Abstract
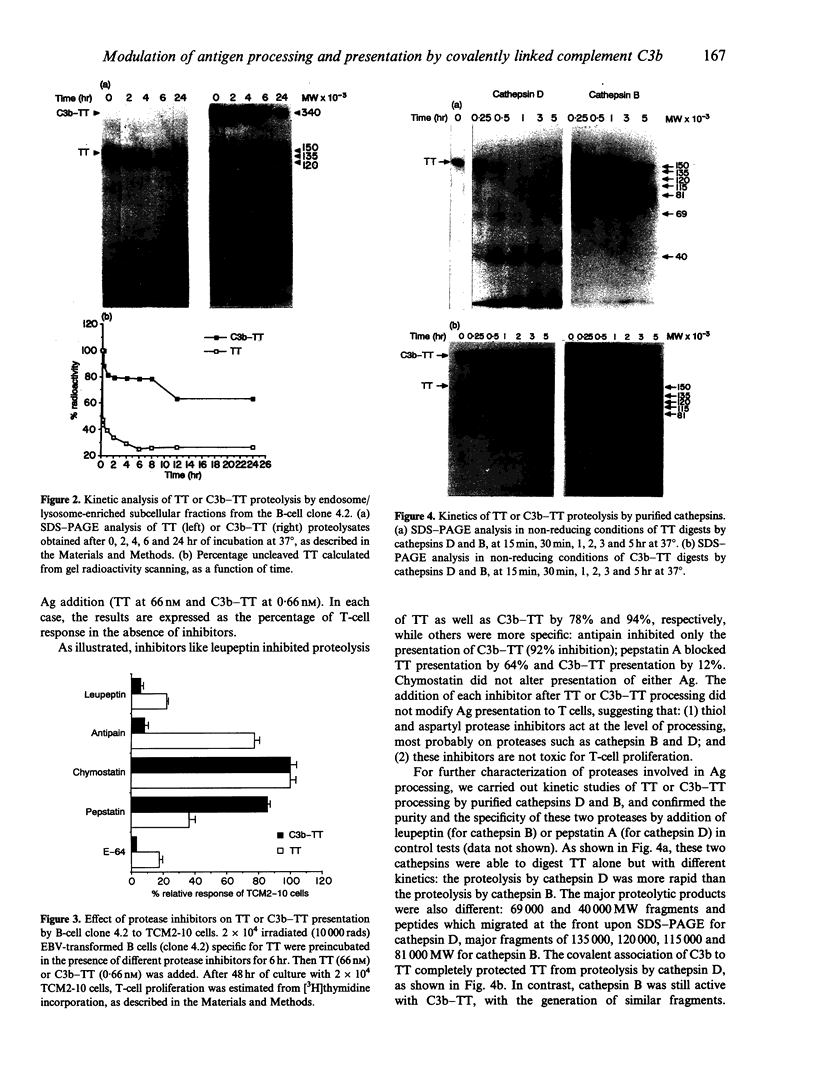
Ligands such as complement fragments (C3, C4), IgG or alpha 2-macroglobulin, which bind antigen (Ag) before their uptake by antigen-presenting cells (APC), are likely to modulate the different steps of Ag processing and presentation. These ligands contribute to internalization and endosomal targeting of Ag; they also influence its processing and, consequently, the binding of resulting peptides to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules before presentation to T cells. Complement protein C3 contains, like other members of the alpha 2-macroglobulin family, an intrachain thiolester bond. Conformational alteration or limited proteolysis of C3 into C3b leads to breaking of the thiolester with transient capacity of the revealed carbonyl group to esterify hydroxyl groups of Ag. Ester-linked complexes including tetanus toxin (TT) and C3b were prepared to analyse the influence of bound C3b on TT processing and presentation by APC. Covalent binding of C3b to TT resulted in increased and prolonged stimulation of specific T-cell proliferation. This effect was observed with non-specific B cells, as well as with a TT-specific B-cell clone, as APC. On the other hand, SDS-PAGE analysis of proteolysates of TT or C3b-TT, obtained with endosome/lysosome-enriched subcellular fractions prepared from human Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-transformed B cells, indicated a delay of TT proteolysis when TT was associated to C3b. Treatment of APC with protease inhibitors, before and during exposure of the cells to Ag, resulted in differences in the inhibition of TT and C3b-TT proteolysis. Using purified cathepsins B and D, we demonstrated that covalent binding of C3b to TT totally abolished TT proteolysis by cathepsin D, while proteolysis by cathepsin B was preserved. This finding and the absence of cathepsin B in endosomes may explain a delay in TT processing when it is associated to C3b. Confirming these data, presentation by formaldehyde-fixed cells of C3b-TT proteolysates showed higher stimulation of specific T-cell clones than formaldehyde-fixed TT proteolysates.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. M., Unanue E. R. Differential requirements for antigen processing by macrophages for lysozyme-specific T cell hybridomas. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1077–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvieux J., Yssel H., Colomb M. G. Antigen-bound C3b and C4b enhance antigen-presenting cell function in activation of human T-cell clones. Immunology. 1988 Oct;65(2):229–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casten L. A., Pierce S. K. Receptor-mediated B cell antigen processing. Increased antigenicity of a globular protein covalently coupled to antibodies specific for B cell surface structures. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):404–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. S., Unanue E. R., Harding C. V. Reduction of disulfide bonds within lysosomes is a key step in antigen processing. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4054–4059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darte C., Beaufay H. Analytical subcellular fractionation of cultivated mouse resident peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1208–1228. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diment S., Leech M. S., Stahl P. D. Cathepsin D is membrane-associated in macrophage endosomes. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6901–6907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds A. W., Law S. K. Structural basis of the binding specificity of the thioester-containing proteins, C4, C3 and alpha-2-macroglobulin. Complement. 1988;5(2):89–97. doi: 10.1159/000463039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guagliardi L. E., Koppelman B., Blum J. S., Marks M. S., Cresswell P., Brodsky F. M. Co-localization of molecules involved in antigen processing and presentation in an early endocytic compartment. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):133–139. doi: 10.1038/343133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Unanue E. R. Antigen processing and intracellular Ia. Possible roles of endocytosis and protein synthesis in Ia function. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):12–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A. Thioredoxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:237–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac L., Isenman D. E. Structural requirements for thioester bond formation in human complement component C3. Reassessment of the role of thioester bond integrity on the conformation of C3. