Abstract
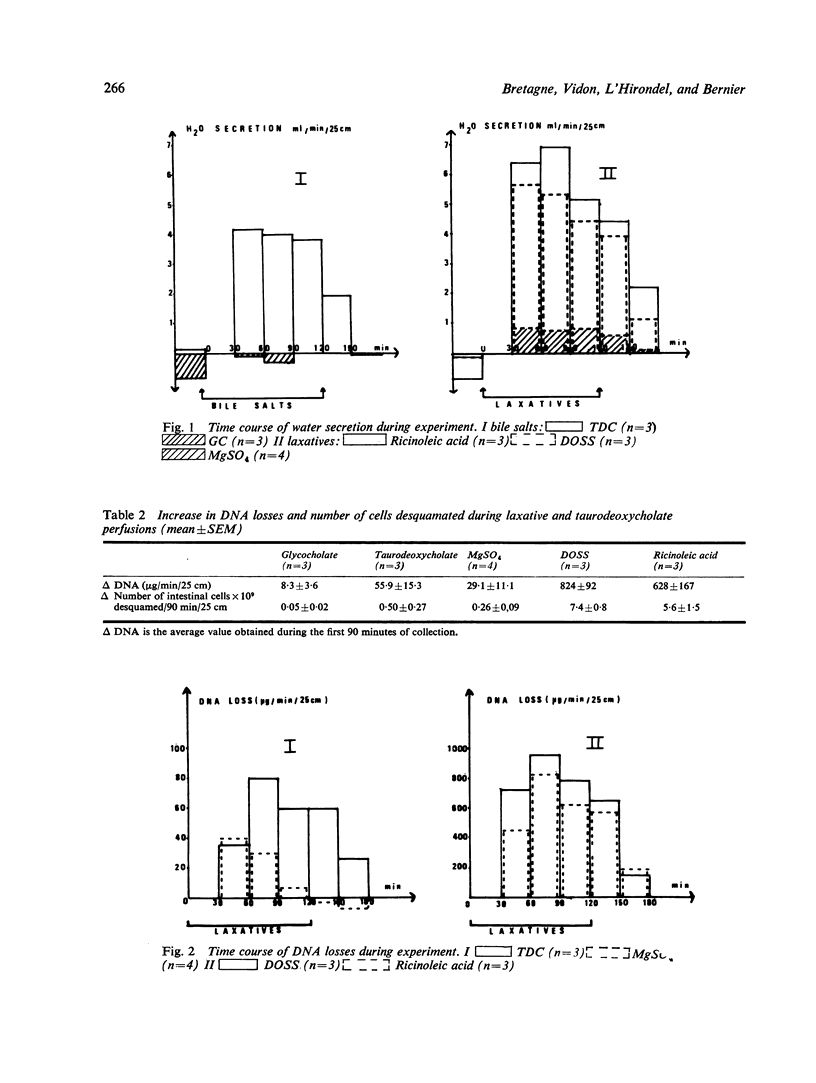
Two conjugated bile salts (10 mmol/l sodium glycocholate, 10 mmol/l sodium taurodeoxycholate) and three laxatives (30 mmol/l magnesium sulphate, 10 mmol/l ricinoleic acid, 2 mmol/l dioctyl sodium sulphosuccinate) were tested on seven subjects with no intestinal lesions in 14 experiments by intestinal perfusion of the jejunum. A 25 cm segment was studied. Each solution was perfused at the rate of 10 ml/min. Water and electrolyte fluxes, losses of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and intestinal cell enzyme activity were measured in the fluids collected. All the laxatives and bile salts tested (except sodium glycocholate) induced water and electrolyte secretion, a rise in intraluminal DNA loss, and enzyme activity. It was possible to establish a significant correlation (p less than 0.001) between the amounts of water fluxes and DNA loss under the effect of dioctyl sodium sulphosuccinate and ricinoleic acid.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammon H. V., Thomas P. J., Phillips S. F. Effects of oleic and ricinoleic acids on net jejunal water and electrolyte movement. Perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):374–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI107569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Filburn C., Volpe B. T. Bile salt alteration of colonic electrolyte transport: role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):503–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline W. S., Lorenzsonn V., Benz L., Bass P., Olsen W. A. The effects of sodium ricinoleate on small intestinal function and structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):380–390. doi: 10.1172/JCI108482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne M. J., Bonorris G. G., Chung A., Conley D., Schoenfield L. J. Propranolol inhibits bile acid and fatty acid stimulation of cyclic AMP in human colon. Gastroenterology. 1977 Nov;73(5):971–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft D. N. Cell turnover and loss and the gastric mucosal barrier. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Apr;22(4):383–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01072198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Binder H. J. Effect of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate on colonic fluid and electrolyte movement. Gastroenterology. 1975 Oct;69(4):941–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiraldes E., Lamabadusuriya S. P., Oyesiku J. E., Whitfield T. E., Harries J. T. A comparative study on the effects of different bile salts on mucosal ATPase and transport in the rat jejunum in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 21;389(3):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullikson G. W., Cline W. S., Lorenzsonn V., Benz L., Olsen W. A., Bass P. Effects of anionic surfactants on hamster small intestinal membrane structure and function: relationship to surface activity. Gastroenterology. 1977 Sep;73(3):501–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries J. T., Sladen G. E. The effects of different bile salts on the absorption of fluid, electrolytes, and monosaccharides in the small intestine of the rat in vivo. Gut. 1972 Aug;13(8):596–603. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.8.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATA T., YAMASAKI K. ENZYMATIC DETERMINATION AND THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS IN BLOOD. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:424–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'hirondel C., Bernier J. J. Déterminations, par la technique de la perfusion interstinale, de la perte de cellules et de protéines dans le jéjunum humain normal. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1979 Feb;3(2):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Pecq J. B., Paoletti C. A new fluorometric method for RNA and DNA determination. Anal Biochem. 