Abstract
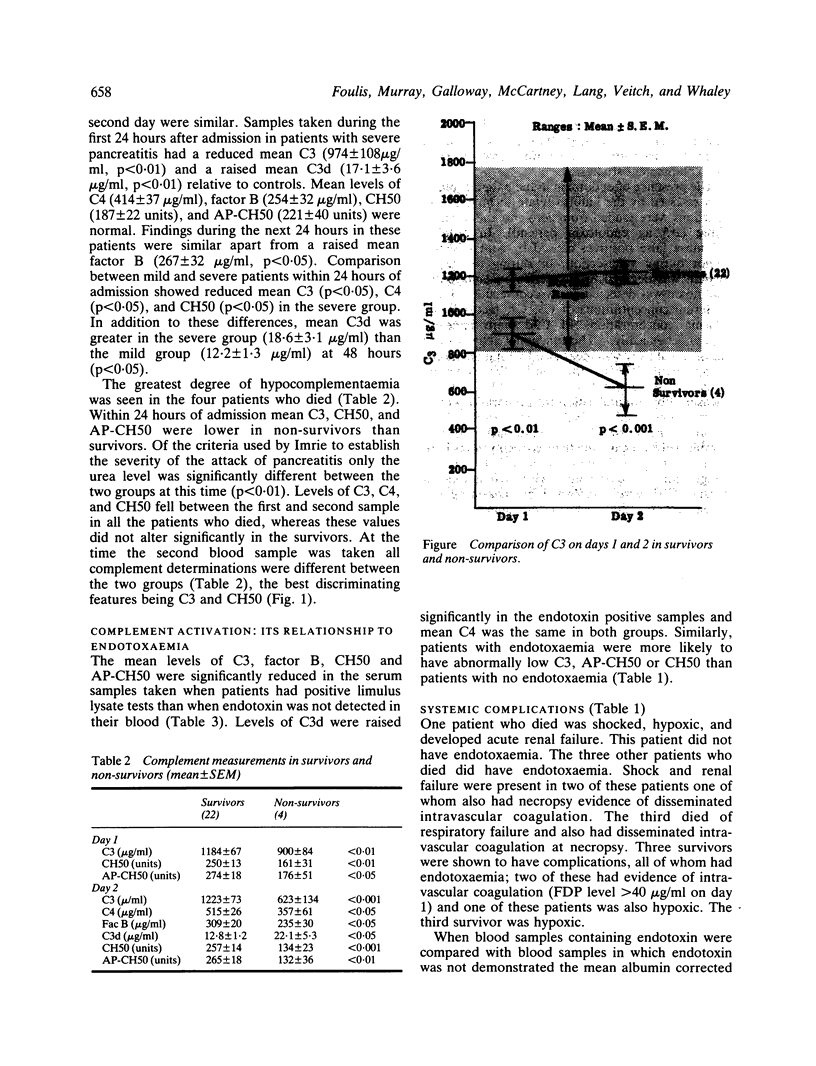
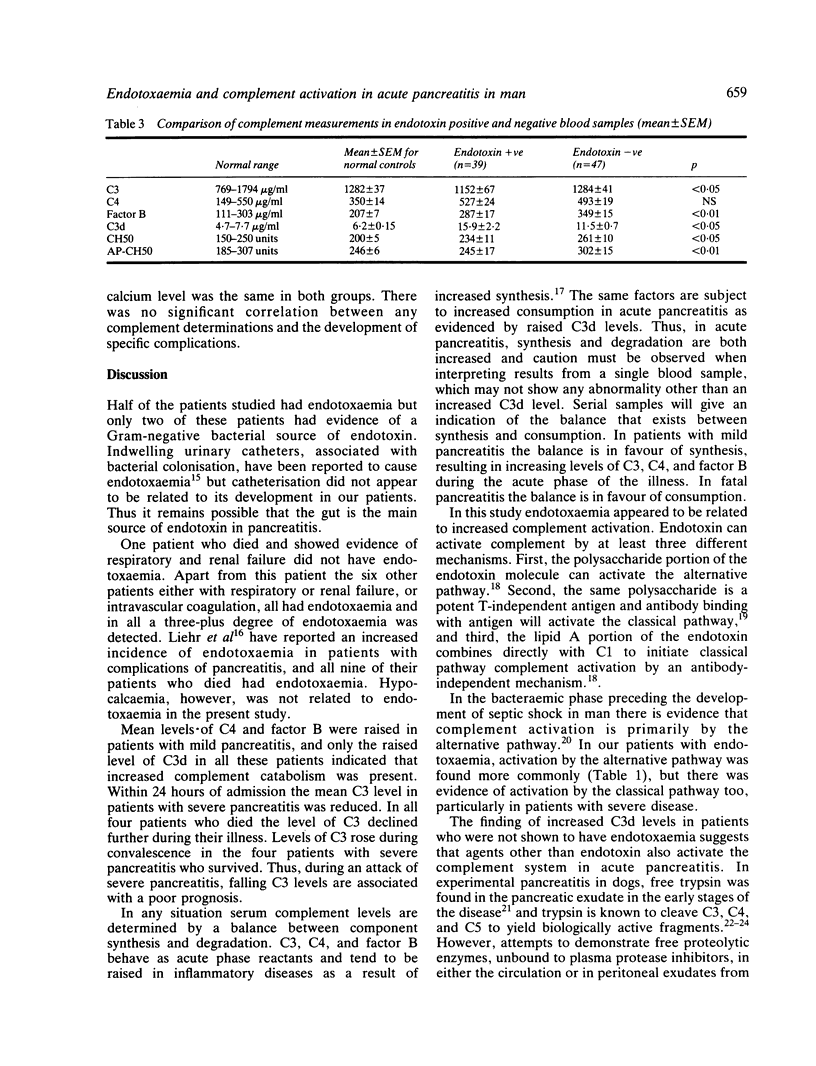
Twenty-four patients who experienced 26 attacks of acute pancreatitis were studied. Endotoxaemia, as measured by the limulus lysate assay, was present in 13 of the attacks. Six out of seven patients with systemic complications of the disease had endotoxaemia. C3 catabolism was increased in all 26 attacks of pancreatitis, and a falling level of C3 during attacks of severe pancreatitis was associated with a fatal outcome. There was statistical evidence of more complement activation in serum samples taken when patients had positive limulus lysate tests than when endotoxin was not detected in their blood.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balldin G., Ohlsson K. Demonstration of pancreatic protease-antiprotease complexes in the peritoneal fluid of patients with acute pancreatitis. Surgery. 1979 Apr;85(4):451–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Dierich M. P., Mūller-Eberhard H. J. Third component of complement (C3): structural properties in relation to functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):1989–1993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzko D. B., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Cleavage of the fourth component of human complement (C4) by C1 esterase: isolation and characteristics of the low molecular weight product. Immunochemistry. 1970 Feb;7(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caridis D. T., Cuevas P., Fine J. Treatment of acute ischemia of the intestine by peritoneal lavage in the rabbit. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1972 Aug;135(2):199–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The derivation of two distinct anaphylatoxin activities from the third and fifth components of human complement. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):371–386. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J., Fine J., Kusano K., McCrea J., Parnas I., Prosser C. L. Potentiation by endotoxin of responses associated with increases in calcium conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3301–3304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas P., Fine J. Role of intraintestinal endotoxin in death from peritonitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1972 Jun;134(6):953–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Ruddy S., Schur P. H., McCabe W. R. Activation of the properdin pathway of complement in patients with gram-negative of bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 1;292(18):937–940. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505012921802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. Letter: Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 1975 May 10;1(7915):1092–1092. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91867-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossard D. P., Kakkar V. V., Elsey P. A. Assessment of limulus test for detecting endotoxaemia. Br Med J. 1974 Jun 1;2(5917):465–468. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5917.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garibaldi R. A., Allman G. W., Larsen D. H., Smith C. B., Burke J. P. Detection of endotoxemia by the limulus test in patients with indwelling urinary catheters. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):551–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Cala D., Radin A., Kaplan H. B., Horn J., Ranson J. Evidence of complement catabolism in acute pancreatitis. Am J Med Sci. 1978 May-Jun;275(3):257–264. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197805000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., Weaver L. J., Hudson L. D., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Association of complement activation and elevated plasma-C5a with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Pathophysiological relevance and possible prognostic value. Lancet. 1980 May 3;1(8175):947–949. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91403-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imrie C. W., Benjamin I. S., Ferguson J. C., McKay A. J., Mackenzie I., O'Neill J., Blumgart L. H. A single-centre double-blind trial of Trasylol therapy in primary acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1978 May;65(5):337–341. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800650514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT J. F., FIFE E. H., Jr Precise standardization of reagents for complement fixation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 Jan;12:103–116. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. H., Rao K. N., Harvey V. S., Lombardi B. Acute hemorrhagic pancreatic necrosis in mice: lack of a pathogenetic role for complement. Acta Hepatogastroenterol (Stuttg) 1979 Aug;26(4):302–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Kline L. F. Activation of the classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley H. L., Whaley K. Control of complement activation in membranous and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1980 Apr;17(4):535–544. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Michael G. Frequency of antigen-sensitive cells to thymus-independent antigens. Cell Immunol. 1971 Aug;2(4):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B., Ruddy S. Enhancing role of IgG in lysis of rabbit erythrocytes by the alternative pathway of human complement. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1994–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. P., Ali M. V. Effect of cholestyramine on endotoxin toxicity and absorption. Am J Dig Dis. 1972 Feb;17(2):161–166. doi: 10.1007/BF02232738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Eddeland A. Release of proteolytic enzymes in bile-induced pancreatitis in dogs. Gastroenterology. 1975 Sep;69(3):668–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranson J. H., Spencer F. C. The role of peritoneal lavage in severe acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1978 May;187(5):565–575. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197805000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig R., Seelig H. P. The possible role of serum complement system in the formal pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis II. Cobra venom factor pancreatitis--sodiumtaurocholate and deoxycholate pancreatitis. Acta Hepatogastroenterol (Stuttg) 1975 Oct;22(5):335–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


