Abstract
Plasma amino-acid concentrations were measured in 167 patients with liver disease of varying aetiology and severity, all free of encephalopathy, and the results compared with those in 57 control subjects matched for age and sex. In the four groups of patients with chronic liver disease (26 patients with chronic active hepatitis, 23 with primary biliary cirrhosis, 11 with cryptogenic cirrhosis, and 48 with alcoholic hepatitis +/- cirrhosis) plasma concentrations of methionine were significantly increased, while concentrations of the three branched chain amino-acids were significantly reduced. In the first three groups of patients plasma concentrations of aspartate, serine, and one or both of the aromatic amino-acids tyrosine and phenylalanine were also significantly increased, while in the patients with alcoholic hepatitis +/- cirrhosis plasma concentrations of glycine, alanine, and phenylalanine were significantly reduced. In the three groups of patients with minimal, potentially reversible liver disease (31 patients with alcoholic fatty liver, 10 with viral hepatitis, and 18 with biliary disease) plasma concentrations of proline and the three branched chain amino-acids were significantly reduced. Patients with alcoholic fatty liver also showed significantly reduced plasma phenylalanine values. Most changes in plasma amino-acid concentrations in patients with chronic liver disease may be explained on the basis of impaired hepatic function, portal-systemic shunting of blood, and hyperinsulinaemia and hyperglucagonaemia. The changes in patients with minimal liver disease are less easily explained.
Full text
PDF

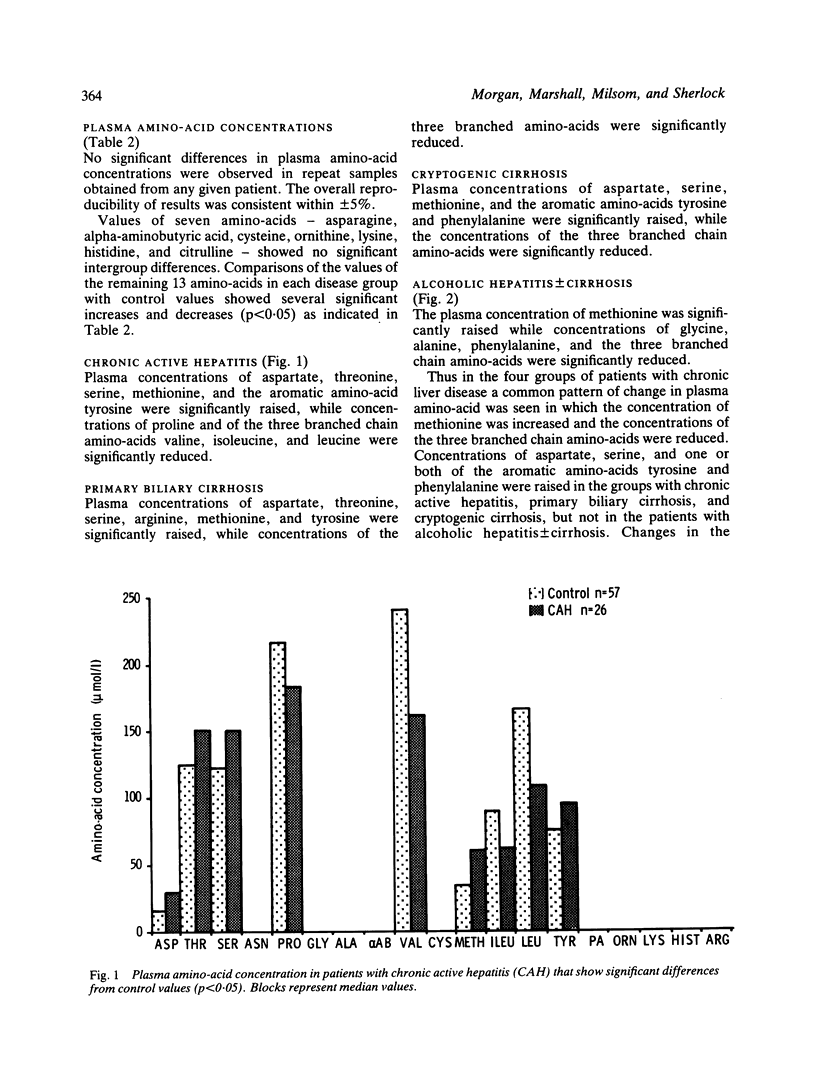
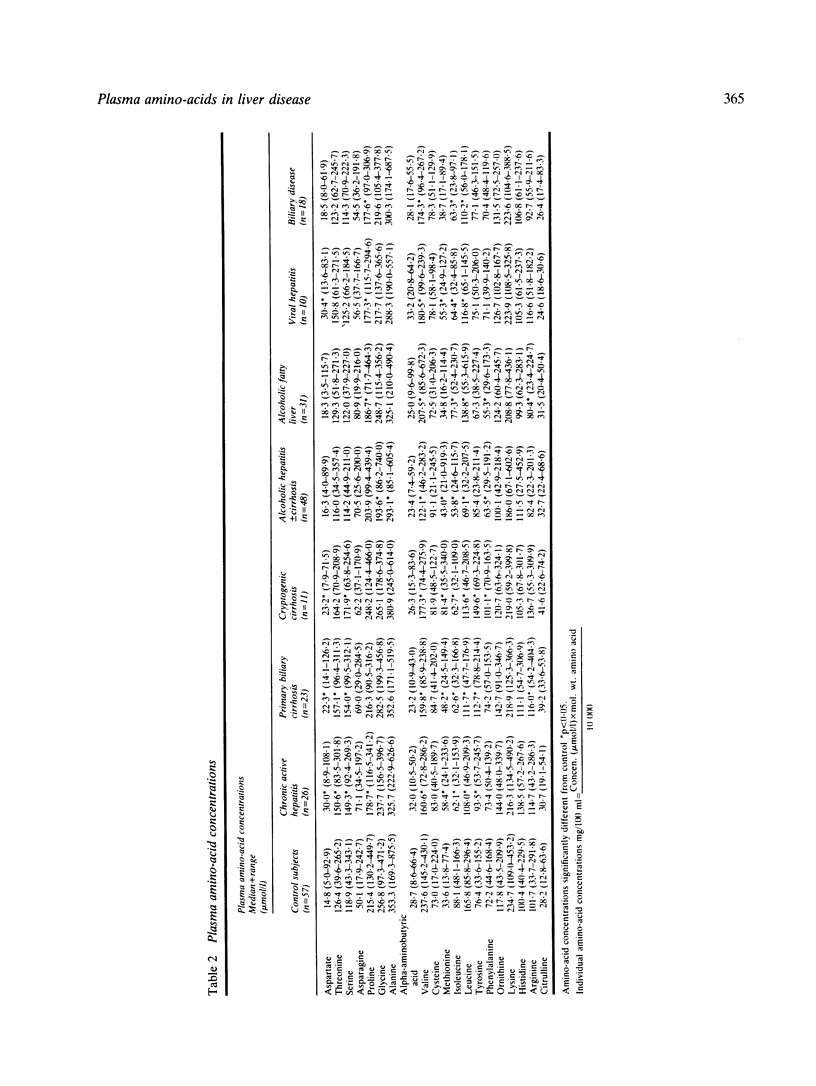
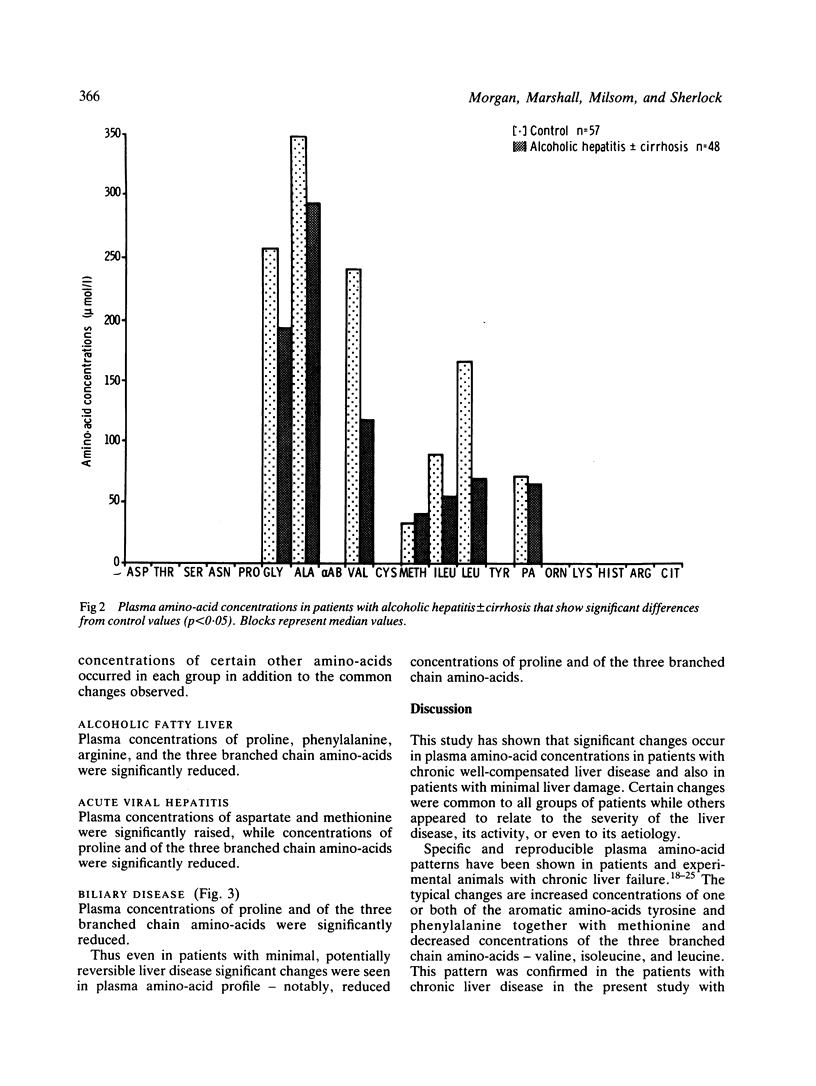
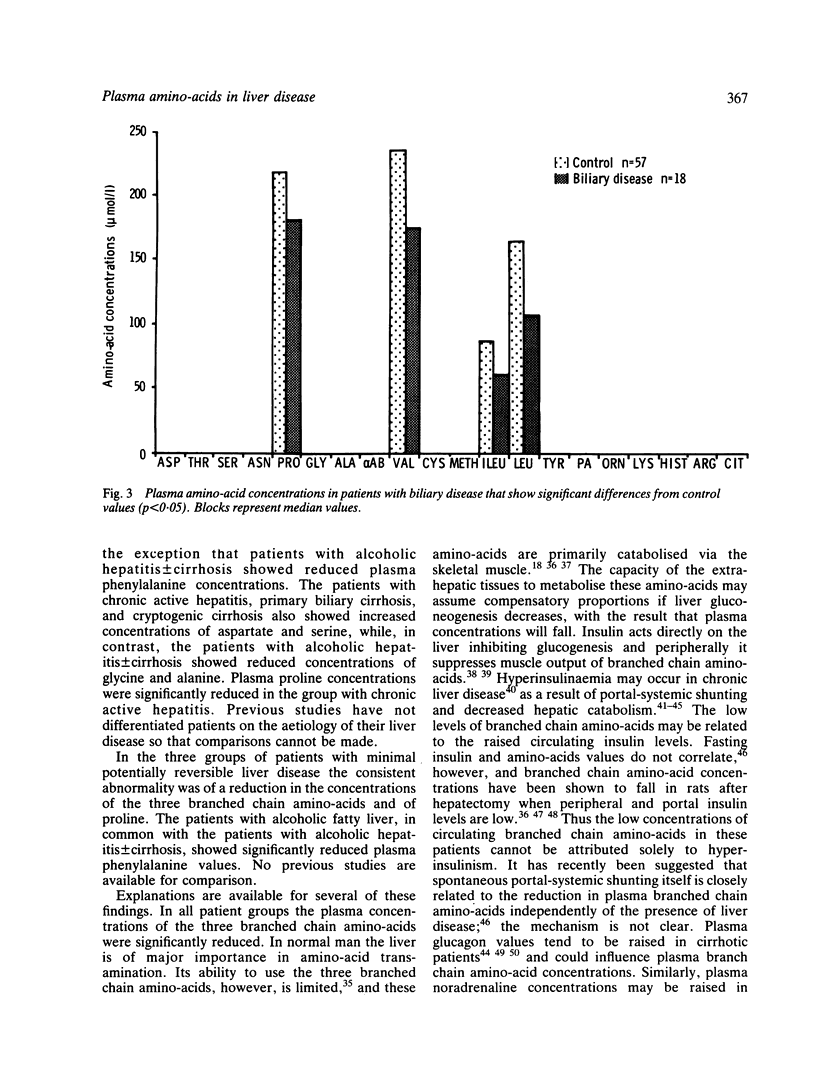



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguirre A., Yoshimura N., Westman T., Fischer J. E. Plasma amino acids in dogs with two experimental forms of liver damage. J Surg Res. 1974 Apr;16(4):339–345. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(74)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambert J. P., Péchery C., Lemonnier A., Housset E., Hartmann L. Dosage et différenciation des acides aminés urinaires chez le cirrhotique avant et après anastomose porto-cave. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1966 Jan-Feb;24(1):41–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong M. D., Stave U. Emergency care for acute poisoning with phosphororganic compounds. Metabolism. 1973 Apr;22(4):571–578. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher N. L., Weir G. C. Insulin, glucagon, liver regeneration, and DNA synthesis. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1423–1425. