Abstract
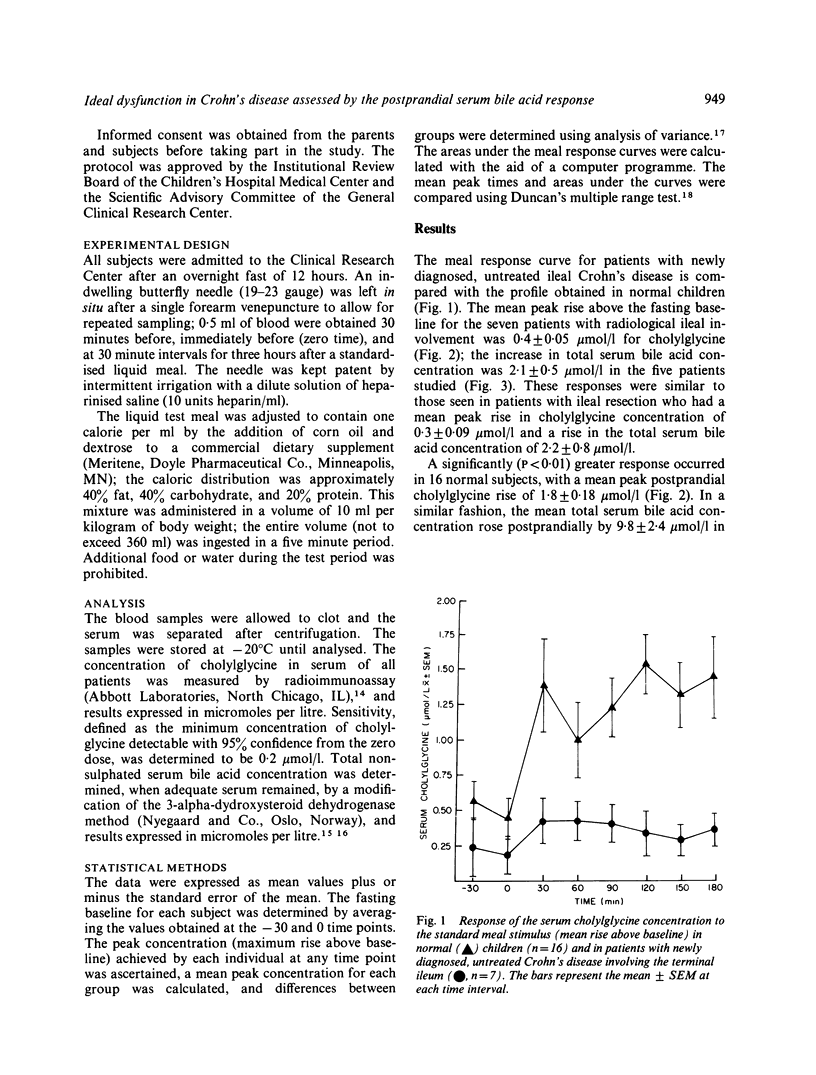
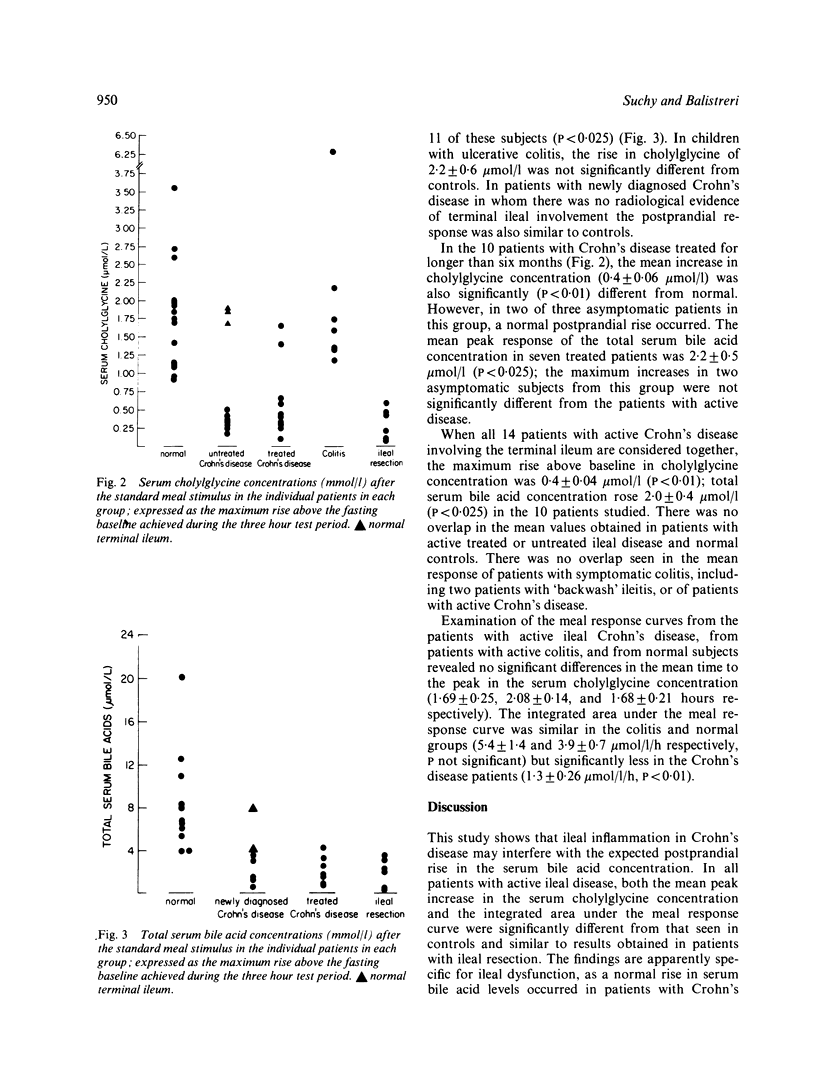
We assessed ileal functional integrity in 20 consecutive patients with Crohn's disease by sequential measurement of the postprandial serum bile acid concentration. In all 14 patients with active Crohn's disease involving the terminal ileum, the mean (+/- SEM) peak response in the cholylglycine (0.4 +/- 0.04 mumol/l, n = 14) as well as in the total serum bile acid concentration (2.0 +/- 0.4 mumol/l, n = 10) was similar to that seen in a group of children who had undergone ileal resection. A significantly greater increase in the cholylglycine (1.8 +/- 0.18 mumol/l, n = 16, P less than 0.01) and in the total serum bile acid concentration (9.8 +/- 2.4 mumol/l, n = 11, P less than 0.025) was noted in normal children. In five of the six remaining patients (three with Crohn's disease shown not to involve the ileum and two of three with asymptomatic, treated Crohn's ileitis) and in seven patients with ulcerative colitis, the meal stimulated responses were normal. These preliminary results suggest that measurement of the serum bile concentration after a meal stimulus may provide a valuable index of ileal inflammation in patients with Crohn's disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balistreri W. F., Suchy F. J., Heubi J. E. Serum bile acid response to a test meal stimulus: a sensitive test of ileal function. J Pediatr. 1980 Mar;96(3 Pt 2):582–589. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80870-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best W. R., Becktel J. M., Singleton J. W., Kern F., Jr Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Hofmann A. F. Breath test for altered bile-acid metabolism. Lancet. 1971 Sep 18;2(7725):621–625. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryboski J. D., Spiro H. M. Prognosis in children with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1978 May;74(5 Pt 1):807–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Korman M. G., Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F. Dynamics of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. Postprandial serum concentrations of conjugates of cholic acid in health, cholecystectomized patients, and patients with bile acid malabsorption. N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 3;291(14):689–692. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410032911401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meihoff W. E., Kern F., Jr Bile salt malabsorption in regional ileitis, ileal resection and mannitol-induced diarrhea. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):261–267. doi: 10.1172/JCI105722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell W. D., Eastwood M. A. Faecal bile acids and neutral steroids in patients with ileal dysfunction. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1972;7(1):29–32. doi: 10.3109/00365527209180734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuga T., Mitamura K., Mashige F., Imai D. Evaluation of fluorimetrically estimated serum bile acid in liver disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Feb 15;75(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90502-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponz De Leon M., Murphy G. M., Dowling R. H. Physiological factors influencing serum bile acid levels. Gut. 1978 Jan;19(1):32–39. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson K., Johansson C., Norman A. Serum bile acids after a test meal in Crohn's disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1979 Oct;39(6):511–518. doi: 10.1080/00365517909108828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalm S. W., LaRusso N. F., Hofmann A. F., Hoffman N. E., van Berge-Henegouwen G. P., Korman M. G. Diurnal serum levels of primary conjugated bile acids. Assessment by specific radioimmunoassays for conjugates of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid. Gut. 1978 Nov;19(11):1006–1014. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.11.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley M. M., Nemchausky B. Fecal C-14-bile acid excretion in normal subjects and patients with steroid-wasting syndromes secondary to ileal dysfunction. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Oct;70(4):627–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vantrappen G., Ghoos Y., Rutgeerts P., Janssens J. Bile acid studies in uncomplicated Crohn's disease. Gut. 1977 Sep;18(9):730–735. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.9.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Roy C. C., Chartrand L., Morin C. L., Van Caillie M. Malabsorption des acides biliaires chez l'enfant, en l'absence de résection intestinale. Union Med Can. 1974 Dec;103(12):2089–2094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Blankenstein M., Hoyset T., Hörchner P., Frenkel M., Wilson J. H. Faecal bile acid radioactivity, a sensitive and relatively simple test for ileal dysfunction. Neth J Med. 1977;20(6):248–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


