Abstract
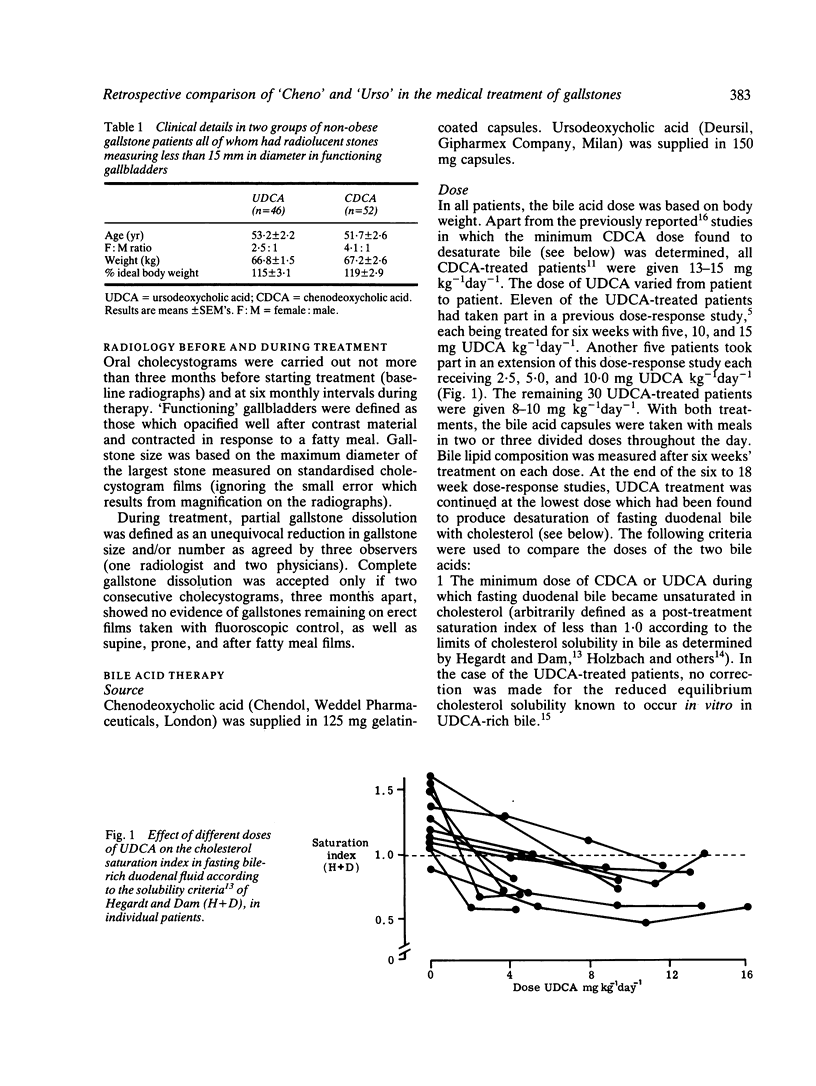
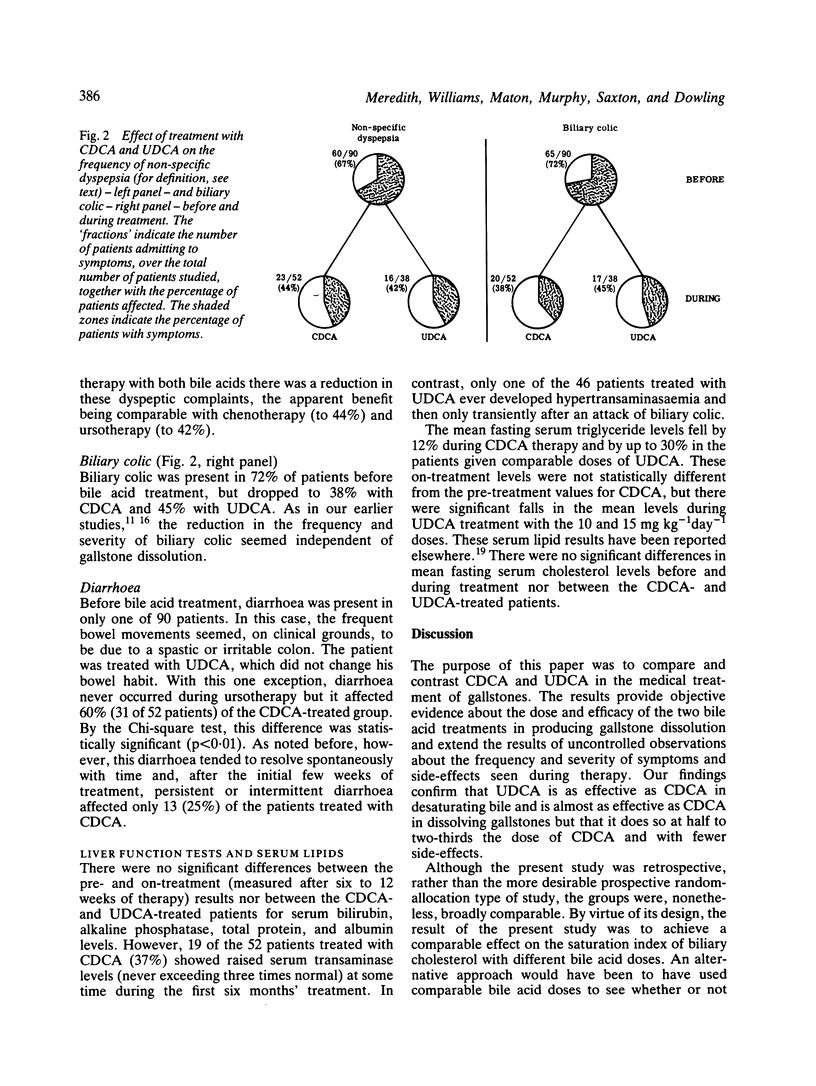
In two groups of gallstone patients ideally suited for medical treatment, the effect of six to 18 months' therapy was compared retrospectively in 52 given chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and 46 given ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). The minimum dose (mg kg-1 day-1) required to desaturate bile consistently was 10.1 for UDCA and 14.3 for CDCA. In patients completing six months' treatment, 23 of 35 (66%) taking a mean of 7.7 (+/- SEM 0.5) mg UDCA and 34 of 42 (81%) taking 14.7 +/- 0.2 mg CDCA showed partial or complete dissolution of gallstones. The mean dose in the UDCA-treated patients, however, was artefactually lowered by previous dose-response studies: in those who had not taken multiple doses, the mean UDCA intake in the 'responders' at six months was 9.1 +/- 0.3 mg kg-1 day-1. At six months, more UDCA (five of 35 or 14.3%) than CDCA (four of 42 or 9.5%)-treated patients showed complete dissolution of gallstones, but, by one year, the situation was reversed, 20 of 41 (49%) CDCA-treated and eight of 30 (27%) UDCA-treated patients showing complete dissolution of gallstones. Cumulative efficacy at one year had risen to 76% for UDCA and 89% for CDCA. Both treatments reduced the frequency of dyspepsia and biliary colic; 37% of CDCA and 2.6% of UDCA-treated patients showed hypertransaminasaemia; diarrhoea developed in 60% of the CDCA group but in none of the UDCA group.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateson M. C., Bouchier I. A., Trash D. B., Maudgal D. P., Northfield T. C. Calcification of radiolucent gall stone during treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Sep 5;283(6292):645–646. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6292.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begemann F., Bandomer G., Herget H. J. The influence of beta-sitosterol on biliary cholesterol saturation and bile acid kinetics in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(1):57–63. doi: 10.3109/00365527809179806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. D., Whitney B., Dowling R. H. Gallstone dissolution in man using chenodeoxycholic acid. Lancet. 1972 Dec 9;2(7789):1213–1216. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C. Critical tables for calculating the cholesterol saturation of native bile. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):945–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne M. J., Bonorris G. G., Goldstein L. I., Schoenfield L. J. Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid and phenobarbital on the rate-limiting enzymes of hepatic cholesterol and bile acid synthesis in patients with gallstones. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Feb;87(2):281–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzinger R. G., Hofmann A. F., Schoenfield L. J., Thistle J. L. Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by chenodeoxycholic acid. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 6;286(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201062860101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorowski T., Salen G., Tint G. S., Mosbach E. Transformation of chenodeoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid by human intestinal bacteria. Gastroenterology. 1979 Nov;77(5):1068–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbach R. T., Marsh M., Olszewski M., Holan K. Cholesterol solubility in bile. Evidence that supersaturated bile is frequent in healthy man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1467–1479. doi: 10.1172/JCI107321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iser J. H., Dowling H., Mok H. Y., Bell G. D. Chenodeoxycholic acid treatment of gallstones. A follow-up report and analysis of factors influencing response to therapy. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 21;293(8):378–383. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508212930804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iser J. H., Maton P. N., Murphy G. M., Dowling R. H. Resistance to chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) treatment in obese patients with gall stones. Br Med J. 1978 Jun 10;1(6126):1509–1512. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6126.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James O., Cullen J., Bouchier I. A. Chenodeoxycholic acid therapy for gallstones: effectiveness, toxicity and influence on bile acid metabolism. Q J Med. 1975 Apr;44(174):349–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutz K., Schulte A. Effectiveness of ursodeoxycholic acid in gallstone therapy. Gastroenterology. 1977 Sep;73(3):632–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad L., Lundholm K., Scherstén T. Influence of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid on biliary cholesterol secretion in man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;7(5):383–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino I., Shinozaki K., Yoshino K., Nakagawa S. [Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by long-term administration of ursodeoxycholic acid]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1975 Jun;72(6):690–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maton P. N., Ellis H. J., Higgins M. J., Dowling R. H. Hepatic HMGCoA reductase in human cholelithiasis: effects of chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acids. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;10(4):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb00040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maton P. N., Murphy G. M., Dowling R. H. Ursodeoxycholic acid treatment of gallstones. Dose-response study and possible mechanism of action. Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1297–1301. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok H. Y., Bell G. D., Dowling R. H. Effect of different doses of chenodeoxycholic acid on bile-lipid composition and on frequency of side-effects in patients with gallstones. Lancet. 