Abstract
A better understanding of the mechanism(s) of cell mediated toxicity for colon cells in vitro may help clarify the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). We have examined both the cytotoxicity of IBD peripheral blood mononuclear cells and the kinetics of induction of such toxicity by soluble plasma factors. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from IBD patients were found to be cytotoxic for the colon cells. With the use of Chang cells, this cytotoxicity was shown not to be due to an increase in spontaneous cell mediated cytotoxicity. Colon cell toxicity in vitro did not correlate with site of disease or severity, but decreased toxicity appeared to be associated with in vivo steroid administration. Plasma from some IBD patients was capable of inducing normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells to be toxic to colon cells. This ability was not affected by steroid therapy. The induction capacity of IBD plasma was not associated with the presence of circulating immune complexes, as measured by Raji RIA, suggesting that large complement fixing complexes are not the inducing and directing factors. Unlike findings in other systems, induction could be demonstrated after a one hour preincubation of mononuclear cells with IBD plasma. The kinetics of induction are consistent with the hypothesis that either cytophilic antibody or small circulating immune complexes arm K cells for specific colon cell lysis.
Full text
PDF

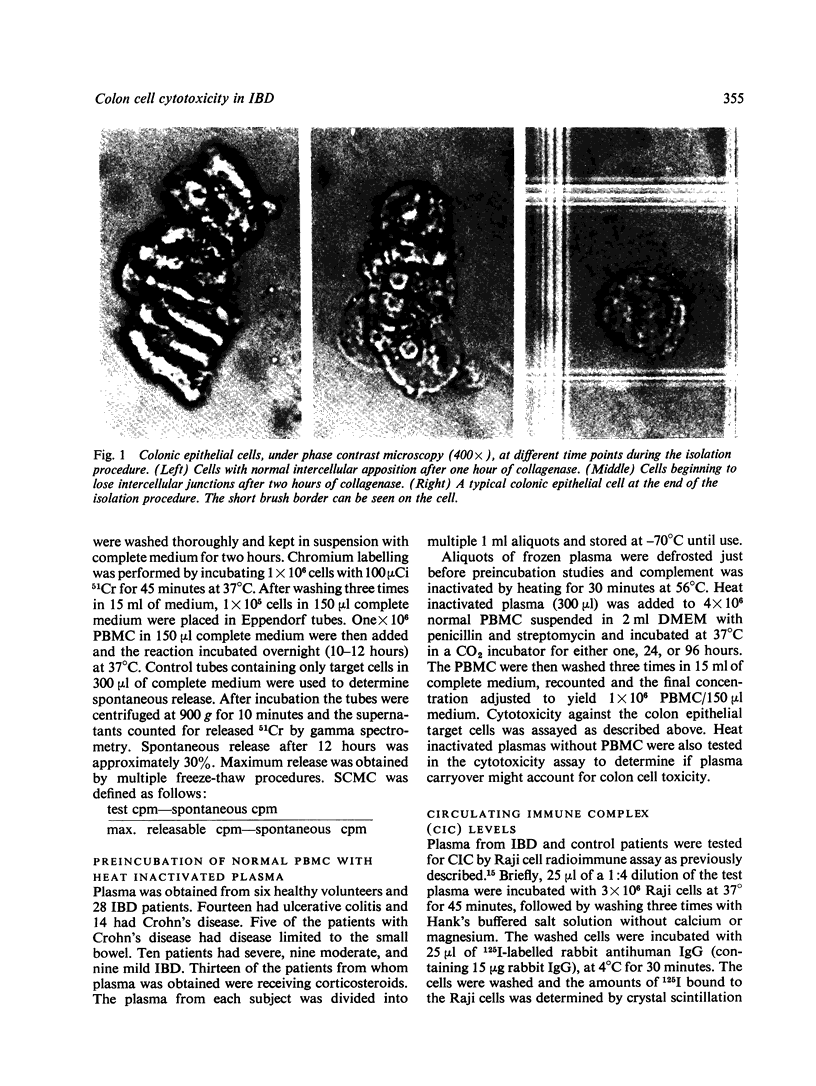
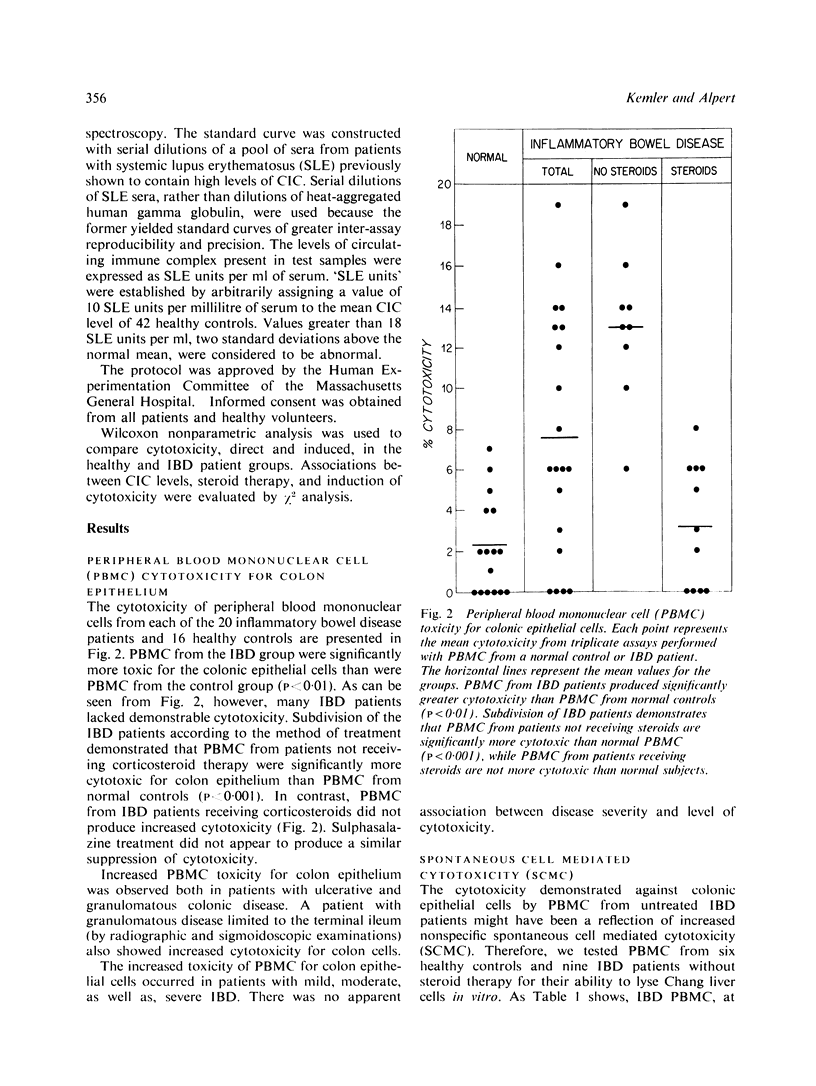
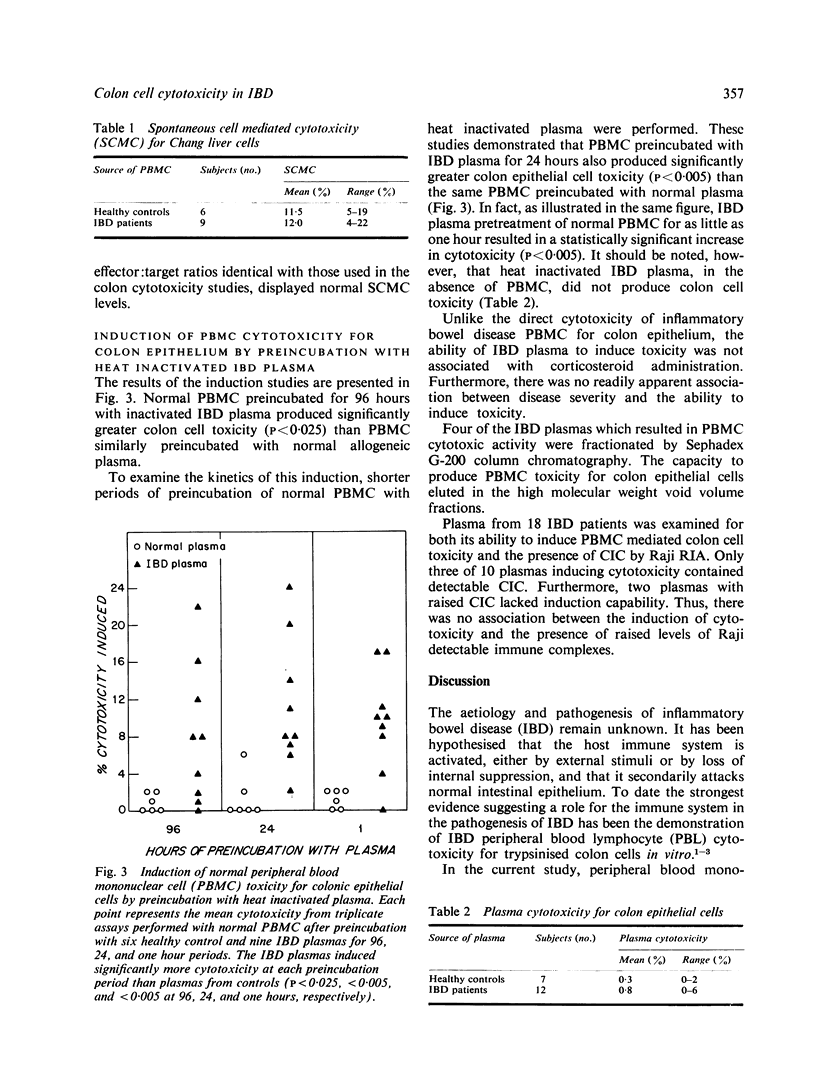


