Abstract
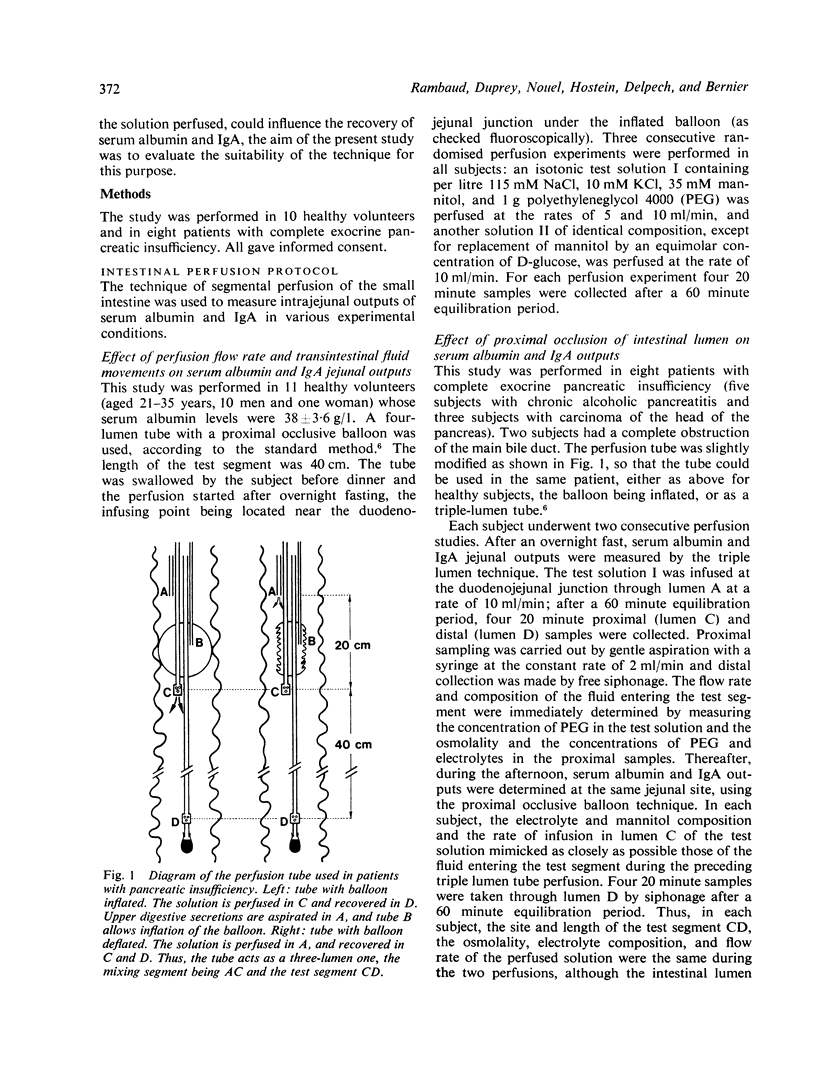
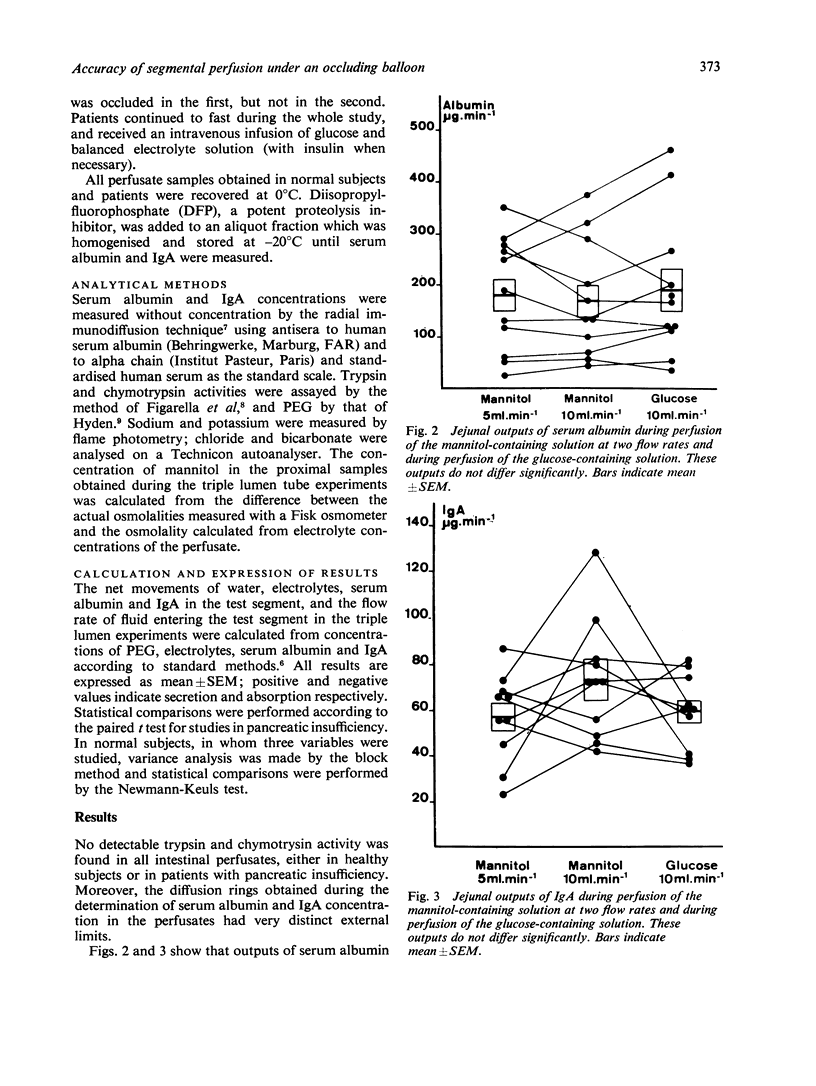
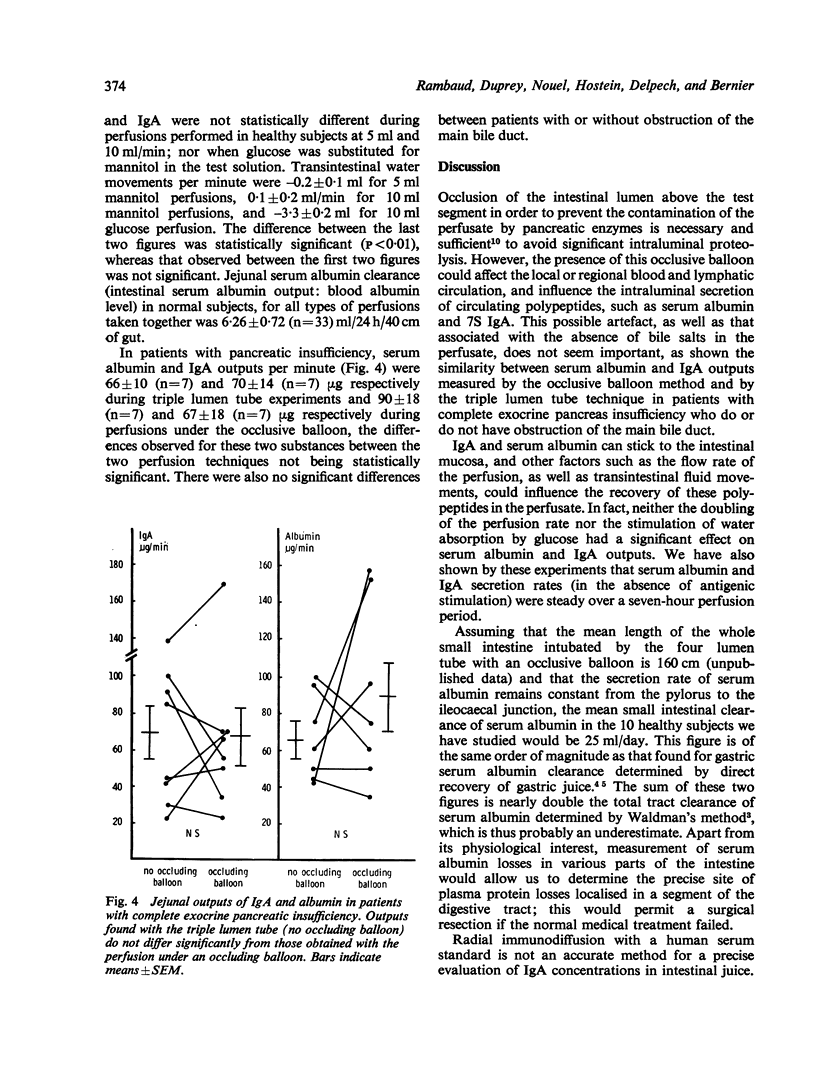
The suitability was investigated of the segmental perfusion technique under an occluding balloon (which prevents the contamination of the test segment by upper digestive secretions and pancreatic proteolytic enzymes) for measuring immunoglobulin A (IgA) and serum albumin outputs into the jejunal lumen. The influence of the perfusion rate and of the transintestinal water movements in the 40 cm long test segment was studied in 11 healthy subjects. IgA and serum albumin outputs did not differ significantly when the same isotonic solution was perfused at rates of 5 or 10 ml/min, nor when water absorption was stimulated by the presence of glucose. A possible artefact linked to intestinal wall distension by the occluding balloon was evaluated in eight subjects with complete exocrine pancreas insufficiency. IgA and serum albumin outputs obtained under the occluding balloon were compared with those found with the triple non-occlusive method. Care was taken to achieve a similar flow rate and solute composition of the fluid entering the test segments with both techniques in each subject. Under these conditions, IgA and serum albumin outputs measured with both methods did not differ significantly. These findings validate the use of the segmental perfusion technique under an occluding balloon to measure IgA and serum albumin outputs into the human small intestine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bull D. M., Bienenstock J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Studies on human intestinal immunoglobulin A. Gastroenterology. 