1974 Aug 3;2(7875):253–257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa S., Makino I., Ishizaki T., Dohi I. Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by ursodeoxycholic acid. Lancet. 1977 Aug 20;2(8034):367–369. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama F. Oral cholelitholysis--cheno versus urso: Japanese experience. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Feb;25(2):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF01308311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., LaRusso N. F., Hofmann A. F., Thistle J. L. Biliary lipid output during three meals and an overnight fast. II. Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid treatment in gallstone subjects. Gut. 1975 Jan;16(1):12–17. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponz de Leon M., Carulli N., Loria P., Iori R., Zironi F. Cholesterol absorption during bile acid feeding. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) administration. Gastroenterology. 1980 Feb;78(2):214–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponz de Leon M., Carulli N., Loria P., Iori R., Zironi F. The effect of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) on cholesterol absorption. Gastroenterology. 1979 Aug;77(2):223–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salen G., Colalillo A., Verga D., Bagan E., Tint G. S., Shefer S. Effect of high and low doses of ursodeoxycholic acid on gallstone dissolution in humans. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jun;78(6):1412–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehl A., Czygan P., Kommerell B., Weis H. J., Holtermüller K. H. Ursodeoxycholic acid versus chenodeoxycholic acid. Comparison of their effects on bile acid and bile lipid composition in patients with cholesterol gallstones. Gastroenterology. 1978 Dec;75(6):1016–1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistle J. L., Hofmann A. F., Yu P. Y., Ott B. Effect of varying doses of chenodeoxycholic acid on bile lipid and biliary bile acid composition in gallstone patients: a dose-response study. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Jan;22(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF01077389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. J., Hofmann A. F. Letter: A simple calculation of the lithogenic index of bile: expressing biliary lipid composition on rectangular coordinates. Gastroenterology. 1973 Oct;65(4):698–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurston H., Bing R. F., Marks E. S., Swales J. D. Response of chronic renovascular hypertension to surgical correction or prolonged blockade of the renin-angiotensin system by two inhibitors in the rat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Jan;58(1):15–20. doi: 10.1042/cs0580015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting M. J., Jarvinen V., Watts J. M. Chemical composition of gallstones resistant to dissolution therapy with chenodeoxycholic acid. Gut. 1980 Dec;21(12):1077–1081. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.12.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