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T., Lewis J., Glazko A. J. Effect of ethanol and other alcohols on the transport of amino acids and glucose by everted sacs of rat small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):1000–1007. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. R., Crofford O. B. Glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in patients with liver disease. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Aug;124(2):142–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutzfeldt W., Frerichs H., Sickinger K. Liver diseases and diabetes mellitus. Prog Liver Dis. 1970;3:371–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. S., Akawaie S., Yeh H. L., Martin H. URINARY EXCRETION OF AMINO ACIDS IN LIVER DISEASE. J Clin Invest. 1950 Mar;29(3):302–312. doi: 10.1172/JCI102258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J. Protein turnover and amino acid metabolism in the regulation of gluconeogenesis. Fed Proc. 1974 Apr;33(4):1092–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. E., Funovics J. M., Aguirre A., James J. H., Keane J. M., Wesdorp R. I., Yoshimura N., Westman T. The role of plasma amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy. Surgery. 1975 Sep;78(3):276–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. E., Yoshimura N., Aguirre A., James J. H., Cummings M. G., Abel R. M., Deindoerfer F. Plasma amino acids in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Effects of amino acid infusions. Am J Surg. 1974 Jan;127(1):40–47. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(74)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GABUZDA G. J., Jr, ECKHARDT R. D., DAVIDSON C. S. Urinary excretion of amino acids in patients with cirrhosis of the liver and in normal adults. J Clin Invest. 1952 Nov;31(11):1015–1022. doi: 10.1172/JCI102686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco A. V., Crucitti F., Ghirlanda G., Manna R., Altomonte L., Rebuzzi A. G., Bertoli A. Insulin and glucagon concentrations in portal and peripheral veins in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Diabetologia. 1979 Jul;17(1):23–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01222973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IBER F. L., ROSEN H., LEVENSON S. M., CHALMERS T. C. The plasma amino acids in patients with liver failure. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Sep;50(3):417–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iob V., Coon W. W., Sloan M. Altered clearance of free amino acids from plasma of patients with cirrhosis of the liver. J Surg Res. 1966 Jun;6(6):233–239. doi: 10.1016/s0022-4804(66)80029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iob V., Mattson W. J., Jr, Sloan M., Coon W. W., Turcotte J. G., Child C. G., 3rd Alterations in plasma-free amino acids in dogs with hepatic insufficiency. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970 May;130(5):794–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel Y., Salazar I., Rosenmann E. Inhibitory effects of alcohol on intestinal amino acid transport in vivo and in vitro. J Nutr. 1968 Dec;96(4):499–504. doi: 10.1093/jn/96.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel Y., Valenzuela J. E., Salazar I., Ugarte G. Alcohol and amino acid transport in the human small intestine. J Nutr. 1969 Jun;98(2):222–224. doi: 10.1093/jn/98.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y., Sato H., Ohkubo A., Sanjo T., Futagawa S., Sugiura M., Tsuji S. Effect of spontaneous portal-systemic shunting on plasma insulin and amino acid concentrations. Gastroenterology. 1980 Apr;78(4):677–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNAUFF H. G., SELMAIR H., REITLINGER A. [Studies on free amino acids in urine and blood plasma of healthy and liver patients]. Klin Wochenschr. 1960 Aug 15;38:812–819. doi: 10.1007/BF01487758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNAUFF H. G., SEYBOLD D., MILLER B. DIE FREIEN PLASMAAMINOSAEUREN BEI LEBERCIRRHOSE UND HEPATITIS. Klin Wochenschr. 1964 Apr 1;42:326–332. doi: 10.1007/BF01483834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsell L. W., Harper H. A., Barton H. C., Hutchin M. E., Hess J. R. STUDIES IN METHIONINE AND SULFUR METABOLISM. I. THE FATE OF INTRAVENOUSLY ADMINISTERED METHIONINE, IN NORMAL INDIVIDUALS AND IN PATIENTS WITH LIVER DAMAGE. J Clin Invest. 1948 Sep;27(5):677–688. doi: 10.1172/JCI102016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffert H., Alexander N. M., Faloona G., Rubalcava B., Unger R. Specific endocrine and hormonal receptor changes associated with liver regeneration in adult rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. J., Conn H. O. Tyrosine metabolism in patients with liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):2012–2020. doi: 10.1172/JCI105690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEHTA S., WALIA B. N., GHAI O. P., TANEJA P. N. A QUALITATIVE STUDY OF PLASMA AND URINARY AMINOACIDS IN INDIAN CHILDHOOD CIRRHOSIS. Indian J Pediatr. 1964 Jun;31:187–190. doi: 10.1007/BF02803818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELLINKOFF S. M., BOYLE D., FRANKLAND M. The effect of amino acid-glucose infusions upon the serum amino acid and blood sugar concentrations in viral hepatitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Oct;46(4):560–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesini G., Forlani G., Zoli M., Angiolini A., Scolari M. P., Bianchi F. B., Pisi E. Insulin and glucagon levels