1966 Oct;17(1):100–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S. Epithelial cell extrusion during fluid transport in canine small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1977 Apr;232(4):E408–E414. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.232.4.E408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R., Holtermuller K. H., McCall J. T., Go V. L. Pancreatic, gallbladder, and intestinal responses to intraluminal magnesium salts in man. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 Jun;23(6):481–485. doi: 10.1007/BF01072690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland J. B., Asplin A., Hallaway H. M. A new method of studying intestinal mucosal dynamics. Br J Surg. 1968 Oct;55(10):786–789. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800551018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modigliani R., Rambaud J. C., Bernier J. J. The method of intraluminal perfusion of the human small intestine. I. Principle and technique. Digestion. 1973;9(2):176–192. doi: 10.1159/000197443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nell G., Forth W., Rummel W., Wanitschke R. Pathway of sodium moving from blood to intestinal lumen under the influence of oxyphenisatin and deoxycholate. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976;293(1):31–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00498868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Müller M., De Duve C. Lysosomes of the arterial wall. I. Isolation and subcellular fractionation of cells from normal rabbit aorta. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1117–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambaud J. C., Thiry C., Bernier J. J. Etude de l'absorption intestinale du sodium et du potassium, par la perfusion intestinale de solutés isotoniques chez l'homme. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1973 Jan-Feb;36(1):9–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. I., Allan J. G., Gerskowitch V. P., Cochran K. M. The effect of conjugated and unconjugated bile acids on water and electrolyte absorption in the human jejunum. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Sep;45(3):301–311. doi: 10.1042/cs0450301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders D. R., Sillery J., Rachmilewitz D. Effect of dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate on structure and function of rodent and human intestine. Gastroenterology. 1975 Aug;69(2):380–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders D. R., Sillery J., Surawica C., Tytgat G. N. Effect of phenolphthalein on the function and structure of rodent and human intestine. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 Oct;23(10):909–913. doi: 10.1007/BF01072465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. J., Gaginella T. S., Olsen W. A., Bass P. Inhibitory actions of laxatives on motility and water and electrolyte transport in the gastrointestinal tract. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Feb;192(2):458–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem M. V., Phillips S. F. Perfusion of the hamster jejunum with conjugated and unconjugated bile acids: inhibition of water absorption and effects on morphology. Gastroenterology. 1972 Feb;62(2):261–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Treanor L. L. Characterization of bile acid binding to rat intestinal brush border membranes. J Membr Biol. 1977 May 12;33(3-4):213–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01869517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Effect of glycine-conjugated bile acids with and without lecithin on water and glucose absorption in perfused human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1230–1236. doi: 10.1172/JCI107290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



