Abstract
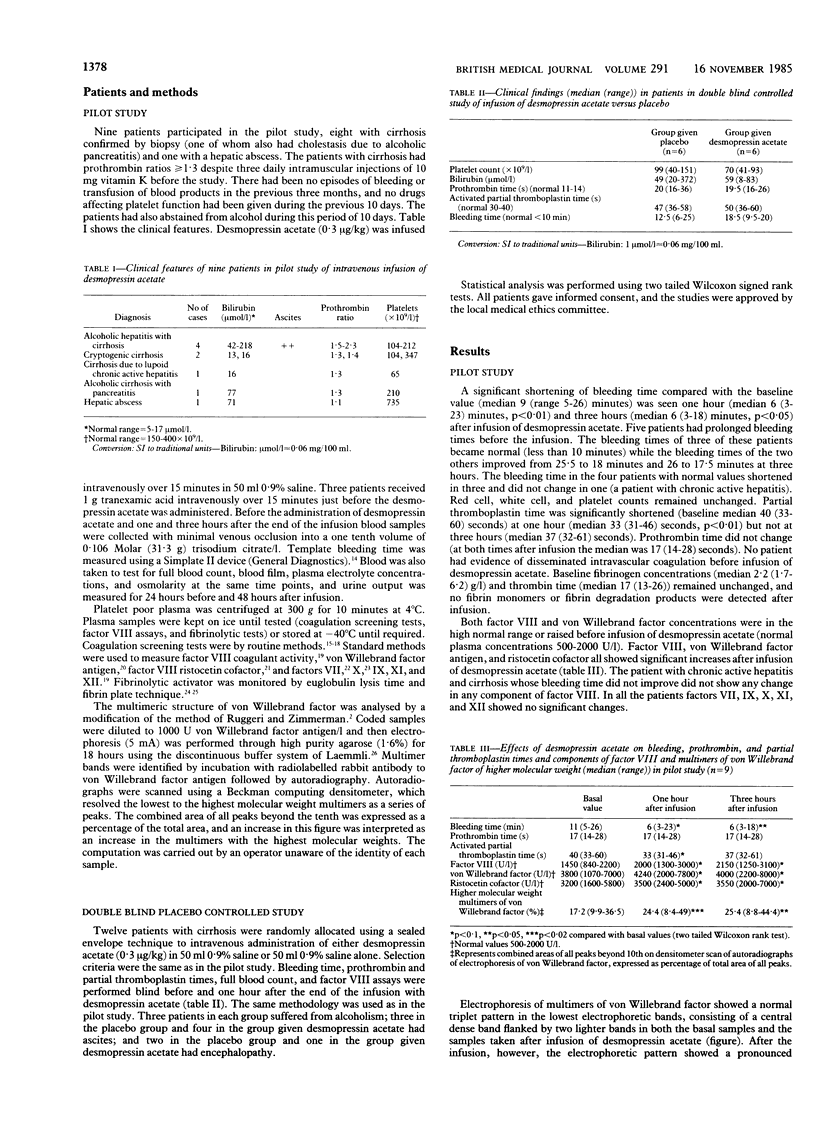
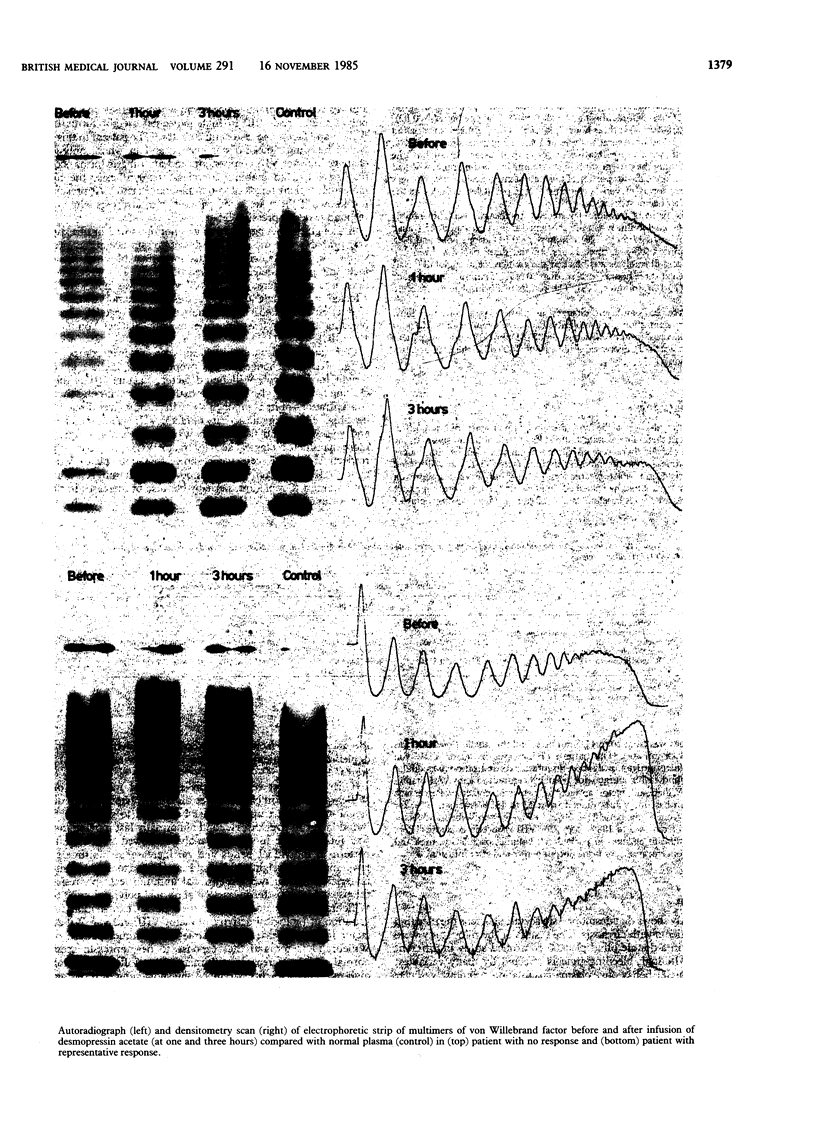
Desmopressin acetate 0.3 microgram/kg was given intravenously to nine patients with chronic liver disease and to a further six such patients in a double blind controlled study versus placebo. Desmopressin acetate significantly shortened the bleeding time compared with basal values in both groups and compared with placebo. There was also a significant decrease in partial thromboplastin time (but not prothrombin time) and significant increases in factor VIII and its components, von Willebrand factor and ristocetin cofactor activity, but not in factors VII, IX, X, XI, or XII. Increased fibrinolysis could be blocked by concomitant administration of tranexamic acid. No important side effects were seen. The multimer pattern of von Willebrand factor was studied for the first time in chronic liver disease. It was normal, but after administration of desmopressin acetate the percentage of multimers of higher molecular weight increased significantly. This may be an important mechanism in the shortening of the bleeding time in cirrhosis, as has been shown in uraemia and other conditions after administration of desmopressin acetate. Desmopressin acetate may be useful in correcting defects in primary haemostasis in chronic liver disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnelli G., Berrettini M., De Cunto M., Nenci G. G. Desmopressin-induced improvement of abnormal coagulation in chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):645–645. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canavese C., Salomone M., Pacitti A., Mangiarotti G., Calitri V. Reduced response of uraemic bleeding time to repeated doses of desmopressin. Lancet. 1985 Apr 13;1(8433):867–868. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENSON K. W. The specific assay of Prower-Stuart factor and factor VII. Acta Haematol. 1961 Feb;25:105–120. doi: 10.1159/000206523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R., Conning D. M. The assay of human factor VII by means of modified factor VII deficient dog plasma. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jan;18(1):57–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. J., Ratnoff O. D. Elevated antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII) procoagulant activity and AHF-like antigen in alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Feb;83(2):189–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G., Dymock I. W., Poller L., Thomson J. M. Use of factor-VII-rich prothrombin complex concentrate in liver disease. Lancet. 1975 Jun 14;1(7920):1311–1314. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92317-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh J. Blood tests for the diagnosis of venous and arterial thrombosis. Blood. 