in liver cirrhosis. Relationship with plasma amino acid imbalance of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Aug;24(8):594–601. doi: 10.1007/BF01333703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata J. M., Kershenobich D., Villarreal E., Rojkind M. Serum free proline and free hydroxyproline in patients with chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1975 May;68(5 Pt 1):1265–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMenamy R. H., Vang J., Drapanas T. Amino acid and alpha-keto acid concentrations in plasma and blood of the liverless dog. Am J Physiol. 1965 Nov;209(5):1046–1052. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.5.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milsom J. P., Morgan M. Y., Sherlock S. Factors affecting plasma amino acid concentrations in control subjects. Metabolism. 1979 Apr;28(4):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro H. N., Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Insulin, plasma aminoacid imbalance, and hepatic coma. Lancet. 1975 Mar 29;1(7909):722–724. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91632-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ning M., Lowenstein L. M., Davidson C. S. Serum amino acid concentrations in alcoholic hepatitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Oct;70(4):554–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda C., Ichihara A. Control of ketogenesis from amino acids. II. Ketone bodies formation from alpha-ketoisocaproate, the keto-analogue of leucine, by rat liver mitochondria. J Biochem. 1974 Nov;76(5):1123–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odessey R., Goldberg A. L. Oxidation of leucine by rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1972 Dec;223(6):1376–1383. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.6.1376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAIN S. K., BANERJEE S. Studies on the nitrogenous constituents of urine in normal subjects and in patients suffering from cirrhosis of liver, subacute nephritis and hypertension. Indian J Med Res. 1957 Jan;45(1):35–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAYET M., CESAIRE O. G., CAMAINGIABICANI R. Renseignements donnés par l'exploration chromatographique des acides aminés libres du sérum dans les cirrhoses et le cancer primitif du foie. Strasb Med. 1958 Apr;9(4):295–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record C. O., Buxton B., Chase R. A., Curzon G., Murray-Lyon I. M., Williams R. Plasma and brain amino acids in fulminant hepatic failure and their relationship to hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep 10;6(5):387–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1976.tb00533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H. M., Yoshimura N., Hodgman J. M., Fischer J. E. Plasma amino acid patterns in hepatic encephalopathy of differing etiology. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):483–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford W. H. Sequelae of concussion caused by minor head injuries. Lancet. 1977 Jan 1;1(8001):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91649-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL F. L., ROACH M. K., POMEROY L. R. PLASMA AMINO ACID PATTERNS IN ALCOHOLISM: THE EFFECTS OF ETHANOL LOADING. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:605–611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S. J., Truswell A. S., Barbezat G. O., Wittman W., Hansen J. D. Plasma free aminoacid pattern in protein-calorie malnutrition. Reappraisal of its diagnostic value. Lancet. 1967 Oct 14;2(7520):795–797. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamoon H., Jacob R., Sherwin R. S. Epinephrine-induced hypoaminoacidemia in normal and diabetic human subjects: effect of beta blockade. Diabetes. 1980 Nov;29(11):875–881. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.11.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R., Joshi P., Hendler R., Felig P., Conn H. O. Hyperglucagonemia in Laennec's cirrhosis. The role of portal-systemic shunting. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 31;290(5):239–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401312900502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Laing G., Sherlock S., Faber O. K. Effects of spontaneous portal-systemic shunting on insulin metabolism. Gastroenterology. 1979 Apr;76(4):685–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Young A. B., Bennett J. P., Mulder A. H. Synaptic biochemistry of amino acids. Fed Proc. 1973 Oct;32(10):2039–2047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSHE J. M. Disturbances of aminoacid metabolism following liver injury; a study by means of paper chromatography. Q J Med. 1953 Oct;22(88):483–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU C., BOLLMAN J. L., BUTT H. R. Changes in free amino acids in the plasma during hepatic coma. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):845–849. doi: 10.1172/JCI103139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YI-YUNG HSIA D., GELLIS S. S. Amino acid metabolism in infectious hepatitis. J Clin Invest. 1954 Dec;33(12):1603–1610. doi: 10.1172/JCI103040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinneman H. H., Seal U. S., Doe R. P. Plasma and urinary amino acids in Laennec's cirrhosis. Am J Dig Dis. 1969 Feb;14(2):118–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02232835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