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10062–10069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier M. R., Gabert F. M., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. Disulfide linkage between C3b and tetanus toxin on tetanus toxin-specific EBV-transformed B cells. J Immunol. 1993 May 15;150(10):4253–4260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. E. Reduction of disulfide bonds during antigen processing: evidence from a thiol-dependent insulin determinant. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1121–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovac Z., Schwartz R. H. The molecular basis of the requirement for antigen processing of pigeon cytochrome c prior to T cell activation. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3233–3240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A. Antigen-specific interaction between T and B cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):537–539. doi: 10.1038/314537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A., Ferrarini M., Celada F. Human T cell lines with antigen specificity and helper activity. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jun;12(6):468–474. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A. Receptor-mediated antigen uptake and its effect on antigen presentation to class II-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:773–793. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.004013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine T. P., Chain B. M. Endocytosis by antigen presenting cells: dendritic cells are as endocytically active as other antigen presenting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8342–8346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz R. G., Blum J. S., Allen P. M. Constitutive competition by self proteins for antigen presentation can be overcome by receptor-enhanced uptake. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1600–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maison C. M., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. Proteolysis of C3 on U937 cell plasma membranes. Purification of cathepsin G. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):921–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Longo D. L., Hedrick S. M., Hannum C., Margoliash E., Schwartz R. H. Clonal analysis of the major histocompatibility complex restriction and the fine specificity of antigen recognition in the T cell proliferative response to cytochrome C. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1527–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigiet V. P., Schuster B. J. Thioredoxin-catalyzed refolding of disulfide-containing proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7643–7647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri J., Factorovich Y. Selective inhibition of antigen presentation to cloned T cells by protease inhibitors. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3313–3317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Millet C. A., Chesne S., Colomb M. G. Associated complement C3b. Towards an understanding of its intracellular modifications. Mol Immunol. 1993 Jul;30(10):855–864. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90009-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez G. M., Diment S. Role of cathepsin D in antigen presentation of ovalbumin. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):2894–2898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouas N., Christophe S., Housseau F., Bellet D., Guillet J. G., Bidart J. M. Influence of protein-quaternary structure on antigen processing. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):782–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salacinski P. R., McLean C., Sykes J. E., Clement-Jones V. V., Lowry P. J. Iodination of proteins, glycoproteins, and peptides using a solid-phase oxidizing agent, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3 alpha,6 alpha-diphenyl glycoluril (Iodogen). Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Adorini L., Colon S. M., Buus S., Grey H. M. Capacity of intact proteins to bind to MHC class II molecules. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1265–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoorvogel W., Geuze H. J., Griffith J. M., Strous G. J. The pathways of endocytosed transferrin and secretory protein are connected in the trans-Golgi reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1821–1829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiers M. B., Villiers C. L., Wright J. F., Maison C. M., Colomb M. G. Formation of covalent C3b-tetanus toxin complexes: a tool for the in vitro study of antigen presentation. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Nov;34(5):585–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb01582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]