Abstract
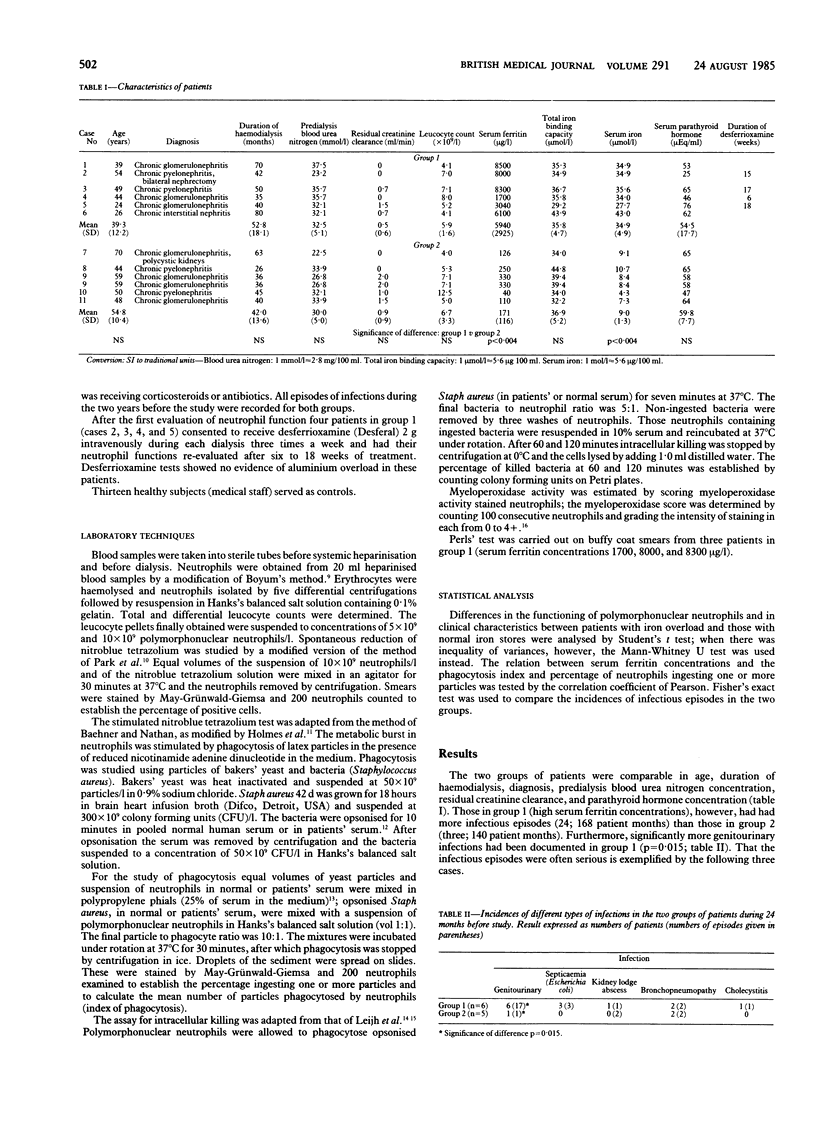
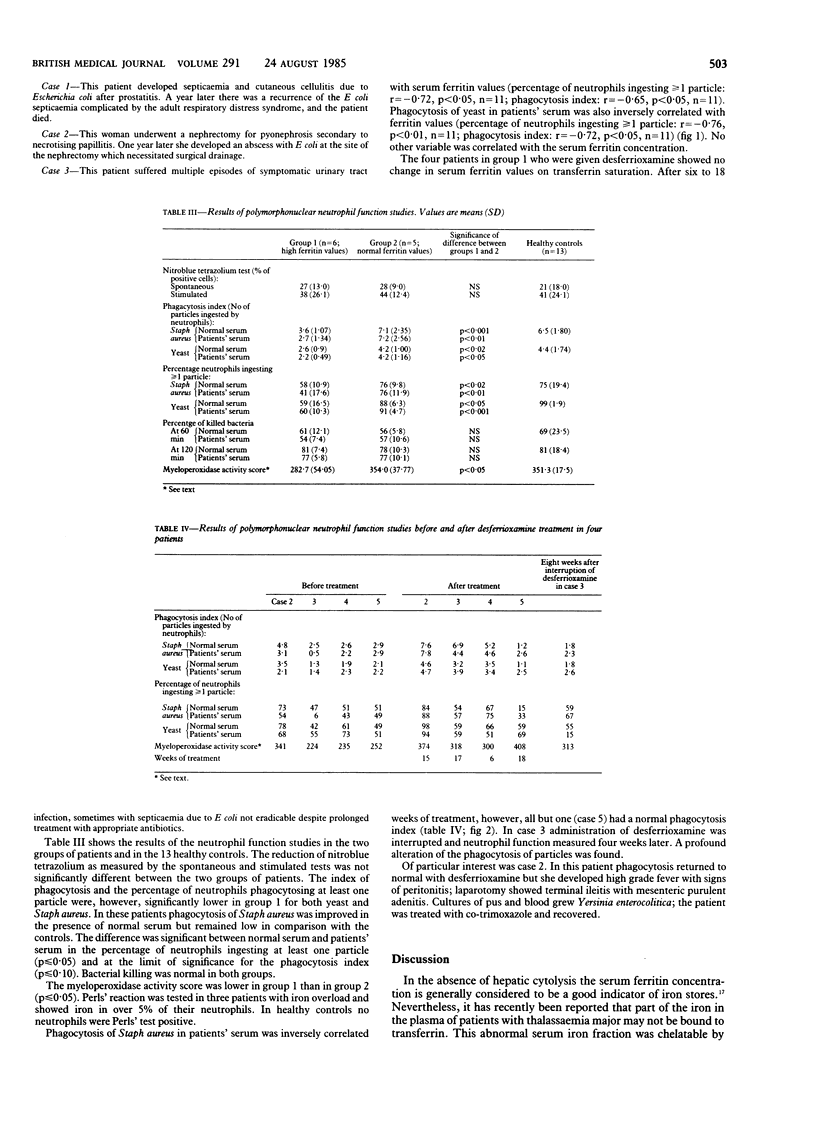
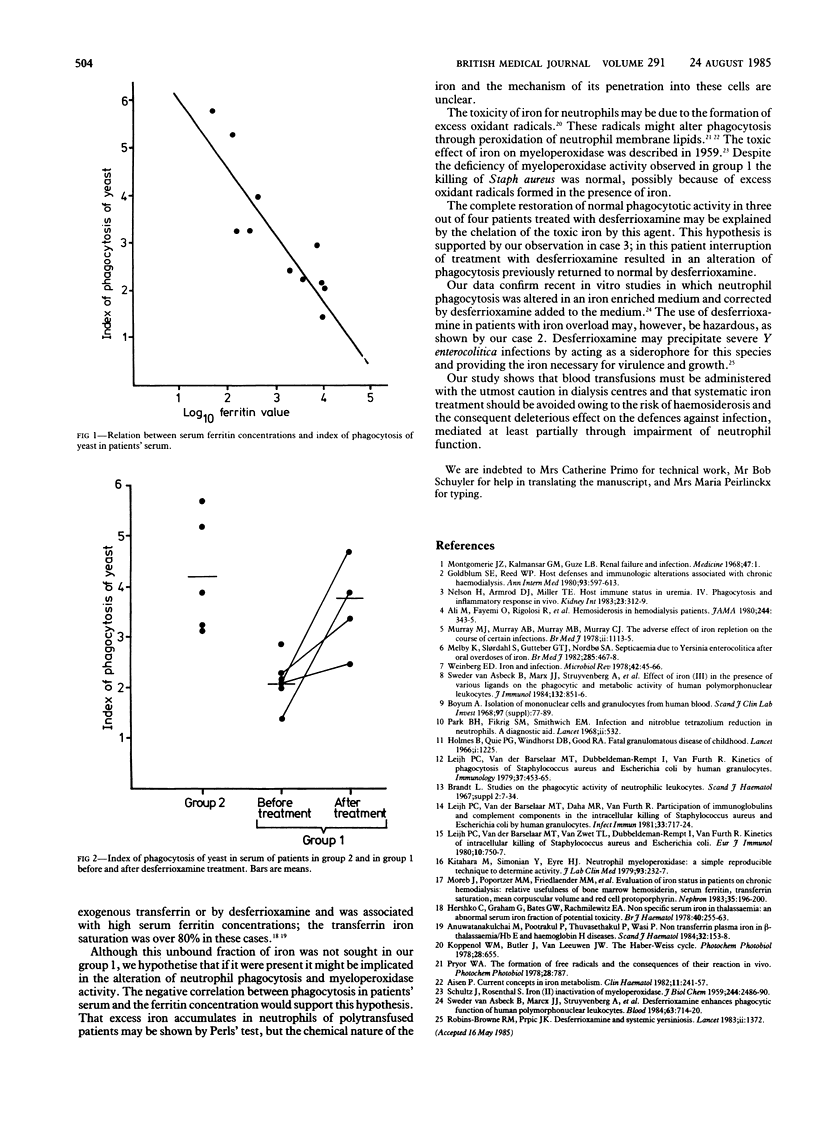
The metabolic burst (as measured by the spontaneous and stimulated nitroblue tetrazolium tests), the phagocytosis of heat inactivated bakers' yeast and of Staphylococcus aureus, the killing of Staph aureus, and the myeloperoxidase activity of polymorphonuclear neutrophils were studied in 11 patients receiving maintenance haemodialysis. Of these patients, six were polytransfused and had high serum ferritin concentrations (mean 5940 (SD 2925) micrograms/l; group 1), and five had normal serum ferritin values (mean 171 (116) micrograms/l; group 2). Patients in group 1 had a history of more infectious episodes (0.167 v 0.025 per patient per month) and significantly more genitourinary infections (p = 0.015) than those in group 2. Phagocytosis and myeloperoxidase activity were severely reduced in group 1 but normal in group 2. Percentages of neutrophils ingesting one or more particles together with the index of phagocytosis in patients' serum were inversely correlated with serum ferritin concentrations. Four patients in group 1 were treated with desferrioxamine, and after six to 18 weeks of treatment phagocytosis and myeloperoxidase activity had returned to normal in three of them. These data suggest that in patients receiving haemodialysis iron overload due to multiple transfusions plays an important part in the mechanisms underlying the susceptibility to bacterial infections, mediated at least partially through impaired neutrophil function.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P. Current concepts in iron metabolism. Clin Haematol. 