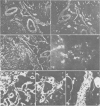
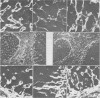
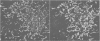
Abstract
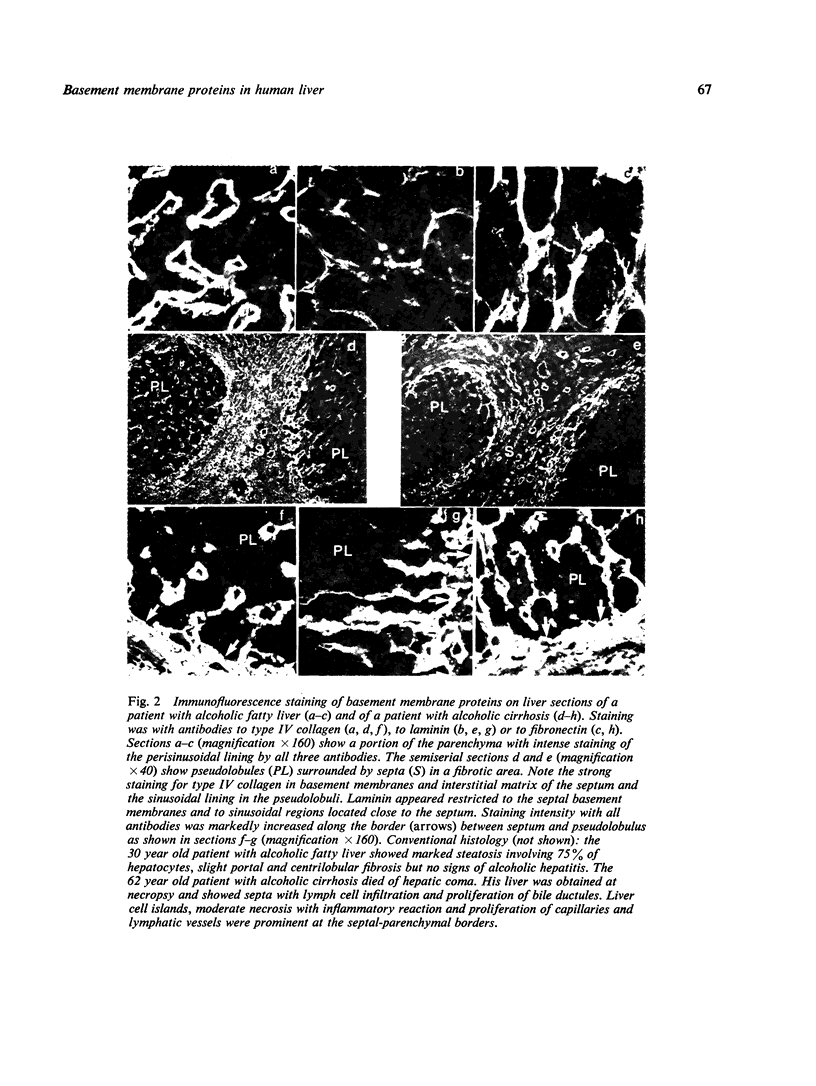
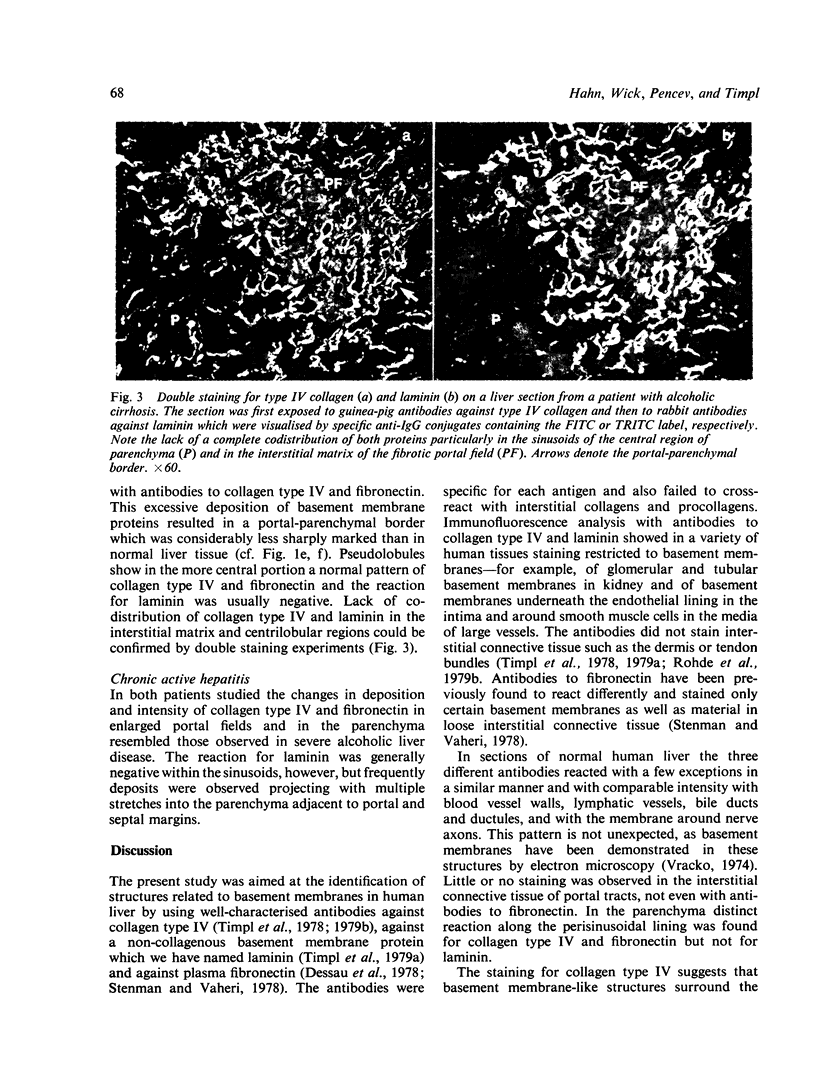
Specific antibodies to collagen type IV, laminin, and fibronectin were used to localise these proteins by indirect immunofluorescence in frozen sections of normal and fibrotic liver. In normal livers distinct staining was found in basement membranes of blood and lymph vessels, of bile ducts and ductules and around nerve axons. Positive reactions for type IV collagen and fibronectin were also observed in the perisinusoidal space, while hepatocytes and most of the interstitial matrix of portal fields remained unstained. Liver specimens obtained from patients with alcoholic liver disease (fatty liver, hepatitis or cirrhosis) and chronic active hepatitis showed a more intense reaction with the antibodies in the perisnusoidal space including now distinct staining for laminin. These patterns were particularly prominent at borders between fibrotic septa and remnants of parenchyma or pseudolobules. Strong reactions were also found for type IV collagen and fibronectin in the periportal interstitium and in large fibrotic areas. The findings support previous electron-microscopical and chemical evidence for increased basement membrane production in human liver fibrosis and demonstrate that this may involve different proteins and occur at different anatomical sites.
Full text
PDF


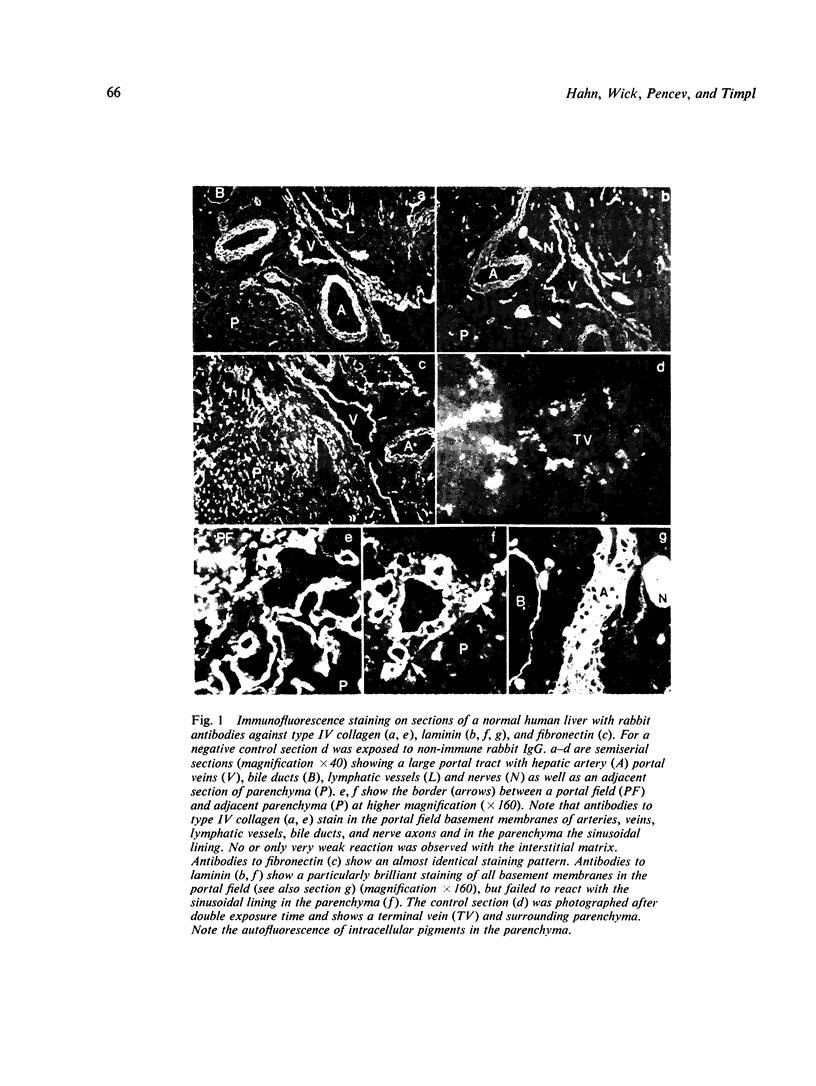



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUCHER N. L. REGENERATION OF MAMMALIAN LIVER. Int Rev Cytol. 1963;15:245–300. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung E., Rhodes K., Miller E. J. Isolation of three collagenous components of probable basement membrane origin from several tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1167–1174. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossel L. Uber akutes Auftreten von Basalmembranen an den Lebersinusoiden. (Beitrag zur Kenntnis der kapillären Basalmembran) Beitr Pathol Anat. 1966 Aug;134(1):103–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessau W., Sasse J., Timpl R., Jilek F., von der Mark K. Synthesis and extracellular deposition of fibronectin in chondrocyte cultures. Response to the removal of extracellular cartilage matrix. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):342–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Fietzek P. P., Remberger K., Eder M., Kühn K. Liver cirrhosis: immunofluorescence and biochemical studies demonstrate two types of collagen. Klin Wochenschr. 