. P. Identification of an additional class of C3-binding membrane proteins of human peripheral blood leukocytes and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):859–863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörig R. E., Marcil A., Chopra A., Richardson C. D. The human CD46 molecule is a receptor for measles virus (Edmonston strain). Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiani R., Ronquist G. Characteristics of membrane-bound 5'-nucleotidase on human prostasomes. Clin Chim Acta. 1993 Jul 16;216(1-2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(93)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fénichel P., Dohr G., Grivaux C., Cervoni F., Donzeau M., Hsi B. L. Localization and characterization of the acrosomal antigen recognized by GB24 on human spermatozoa. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990 Oct;27(2):173–178. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080270214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Kuriyama S., Kiyohara H., Nagase Y., Matsumoto M., Seya T. Soluble forms of membrane cofactor protein (CD46, MCP) are present in plasma, tears, and seminal fluid in normal subjects. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Sep;89(3):490–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Matsumoto M., Fukumori Y., Miyagawa S., Hatanaka M., Kinoshita T., Seya T., Akedo H. A monoclonal antibody against human decay-accelerating factor (DAF, CD55), D17, which lacks reactivity with semen-DAF. Immunol Lett. 1993 Aug;37(2-3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(93)90024-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes C. H., Simpson K. L. Complement and pregnancy: new insights into the immunobiology of the fetomaternal relationship. Baillieres Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 1992 Sep;6(3):439–460. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3552(05)80005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone R. W., Russell S. M., Loveland B. E., McKenzie I. F. Polymorphic expression of CD46 protein isoforms due to tissue-specific RNA splicing. Mol Immunol. 1993 Oct;30(14):1231–1241. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90038-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. W., Holland P., Skibinski G., Harrison C., McMillan L., Hargreave T., James K. Extracellular organelles (prostasomes) are immunosuppressive components of human semen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Dec;86(3):550–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb02968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima A., Iwata K., Seya T., Matsumoto M., Ariga H., Atkinson J. P., Nagasawa S. Membrane cofactor protein (CD46) protects cells predominantly from alternative complement pathway-mediated C3-fragment deposition and cytolysis. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1519–1527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B., Weiber H., Ohlsson K., Rannevik G. A zinc-dependent peptidase in prostatic organelles present in seminal plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Dec 9;126(2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liszewski M. K., Post T. W., Atkinson J. P. Membrane cofactor protein (MCP or CD46): newest member of the regulators of complement activation gene cluster. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:431–455. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lublin D. M., Liszewski M. K., Post T. W., Arce M. A., Le Beau M. M., Rebentisch M. B., Lemons L. S., Seya T., Atkinson J. P. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of human membrane cofactor protein (MCP). Evidence for inclusion in the multigene family of complement-regulatory proteins. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):181–194. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M., Seya T., Nagasawa S. Polymorphism and proteolytic fragments of granulocyte membrane cofactor protein (MCP, CD46) of complement. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):493–499. doi: 10.1042/bj2810493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInerney T. L., Howlett G. J., Gruen L. C., Jackson D. C. Quantitative analysis of the interaction between lysozyme and monoclonal antibody D1.3. Mol Immunol. 1993 Jan;30(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90425-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Rutgers J. L., Knowles D. M., Nussenzweig V. Identification of the complement decay-accelerating factor (DAF) on epithelium and glandular cells and in body fluids. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):848–864. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth J. L., Morgan E. L., DiSipio R. G., Hugli T. E. Suppression of T lymphocyte functions by human C3 fragments. I. Inhibition of human T cell proliferative responses by a kallikrein cleavage fragment of human iC3b. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2605–2611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Ichihara C., Stroud R. M. Cleavage of C4b by C3b inactivator: production of a nicked form of C4b, C4b', as an intermediate cleavage product of C4b by C3b inactivator. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):578–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naniche D., Varior-Krishnan G., Cervoni F., Wild T. F., Rossi B., Rabourdin-Combe C., Gerlier D. Human membrane cofactor protein (CD46) acts as a cellular receptor for measles virus. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6025–6032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6025-6032.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi K., Saji F., Kato M., Okabe M., Mimura T., Tanizawa O. Evaluation of acrosomal status using MH61-beads test and its clinical application. Fertil Steril. 1992 Oct;58(4):803–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post T. W., Liszewski M. K., Adams E. M., Tedja I., Miller E. A., Atkinson J. P. Membrane cofactor protein of the complement system: alternative splicing of serine/threonine/proline-rich exons and cytoplasmic tails produces multiple isoforms that correlate with protein phenotype. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):93–102. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Taylor C. T., Melling G. C., Kingsland C. R., Johnson P. M. Expression of the CD46 antigen, and absence of class I MHC antigen, on the human oocyte and preimplantation blastocyst. Immunology. 1992 Jan;75(1):202–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist G., Brody I. The prostasome: its secretion and function in man. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 9;822(2):203–218. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney I. A., Atkinson J. P., Krul E. S., Schonfeld G., Polakoski K., Saffitz J. E., Morgan B. P. Physiologic relevance of the membrane attack complex inhibitory protein CD59 in human seminal plasma: CD59 is present on extracellular organelles (prostasomes), binds cell membranes, and inhibits complement-mediated lysis. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1409–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Sparrow R. L., McKenzie I. F., Purcell D. F. Tissue-specific and allelic expression of the complement regulator CD46 is controlled by alternative splicing. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1513–1518. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seya T., Hara T., Matsumoto M., Akedo H. Quantitative analysis of membrane cofactor protein (MCP) of complement. High expression of MCP on human leukemia cell lines, which is down-regulated during cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):238–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seya T., Hara T., Matsumoto M., Kiyohara H., Nakanishi I., Kinouchi T., Okabe M., Shimizu A., Akedo H. Membrane cofactor protein (MCP, CD46) in seminal plasma and on spermatozoa in normal and "sterile" subjects. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jun;23(6):1322–1327. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seya T., Nagasawa S. Limited proteolysis of complement protein C3b by regulatory enzyme C3b inactivator: isolation and characterization of a biologically active fragment, C3d,g. J Biochem. 1985 Jan;97(1):373–382. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seya T., Okada M., Nishino H., Atkinson J. P. Regulation of proteolytic activity of complement factor I by pH: C3b/C4b receptor (CR1) and membrane cofactor protein (MCP) have different pH optima for factor I-mediated cleavage of C3b. J Biochem. 1990 Feb;107(2):310–315. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seya T., Turner J. R., Atkinson J. P. Purification and characterization of a membrane protein (gp45-70) that is a cofactor for cleavage of C3b and C4b. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):837–855. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson K. L., Holmes C. H. Differential expression of complement regulatory proteins decay-accelerating factor (CD55), membrane cofactor protein (CD46) and CD59 during human spermatogenesis. Immunology. 1994 Mar;81(3):452–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stites D. P., Erickson R. P. Suppressive effect of seminal plasma on lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1975 Feb 27;253(5494):727–729. doi: 10.1038/253727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita Y., Ito K., Shiozuka K., Suzuki H., Gushima H., Tomita M., Masuho Y. Recombinant soluble CD59 inhibits reactive haemolysis with complement. Immunology. 1994 May;82(1):34–41. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts M. J., Dankert J. R., Morgan E. P. Isolation and characterization of a membrane-attack-complex-inhibiting protein present in human serum and other biological fluids. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):471–477. doi: 10.1042/bj2650471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon S. H., Fearon D. T. Characterization of a soluble form of the C3b/C4b receptor (CR1) in human plasma. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3332–3338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]