1981 Jan;57(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAM I. C. The determination of plasma fibrinogen by the clot-weight method. Biochem J. 1952 Aug;51(5):583–585. doi: 10.1042/bj0510583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livio M., Gotti E., Marchesi D., Mecca G., Remuzzi G., de Gaetano G. Uraemic bleeding: role of anaemia and beneficial effect of red cell transfusions. Lancet. 1982 Nov 6;2(8306):1013–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane D. E., Stibbe J., Kirby E. P., Zucker M. B., Grant R. A., McPherson J. Letter: A method for assaying von Willebrand factor (ristocetin cofactor). Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Sep 30;34(1):306–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonneuve P., Sultan Y. Modification of factor VIII complex properties in patients with liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Mar;30(3):221–227. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.3.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Aberg M., Nilsson I. M., Robertson B. Mechanism of plasminogen activator and factor VIII increase after vasoactive drugs. Br J Haematol. 1975 May;30(1):81–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Franchi F., Dioguardi N. Correction of abnormal coagulation in chronic liver disease by combined use of fresh-frozen plasma and prothrombin complex concentrates. Lancet. 1976 Sep 11;2(7985):542–545. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91794-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. E., Marder V. J., Francis C. W., Barlow G. H. Structural studies of the functional heterogeneity of von Willebrand protein polymers. Blood. 1981 Feb;57(2):313–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke C. H., Jr, Kaneshiro M. M., Maher I. A., Weiner J. M., Rapaport S. I. The standardized normal Ivy bleeding time and its prolongation by aspirin. Blood. 1969 Aug;34(2):204–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR R. R., RAPAPORT S. I. The partial thromboplastin time with kaolin. A simple screening test for first stage plasma clotting factor deficiencies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;36:212–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Mannucci P. M., Lombardi R., Federici A. B., Zimmerman T. S. Multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor following administration of DDAVP: implications for pathophysiology and therapy of von Willebrand's disease subtypes. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1272–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H. Studies on the pathophysiology and treatment of von Willebrand's disease. V. Properties of factor VIII after DDAVP infusion in variant von Willebrand's disease. 1981 Feb 15-Mar 1Thromb Res. 21(4-5):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente V., Alberca I., Mannucci P. M. Reduced effect of exercise and DDAVP on factor VIII-von Willebrand Factor and plasminogen activator after sequential application of both the stimuli. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Feb 28;51(1):129–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]