Abstract
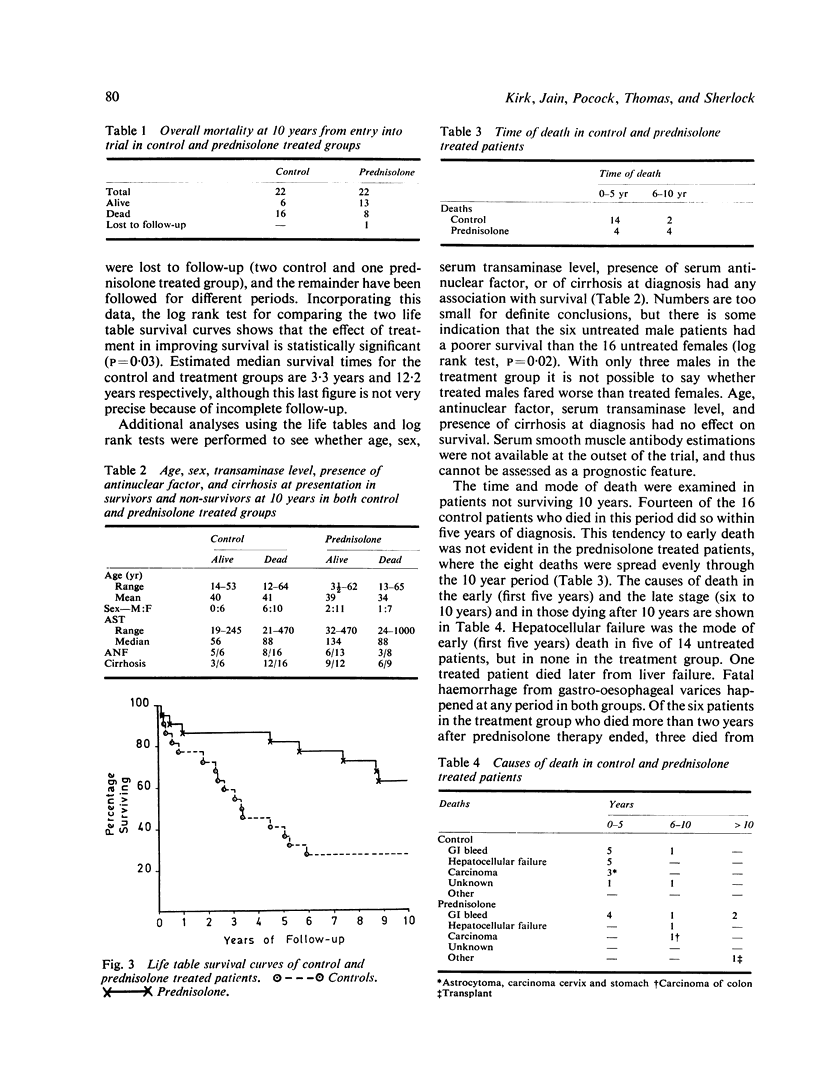
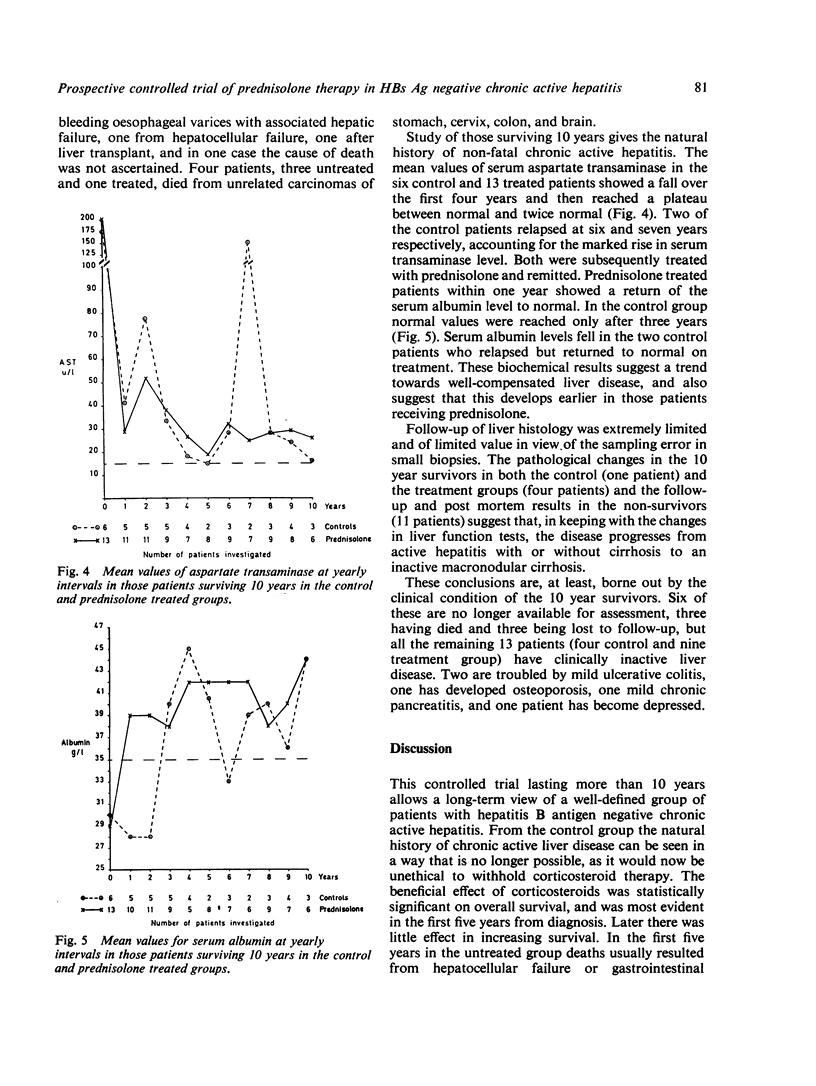
A long-term follow-up of at least 10 years or until death of 44 patients taking part in a controlled prospective trial of prednisolone therapy in hepatitis B antigen negative chronic active hepatitis (lupoid hepatitis) has been performed at the Royal Free Hospital, London. Patients presenting between 1963 and 1967 were randomly allocated into control and treatment groups. Ten year life table survival curves showed a significantly improved survival in the treatment group where 63% of patients were alive at 10 years compared with only 27% in the control group (log rank test, P = 0.03). The median survival in the treatment group was 12.2 years compared with 3.3 years in the control group. The mean duration of treatment was 4.5 years. Age, presence of antinuclear factor, cirrhosis, or level of serum transaminases at presentation did not appear to affect survival. Male patients if untreated had a poorer prognosis than females (P = 0.02). The natural history of chronic active hepatitis appeared from clinical, biochemical, and histological findings to be from an active hepatitis or cirrhosis to inactive macronodular cirrhosis. Prednisolone therapy significantly improved survival by reducing mortality in the early active phase of the disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony P. P., Ishak K. G., Nayak N. C., Poulsen H. E., Scheuer P. J., Sobin L. H. The morphology of cirrhosis. Recommendations on definition, nomenclature, and classification by a working group sponsored by the World Health Organization. J Clin Pathol. 1978 May;31(5):395–414. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.5.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson J. P., Frank M. M. Effect of cortisone therapy on serum complement components. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1061–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEARN A. G., KUNKEL H. G., SLATER R. J. The problem of chronic liver disease in young women. Am J Med. 1956 Jul;21(1):3–15. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain G. D., Mayer G., Jones E. A. Augmentation of albumin but not fibrinogen synthesis by corticosteroids in patients with hepatocellular disease. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2198–2204. doi: 10.1172/JCI106438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N. Corticosteroids and lymphoid cells. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 24;287(8):388–397. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208242870806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. C., Mulligan R., Sherlock S. Controlled prospective trial of corticosteroid therapy in active chronic hepatitis. Q J Med. 1971 Apr;40(158):159–185. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.qjmed.a067264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliastam M., Holmes A. W. Hepatitis, arthritis and lupus cell phenomena caused by methyldopa. Am J Dig Dis. 1971 Nov;16(11):1014–1018. doi: 10.1007/BF02235014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSWORTH C. D., HALL E. W., DAWSON A. M., SHERLOCK S. ULCERATIVE COLITIS IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE. Q J Med. 1965 Apr;34:211–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Hopf U. Studies on the pathogenesis of experimental chronic active hepatitis in rabbits. I. Induction of the disease and protective effect of allogeneic liver specific proteins. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Oct;55(5):498–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mistilis S. P., Blackburn C. R. Active chronic hepatitis. Am J Med. 1970 Apr;48(4):484–495. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray-Lyon I. M., Stern R. B., Williams R. Controlled trial of prednisone and azathioprine in active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):735–737. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- READ A. E., SHERLOCK S., HARRISON C. V. ACTIVE 'JUVENILE' CIRRHOSIS CONSIDERED AS PART OF A SYSTEMIC DISEASE AND THE EFFECT OF CORTICOSTEROID THERAPY. Gut. 1963 Dec;4:378–393. doi: 10.1136/gut.4.4.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild M. A., Oratz M., Schreiber S. S. Regulation of albumin metabolism. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:91–104. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Gollan J. L., Samourian S., Sherlock S. Wilson's disease, presenting as chronic active hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Apr;74(4):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S., Fox R. A., Niazi S. P., Scheuer P. J. Chronic liver disease and primary liver-cell cancer with hepatitis-associated (Australia) antigen in serum. Lancet. 1970 Jun 13;1(7659):1243–1247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91737-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway R. D., Summerskill W. H., Baggenstoss A. H., Geall M. G., Gitnićk G. L., Elveback I. R., Schoenfield L. J. Clinical, biochemical, and histological remission of severe chronic active liver disease: a controlled study of treatments and early prognosis. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):820–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C. The immune response in hepatic cirrhosis: animal and human studies. Proc R Soc Med. 1977 Aug;70(8):521–525. doi: 10.1177/003591577707000803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., van Furth R. The effect of glucocorticosteroids on the kinetics of mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Mar 1;131(3):429–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. W., Granger G. A. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: mechanism of lymphotoxin-induced target cell destruction. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):911–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. C., Seeff L. B., Berk P. D., Jones A., Plotz P. H. Treatment of chronic active hepatitis. An analysis of three controlled trials. Gastroenterology. 1977 Dec;73(6):1422–1430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


