Abstract
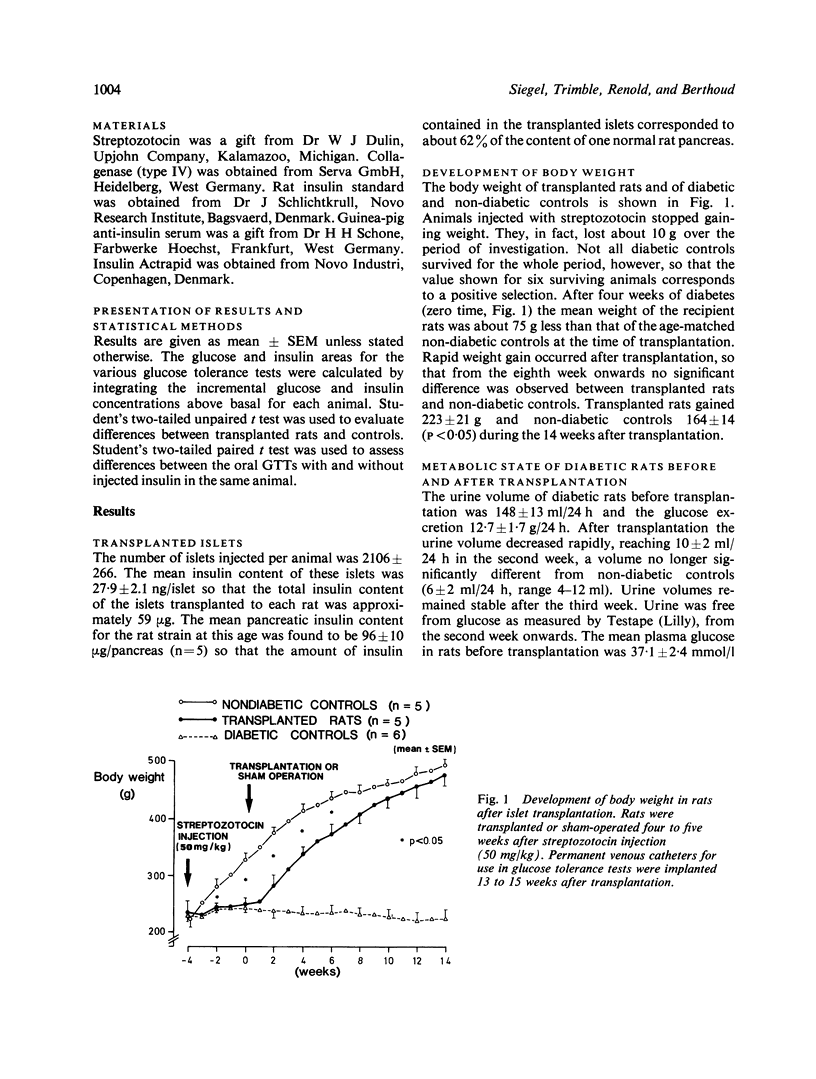
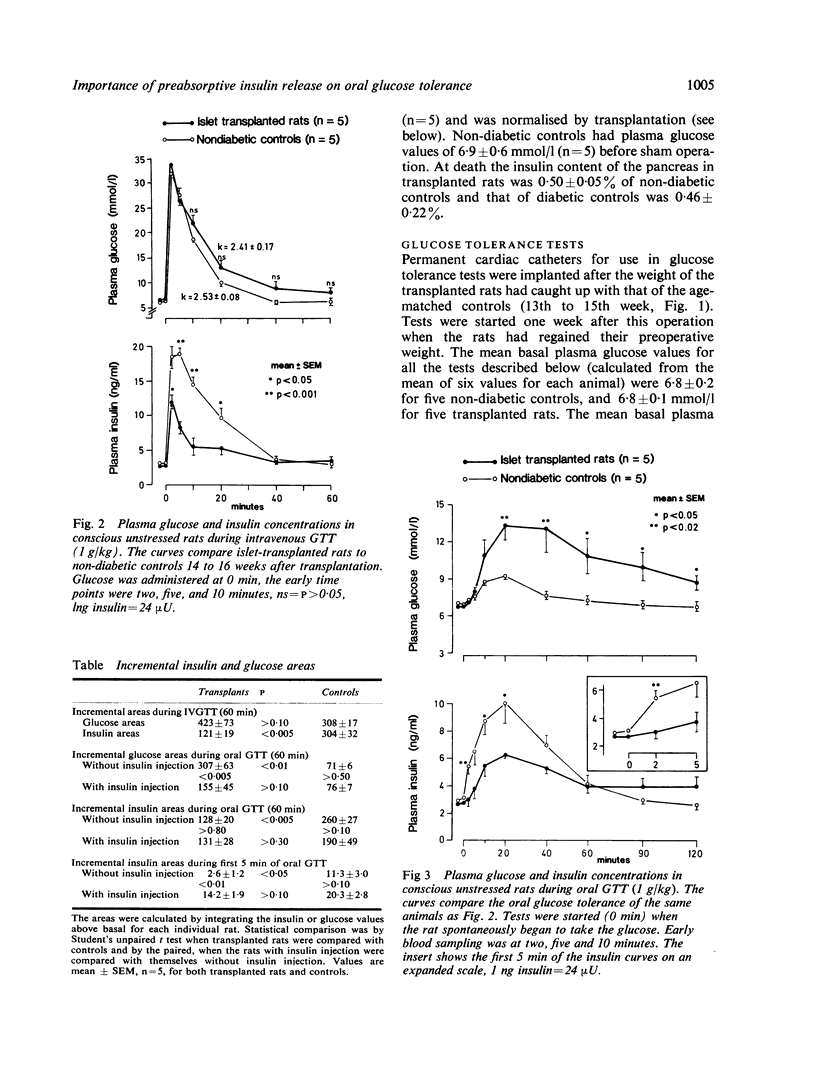
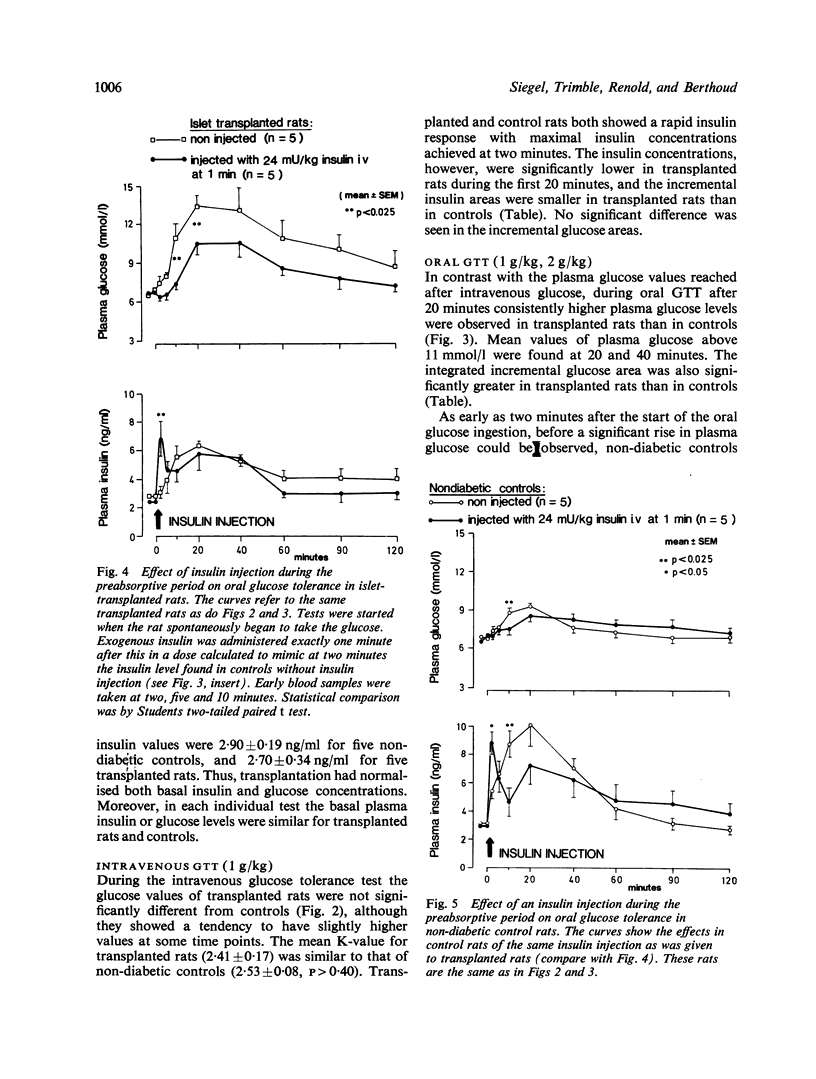
The role of preabsorptive (cephalic phase) insulin release in oral glucose tolerance was investigated using diabetic rats treated by intraportal transplantation of isogenic islets. This early neurally mediated phase of insulin release has been shown to be absent in such rats. When the body weight of transplanted rats was normalised, glucose tolerance tests (GTTs) were performed in the unstressed state using permanent cardiac catheters. Transplanted rats had a normalised intravenous GTT, whereas, as we have shown previously, their oral GTT remained clearly pathological. During both tests peripheral insulin levels were decreased compared with controls. While during intravenous GTT the onset of insulin release occurred as early in transplanted rats as in controls, during oral GTT there was a clear delay, probably because of the absence of the cephalic phase. Re-establishment of normal preabsorptive insulin levels was attempted by a small intravenous insulin injection during this period. This resulted in a transient increase in peripheral insulin levels, which, at two minutes after glucose ingestion, gave values similar to those found in controls at that time. This small insulin injection caused a marked improvement of the oral GTT which was most evident after exogenous insulin had disappeared from the blood. While the injection did not affect the 60 minute incremental insulin area, the glucose area was decreased by 50%, to a value not significantly different from that of control rats. The cephalic phase of insulin release appears, therefore, to be one important factor in the control of glycaemia during food intake. Its absence plays a major role in the pathological oral glucose tolerance of diabetic rats treated by intraportal islet transplantation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albisser A. M., Leibel B. S., Ewart T. G., Davidovac Z., Botz C. K., Zingg W. An artificial endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1974 May;23(5):389–396. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.5.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthoud H. R., Trimble E. R., Siegel E. G., Bereiter D. A., Jeanrenaud B. Cephalic-phase insulin secretion in normal and pancreatic islet-transplanted rats. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):E336–E340. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.4.E336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal and peripheral vein immunoreactive insulin concentrations before and after glucose infusion. Diabetes. 1970 May;19(5):302–306. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.5.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J., Mullen Y., Clark W. R., Molnar I. G., Heininger D. Importance of hepatic portal circulation for insulin action in streptozotocin-diabetic rats transplanted with fetal pancreases. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1688–1694. doi: 10.1172/JCI109631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunzell J. D., Robertson R. P., Lerner R. L., Hazzard W. R., Ensinck J. W., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr Relationships between fasting plasma glucose levels and insulin secretion during intravenous glucose tolerance tests. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Feb;42(2):222–229. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-2-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R., Efendic S. Decreased sensitivity of the pancreatic beta cells to glucose in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. A glucose dose-response study. Diabetes. 1972 Apr;21(4):224–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.4.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutzfeldt W. The incretin concept today. Diabetologia. 1979 Feb;16(2):75–85. doi: 10.1007/BF01225454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Hendler R., Wahren J., Felig P. Influence of hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and the route of glucose administration on splanchnic glucose exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Hendler R. Influence of oral glucose ingestion on splanchnic glucose and gluconeogenic substrate metabolism in man. Diabetes. 1975 May;24(5):468–475. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.5.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Hommel H., Freyse E. J., Fiedler H. Der Mechanismus der Insulinsekretion nach oraler Glukoseverabfolgung. IV. Verhinderung der reflektorischen Frühphase des Plasmainsulin-Anstieges durch Atropin. Endokrinologie. 1975 Feb;65(1):91–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Hommel H., Ziegler M., Jutzi E. The mechanism of insulin secretion after oral glucose administration. 3. Investigations on the mechanism of a reflectoric insulin mobilization after oral stimulation. Diabetologia. 1972 Dec;8(6):385–390. doi: 10.1007/BF01212164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Berger M., Offord R. E. Distribution and metabolism of intravenously injected tritiated insulin in rats. Metabolism. 1979 Nov;28(11):1097–1104. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. R., Jefferys D. B., Jones R. H., Stanley D. The effect of atropine on the insulin release caused by oral and intravenous glucose in human subjects. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1976 Dec;83(4):772–780. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0830772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel H. H., Fischer U. The mechanism of insulin secretion after oral glucose administration V. Portal venous IRI concentration in dogs after ingestion of glucose. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):269–272. doi: 10.1007/BF01219711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel H., Fischer U., Retzlaff K., Knöfler H. The mechanism of insulin secretion after oral glucose administration. II. Reflex insulin secretion in conscious dogs bearing fistulas of the digestive tract by sham-feeding of glucose or tap water. Diabetologia. 1972 Apr;8(2):111–116. doi: 10.1007/BF01235635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakash C., Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Jeanrenaud B. An anomaly of insulin removal in perfused livers of obese-hyperglycemic (ob/ob) mice. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1117–1124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis-Sylvestre J. Preabsorptive insulin release and hypoglycemia in rats. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jan;230(1):56–60. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis-Sylvestre J. Relationship between two stages of prandial insulin release in rats. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E103–E111. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondon C. E., Olefsky J. M., Dolkas C. B., Reaven G. M. Removal of insulin by perfused rat liver: effect of concentration. Metabolism. 1975 Feb;24(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navalesi R., Pilo A., Ferrannini E. Insulin kinetics after portal and peripheral injection of [125I] insulin: II. Experiments in the intact dog. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jun;230(6):1630–1636. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.6.1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A., Karl I. E., Kipnis D. M. Secretory capability of islets transplanted intraportally in the diabetic rat. Diabetes. 1978 Aug;27(8):817–824. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.8.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powley T. L. The ventromedial hypothalamic syndrome, satiety, and a cephalic phase hypothesis. Psychol Rev. 1977 Jan;84(1):89–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfeld J. F., Stadil F. The effect of gastrin on basal- and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1415–1426. doi: 10.1172/JCI107315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens A. B. Influence of the oral cavity on insulin release in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1976 May;230(5):1411–1415. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.5.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubbe J. H., Steffens A. B. Rapid insulin release after ingestion of a meal in the unanesthetized rat. Am J Physiol. 1975 Oct;229(4):1019–1022. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.4.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble E. R., Siegel E. G., Berthoud H. R., Renold A. E. Intraportal islet transplantation: functional assessment in conscious unrestrained rats. Endocrinology. 1980 Mar;106(3):791–797. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-3-791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


