Abstract
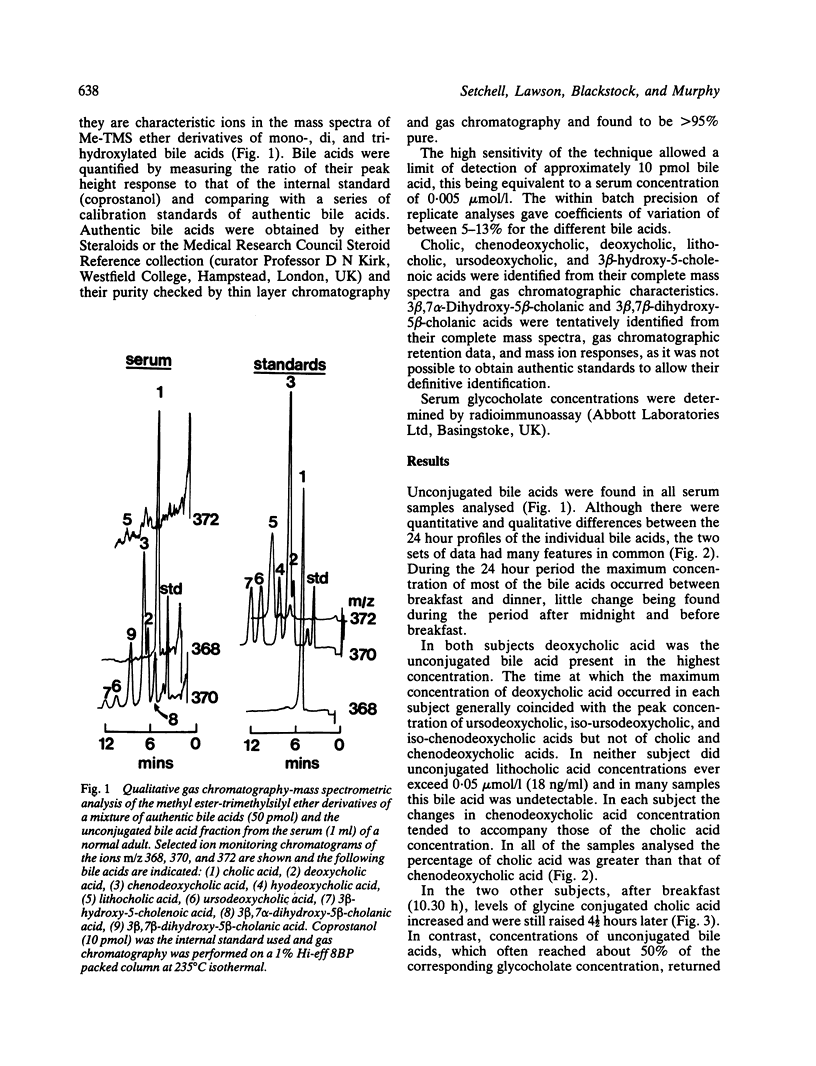
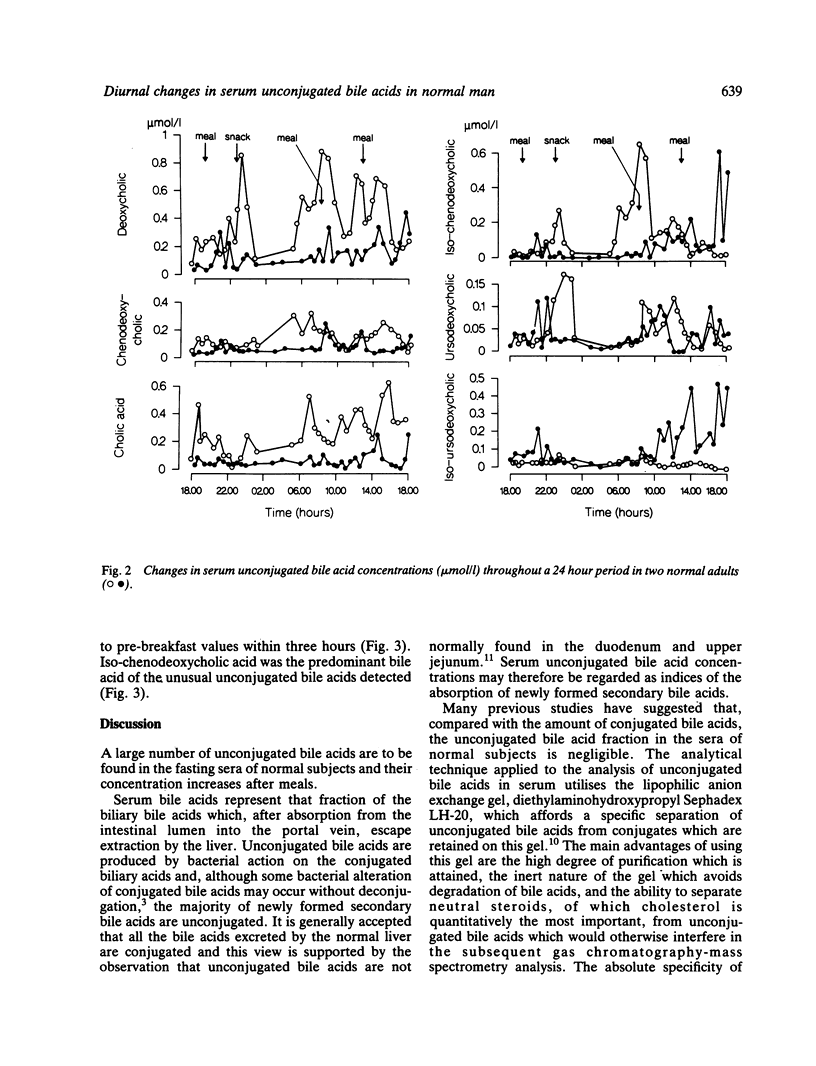
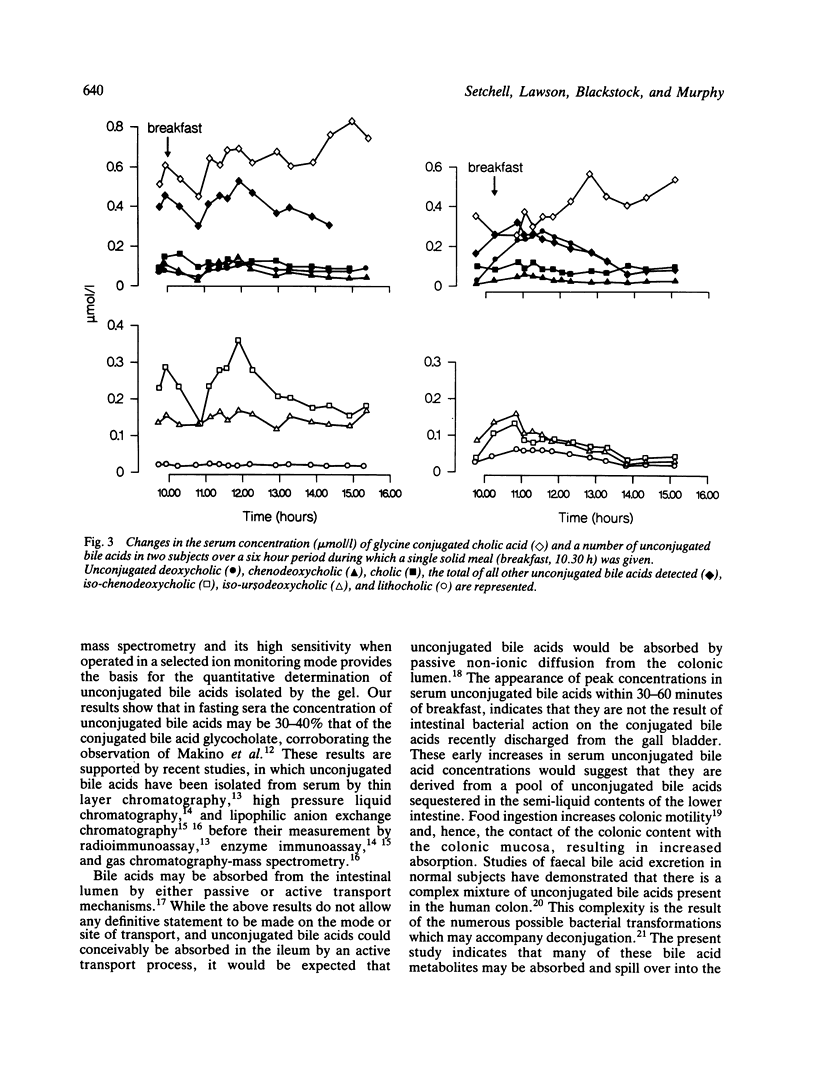
Unconjugated bile acids were measured using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in the serum of two subjects throughout a 24 hour period and in two other subjects over a six hour period after breakfast. Unconjugated bile acids were found in all samples of serum and included cholic, chenodeoxycholic, deoxycholic, 3 beta, 7 alpha-dihydroxy-5 beta-cholanic (iso-chenodeoxycholic), ursodeoxycholic, 3 beta, 7 beta-dihydroxy-5 beta-cholanic (iso-ursodeoxycholic), 3 beta-hydroxy-5-cholenoic, and lithocholic acids. The maximum concentration of each bile acid generally occurred between breakfast and dinner and total unconjugated bile acid concentrations attained levels of between 2-3 mumol/l. Concentrations increased after breakfast and were often as high as 30-40% of the conjugated bile acid glycocholate, but returned to fasting levels in the absence of lunch. The intestinal absorption of unconjugated bile acids is therefore of greater quantitative importance than was previously thought.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almé B., Bremmelgaard A., Sjövall J., Thomassen P. Analysis of metabolic profiles of bile acids in urine using a lipophilic anion exchanger and computerized gas-liquid chromatorgaphy-mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):339–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes S., Gallo G. A., Trash D. B., Morris J. S. Diagnositic value of serum bile acid estimations in liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jun;28(6):506–509. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.6.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremmelgaard A., Almé B. Analysis of plasma bile acid profiles in patients with liver diseases associated with cholestasis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(5):593–600. doi: 10.3109/00365528009182221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M. Mechanisms for the intestinal absorption of bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):297–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eneroth P., Gordon B., Sjövall J. Characterization of trisubstituted cholanoic acids in human feces. