Abstract
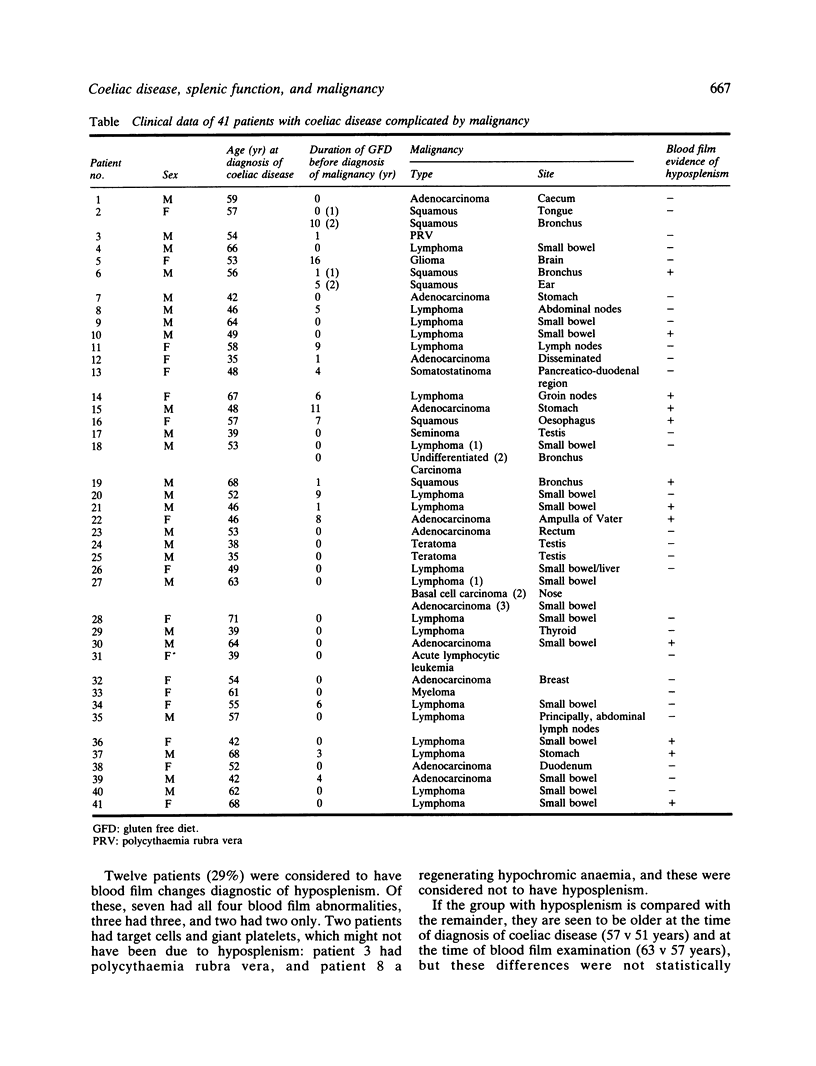
Blood films from 41 cases of coeliac disease complicated by malignancy were examined and evidence of hyposplenism found in 12 cases (29%). This is similar to the proportion of adult coeliacs without malignancy who have hypoplenism and it is concluded that impaired splenic function is not associated with the development of malignancy in coeliac disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brzechwa-Ajdukiewicz A., McCarthy C. F., Austad W., Cornes J., Harrison W. J., Read A. E. Carcinoma, villous atrophy, and steatorrhoea. Gut. 1966 Dec;7(6):572–577. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.6.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish J. C., Beathard G., Sarles H. E., Remmers A. R., Jr, Ritzmann S. E. Circulating lymphocyte depletion: effect on lymphoid tissue. Surgery. 1970 Apr;67(4):658–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUGH K. R., READ A. E., NAISH J. M. Intestinal reticulosis as a complication of idiopathic steatorrhoea. Gut. 1962 Sep;3:232–239. doi: 10.1136/gut.3.3.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. K., Stokes P. L., Sorahan T. M., Prior P., Waterhouse J. A., Cooke W. T. Coeliac disease, gluten-free diet, and malignancy. Gut. 1976 Aug;17(8):612–619. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.8.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSON R. L., BAYRD E. D., WATKINS C. H. The postsplenectomy blood picture. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Dec;32:526–532. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/32.6.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster-Smith M. J., Perrin J., Swarbrick E. T., Wright J. T. Coeliac disease and autoimmunity. Postgrad Med J. 1974 Jan;50(579):45–48. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.50.579.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh G. W., Lewis S. M., Szur L. The use of 51Cr-labelled heat-damaged red cells to study splenic function. I. Evaluation of method. Br J Haematol. 1966 Mar;12(2):161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb05620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh G. W., Stewart J. S. Splenic function in adult coeliac disease. Br J Haematol. 1970 Oct;19(4):445–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb06972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy C. F., Fraser I. D., Evans K. T., Read A. E. Lymphoreticular dysfunction in idiopathic steatorrhoea. Gut. 1966 Apr;7(2):140–148. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre P. A., Wagner H. N., Jr Current procedures for scanning of the spleen. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Dec;73(6):995–1001. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-6-995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit J. E., Hoffbrand A. V., Seah P. P., Fry L. Splenic atrophy in dermatitis herpetiformis. Br Med J. 1972 May 20;2(5811):438–440. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5811.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinette C. D., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Splenectomy and subsequent mortality in veterans of the 1939-45 war. Lancet. 1977 Jul 16;2(8029):127–129. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Bullen A. W., Hall R., Brown R. C., Baxter P., Losowsky M. S. Splenic size and function in adult coeliac disease. Br J Radiol. 1980 Jun;53(630):532–537. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-53-630-532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. Necropsy studies on adult coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Sep;27(9):710–721. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.9.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M., Le Roux A., Small W. P., Sircus W. Malignant lymphoma and extensive viral wart formation in a patient with intestinal lymphangiectasia and lymphocyte depletion. Postgrad Med J. 1977 Dec;53(626):753–757. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.53.626.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


