Abstract
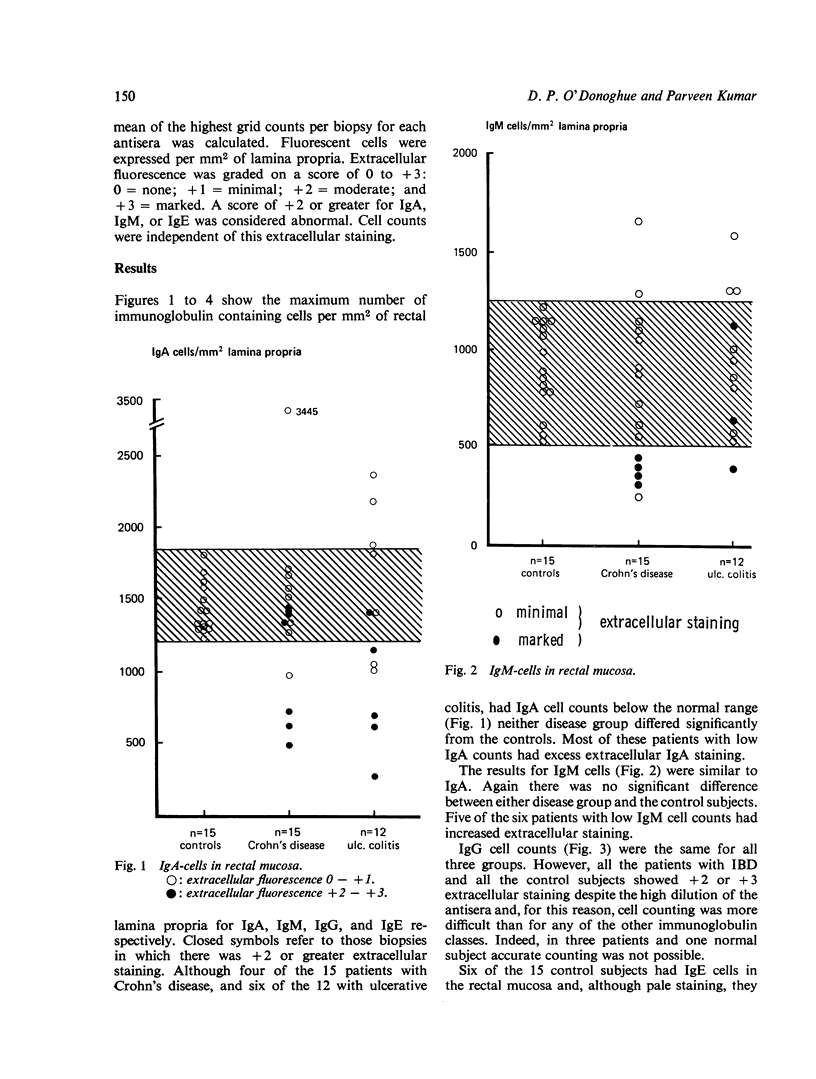
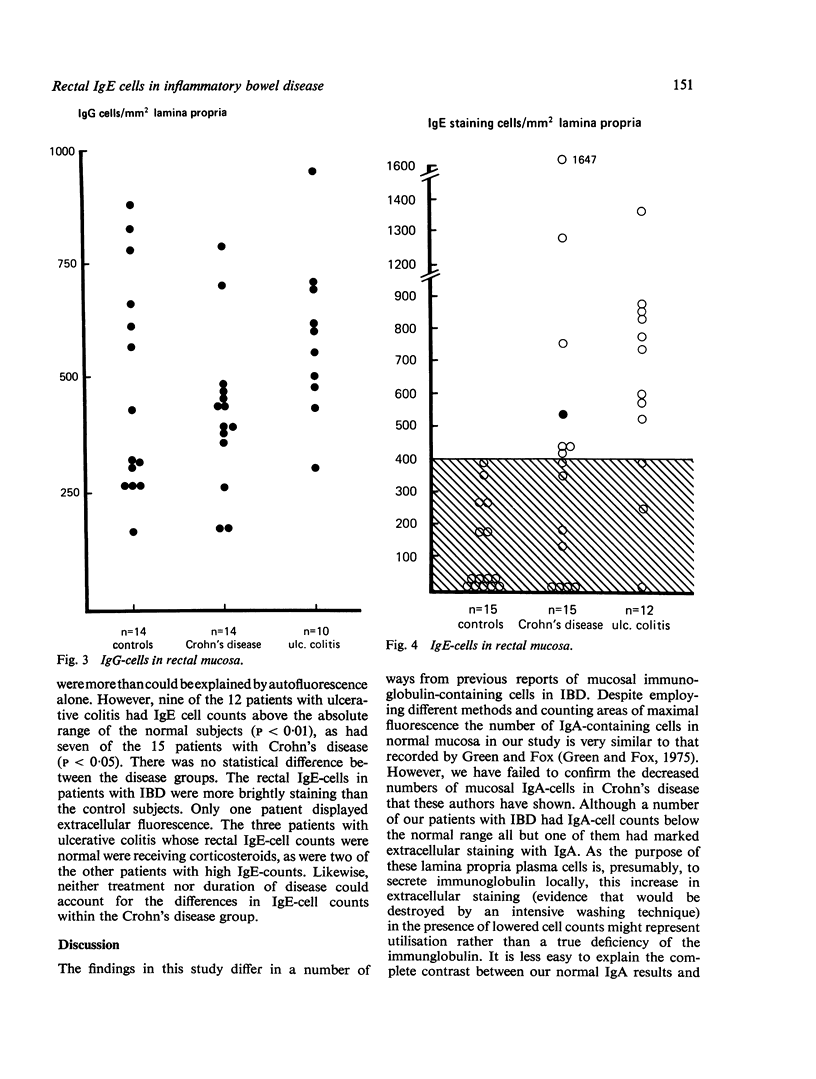
Immunoglobulin-contained cells in the rectal mucosa of patients suffering from non-specific inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) were counted and compared with those in a control population. While the numbers of IgA, IgM, and IgG-containing cells in both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease did not differ from normal, both disease groups exhibited a marked increase in IgE-staining cells. This increase in IgE-cells did not correlate with severity, duration, or treatment of disease and it did not prove possible, using these immunological studies, to differentiate between Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baklien K., Brandtzaeg P. Comparative mapping of the local distribution of immunoglobulin-containing cells in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease of the colon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Nov;22(2):197–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Borthistle B. K., Chen S. T. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) and IgE-containing cells in human gastrointestinal fluids and tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):227–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cave D. R., Mitchell D. N., Brooke B. N. Evidence of an agent transmissible from ulcerative colitis tissue. Lancet. 1976 Jun 19;1(7973):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92649-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Paronetto F., Kochwa S. Immunohistochemical localization of IgE in asthmatic lungs. Am J Pathol. 1971 Mar;62(3):339–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. J., Kirsner J. B., Riddell R. H. Usefulness of rectal biopsy in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1977 May;72(5 Pt 1):952–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green F. H., Fox H. The distribution of mucosal antibodies in the bowel of patients with Crohn's disease. Gut. 1975 Feb;16(2):125–131. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley R. V., Calcraft B. J., Fifield R., Rhodes J., Whitehead R. H., Newcombe R. G. Immunoglobulin E in rectal mucosa of patients with proctitis. Lancet. 1975 Nov 22;2(7943):1010–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley R. V., Calcraft B. J., Rhodes J., Owen E., Evans B. K. Disodium cromoglycate in the treatment of chronic proctitis. Gut. 1975 Jul;16(7):559–563. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.7.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilby A., Walker-Smith J. A., Wood C. B. Letter: Small intestinal mucosa in cow's milk allergy. Lancet. 1975 Mar 1;1(7905):531–531. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92887-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard-Jones J. E., Lockhart-Mummery H. E., Morson B. C. Clinical and pathological differentiation of Crohn's disease and proctocolitis. Gastroenterology. 1968 Jun;54(6):1162–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd G., Green F. H., Fox H., Mani V., Turnberg L. A. Mast cells and immunoglobulin E in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1975 Nov;16(11):861–865. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.11.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell-Tuck J., Ritchie J. K., Lennard-Jones J. E. The prognosis of idiopathic proctitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(6):727–732. doi: 10.3109/00365527709181711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E. Immunoglobulin-containing cells in the intestinal mucosa and immunoglobulins in the intestinal juice in children. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Jul;11(3):415–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner J. M., Whitehead R. The plasma cells in inflammatory disease of the colon: a quantitative study. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Aug;27(8):643–646. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.8.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