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):524–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floch M. H., Gershengoren W., Elliott S., Spiro H. M. Bile acid inhibition of the intestinal microflora--a function for simple bile acids? Gastroenterology. 1971 Aug;61(2):228–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbutt J. T., Wilkins R. M., Lack L., Tyor M. P. Bacterial modification of taurocholate during enterohepatic recirculation in normal man and patients with small intestinal disease. Gastroenterology. 1970 Oct;59(4):553–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. II. Glycine-conjugated dihydroxy bile acids. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1898–1905. doi: 10.1172/JCI106992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplowitz N., Kok E., Javitt N. B. Postprandial serum bile acid for the detection of hepatobiliary disease. JAMA. 1973 Jul 16;225(3):292–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman M. G., Hofmann A. F., Summerskill W. H. Assessment of activity in chronic active liver disease. Serum bile acids compared with conventional tests and histology. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 20;290(25):1399–1402. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406202902503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B., Tabaqchali S., Panveliwalla D., Wootton I. D. Serum-bile-acids in the stagnant-loop syndrome. Lancet. 1969 Feb 1;1(7588):219–220. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Nutter S. Colonic bacterial activity, biliary cholesterol saturation, and pathogenesis of gallstones. Lancet. 1978 Nov 18;2(8099):1063–1065. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino I., Nakagawa S., Mashimo K. Conjugated and unconjugated serum bile acid levels n patients with hepatobiliary diseases. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jun;56(6):1033–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekhjian H. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Colonic absorption of unconjugated bile acids: perfusion studies in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Jul;24(7):545–550. doi: 10.1007/BF01489324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Norman A. Bile acid transformations by microbial strains belonging to genera found in intestinal contents. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;71(4):629–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb05183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., Drasar B. S., Wright J. T. Value of small intestinal bile acid analysis in the diagnosis of the stagnant loop syndrome. Gut. 1973 May;14(5):341–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., McColl I. Postprandial concentrations of free and conjugated bile acids down the length of the normal human small intestine. Gut. 1973 Jul;14(7):513–518. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.7.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Máille E. R., Richards T. G., Short A. H. The influence of conjugation of cholic acid on its uptake and secretion: hepatic extraction of taurocholate and cholate in the dog. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):337–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpello J. H., Sladen G. E. Appraisal of the 14C-glycocholate acid test with special reference to the measurement of faecal 14C excretion. Gut. 1977 Sep;18(9):742–748. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.9.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerfield J. A., Billing B. H., Shackleton C. H. Identification of bile acids in the serum and urine in cholestasis. Evidence for 6alpha-hydroxylation of bile acids in man. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj1540507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