1975 Mar 1;53(5):205–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01468808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville R. W., Rauter A., Fietzek P. P. Isolation and characterization of a native placental basement-membrane collagen and its component alpha chains. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr 2;95(2):383–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban Z., Russell R. M., Boyer J. L., Glagov S., Bagheri S. A. Ultrastructural changes in livers of two patients with hypervitaminosis A. Am J Pathol. 1974 Sep;76(3):451–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Structure and biosynthesis of basement membranes. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1973;6:63–104. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363706-2.50008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder E., Stenman S., Lehto V. P., Vaheri A. Distribution of fibronectin in human tissues and relationship to other connective tissue components. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:151–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischner M. W., Alexander J. F., Galambos J. T. Natural history of alcoholic hepatitis. I. The acute disease. Am J Dig Dis. 1971 Jun;16(6):481–494. doi: 10.1007/BF02235538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin R. W., Gehron P., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Valentine T., Swarm R. A murine tumor producing a matrix of basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):204–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott U., Hahn E., Moshudis E., Bode J. C., Martini G. A. Immunhistologischer Nachweis von Typ I- und Typ III-Kollagen in Leberbiopsien: Frühe und späte Veränderungen bei alkoholischer Lebererkrankung. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1977 Apr 17;83:537–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Steiner J. W. Electron microscopy of cirrhotic nodule Tubularization of the parenchyma by biliary hepatocytes. Lab Invest. 1966 May;15(5):801–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M., Giambrone M. A., Biempica L. Collagen types in normal and cirrhotic liver. Gastroenterology. 