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Dombal F. T., Burton I. L., Clamp S. E., Goligher J. C. Short-term course and prognosis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1974 Jun;15(6):435–443. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson H. J., Potter B. J., Jewell D. P. Immune complexes in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Aug;29(2):187–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Perlmann P. Quantitative studies on phytohaemagglutinin-induced cytotoxicity by human lymphocytes against homologous cells in tissue culture. Immunology. 1967 May;12(5):525–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell D. P., MacLennan I. C. Circulating immune complexes in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E. Multiple target cell killing by the cytolytic T lymphocyte and the mechanism of cytotoxicity. Transplantation. 1976 Jan;21(1):5–11. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197601000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMANN P., BROBERGER O. In vitro studies of ulcerative colitis. II. Cytotoxic action of white blood cells from patients on human fetal colon cells. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:717–733. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E., Fauci A. S. Apparent direct cellular cytotoxicity mediated via cytophilic antibody. Multiple Fc receptor bearing effector cell populations mediating cytophilic antibody induced cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1977 Dec;33(6):839–850. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Biberfeld P. Specifically cytotoxic lymphocytes produced by preincubation with antibody-complexed target cells. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):558–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorter R. G., Cardoza M., Spencer R. J., Huizenga K. A. Further studies on in vitro cytotoxicity of lymphocytes from patients with ulcerative and granulomatous colitis for allogeneic colonic epithelial cells, including the effects of colectomy. Gastroenterology. 1969 Feb;56(2):304–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorter R. G., Huizenga K. A., ReMine S. G., Spencer R. J. Effects of preliminary incubation of lymphocytes with serum on their cytotoxicity for colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jun;58(6):843–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorter R. G., Tomasi T. B., Huizenga K. A., Spencer R. J., Stobo J. D. The immunology of chronic ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;278:586–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorter T. G., Huizenga K. A., Spencer R. J., Aas J., Guy S. K. Inflammatory bowel disease. Cytophilic antibody and the cytotoxicity of lymphocytes for colonic cells in vitro. Am J Dig Dis. 1971 Aug;16(8):673–680. doi: 10.1007/BF02239587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Tomasi T. B., Huizenga K. A., Spencer R. J., Shorter R. G. In vitro studies of inflammatory bowel disease. Surface receptors of the mononuclear cell required to lyse allogeneic colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 1976 Feb;70(2):171–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUELOVE S. C., WITTS L. J. Cortisone in ulcerative colitis; final report on a therapeutic trial. Br Med J. 1955 Oct 29;2(4947):1041–1048. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4947.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. W., Quigley A., Bolt R. J. Effect of lymphocytes from patients with ulcerative colitis on human adult colon epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 1966 Dec;51(6):985–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]