1982 Jun;11(2):241–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali M., Fayemi A. O., Rigolosi R., Frascino J., Marsden T., Malcolm D. Hemosiderosis in hemodialysis patients. An autopsy study of 50 cases. JAMA. 1980 Jul 25;244(4):343–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anuwatanakulchai M., Pootrakul P., Thuvasethakul P., Wasi P. Non-transferrin plasma iron in beta-thalassaemia/Hb E and haemoglobin H diseases. Scand J Haematol. 1984 Feb;32(2):153–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1984.tb02171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum S. E., Reed W. P. Host defenses and immunologic alterations associated with chronic hemodialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Oct;93(4):597–613. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-4-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko C., Graham G., Bates G. W., Rachmilewitz E. A. Non-specific serum iron in thalassaemia: an abnormal serum iron fraction of potential toxicity. Br J Haematol. 1978 Oct;40(2):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb03662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Quie P. G., Windhorst D. B., Good R. A. Fatal granulomatous disease of childhood. An inborn abnormality of phagocytic function. Lancet. 1966 Jun 4;1(7449):1225–1228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara M., Simonian Y., Eyre H. J. Neutrophil myeloperoxidase: a simple, reproducible technique to determine activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Feb;93(2):232–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., Dubbeldeman-Rempt I., van Furth R. Kinetics of intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by human granulocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Oct;10(10):750–757. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Zwet T. L., Dubbeldeman-Rempt I., van Furth R. Kinetics of phagocytosis of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli by human granulocytes. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):453–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melby K., Slørdahl S., Gutteberg T. J., Nordbø S. A. Septicaemia due to Yersinia enterocolitica after oral overdoses of iron. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Aug 14;285(6340):467–468. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6340.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomerie J. Z., Kalmanson G. M., Guze L. B. Renal failure and infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1968 Jan;47(1):1–32. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196801000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreb J., Popovtzer M. M., Friedlaender M. M., Konijn A. M., Hershko C. Evaluation of iron status in patients on chronic hemodialysis: relative usefulness of bone marrow hemosiderin, serum ferritin, transferrin saturation, mean corpuscular volume and red cell protoporphyrin. Nephron. 1983;35(3):196–200. doi: 10.1159/000183074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J., Ormrod D. J., Miller T. E. Host immune status in uremia. IV. Phagocytosis and inflammatory response in vivo. Kidney Int. 1983 Feb;23(2):312–319. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor W. A. The formation of free radicals and the consequences of their reactions in vivo. Photochem Photobiol. 1978 Oct-Nov;28(4-5):787–801. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1978.tb07020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Prpic J. K. Desferrioxamine and systemic yersiniosis. Lancet. 1983 Dec 10;2(8363):1372–1372. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ J., ROSENTHAL S. Iron (II) inactivation of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2486–2490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Asbeck B. S., Marx J. J., Struyvenberg A., van Kats J. H., Verhoef J. Deferoxamine enhances phagocytic function of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1984 Mar;63(3):714–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