1979 Apr;76(4):710–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M., Martinez-Palomo A. Increase in type I and type III collagens in human alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):539–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph R., McClure W. J., Woodward M. Contractile fibroblasts in chronic alcoholic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1979 Apr;76(4):704–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFNER F., POPER H. Capillarization of hepatic sinusoids in man. Gastroenterology. 1963 Mar;44:239–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer J. M., Hutcheson E. T., Kang A. H. Collagen polymorphism in normal and cirrhotic human liver. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):241–248. doi: 10.1172/JCI108634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman S., Vaheri A. Distribution of a major connective tissue protein, fibronectin, in normal human tissues. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1054–1064. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Glanville R. W., Wick G., Martin G. R. Immunochemical study on basement membrane (type IV) collagens. Immunology. 1979 Sep;38(1):109–116. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Martin G. R., Bruckner P., Wick G., Wiedemann H. Nature of the collagenous protein in a tumor basement membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):43–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Risteli J., Bächinger H. P. Identification of a new basement membrane collagen by the aid of a large fragment resistant to bacterial collagenase. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 15;101(2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Kurkinen M., Lehto V. P., Linder E., Timpl R. Codistribution of pericellular matrix proteins in cultured fibroblasts and loss in transformation: fibronectin and procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4944–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vracko R. Basal lamina scaffold-anatomy and significance for maintenance of orderly tissue structure. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):314–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick G., Brunner H., Penner E., Timpl R. The diagnostic application of specific antiprocollagen sera. II. Analysis of liver biopsies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1978;56(4):316–324. doi: 10.1159/000232037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick G., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Purified antibodies to collagen: an immunofluorescence study of their reaction with tissue collagen. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(5):664–679. doi: 10.1159/000231354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]