1971 Mar;60(3):370–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIGARELLA C., TAULIER J., SARLES H. DOSAGE DE LA CHYMOTRYPSINE ET DE LA TRYPSINE DANS LE SUC DUOD'ENAL. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1965;47:679–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindh E. Increased risistance of immunoglobulin A dimers to proteolytic degradation after binding of secretory component. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):284–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modigliani R., Rambaud J. C., Bernier J. J. The method of intraluminal perfusion of the human small intestine. I. Principle and technique. Digestion. 1973;9(2):176–192. doi: 10.1159/000197443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomasi T. B., Jr Secretory immunoglobulins. N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 7;287(10):500–506. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209072871008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidon N., Bernier J. J. Détermination par la sérum albumine marquée au 51 Cr des pertes d'albumine plasmatique dans l'estomac chez l'homme. Valuers normales et pathologiques; relation avec la sécrétion alcaline gastrique. Biol Gastroenterol (Paris) 1971;2:153–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Wochner R. D., Strober W. The role of the gastrointestinal tract in plasma protein metabolism. Studies with 51Cr-albumin. Am J Med. 1969 Feb;46(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Wu M., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. IV.--The effect of pancreatic duct ligation on the breakdown of antigen and antigen-antibody complexes on the intestinal surface. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1223–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


