Abstract
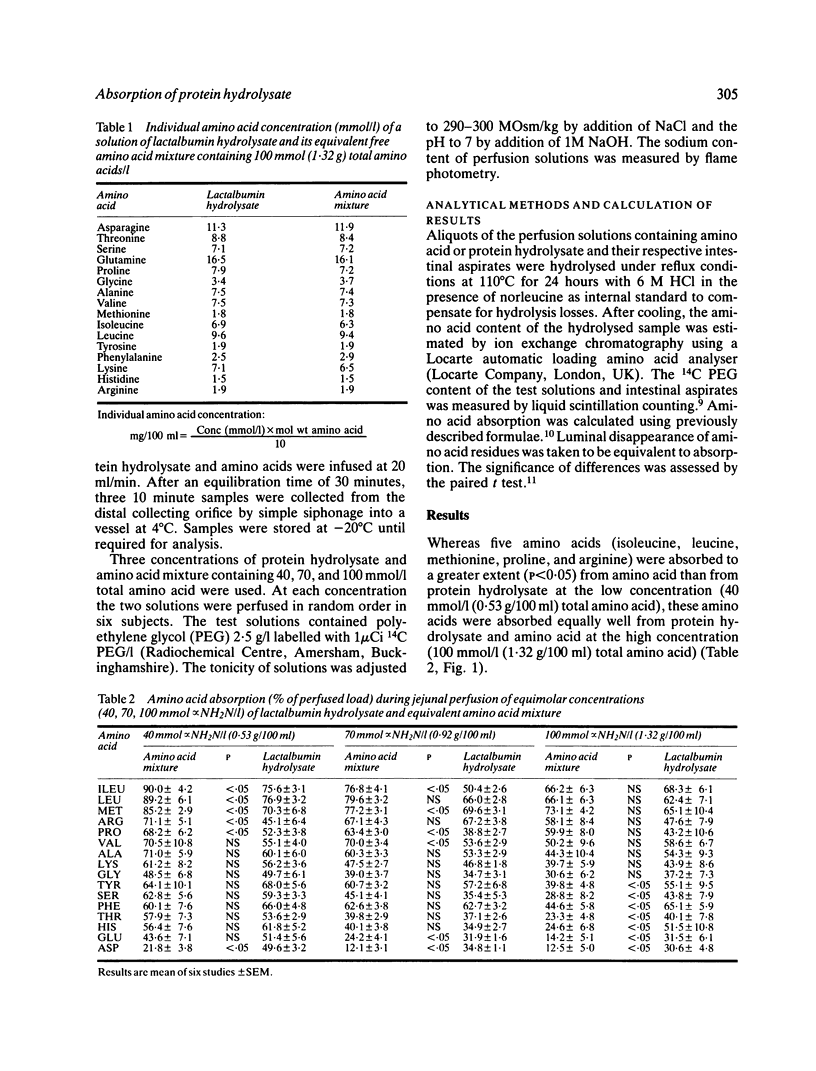
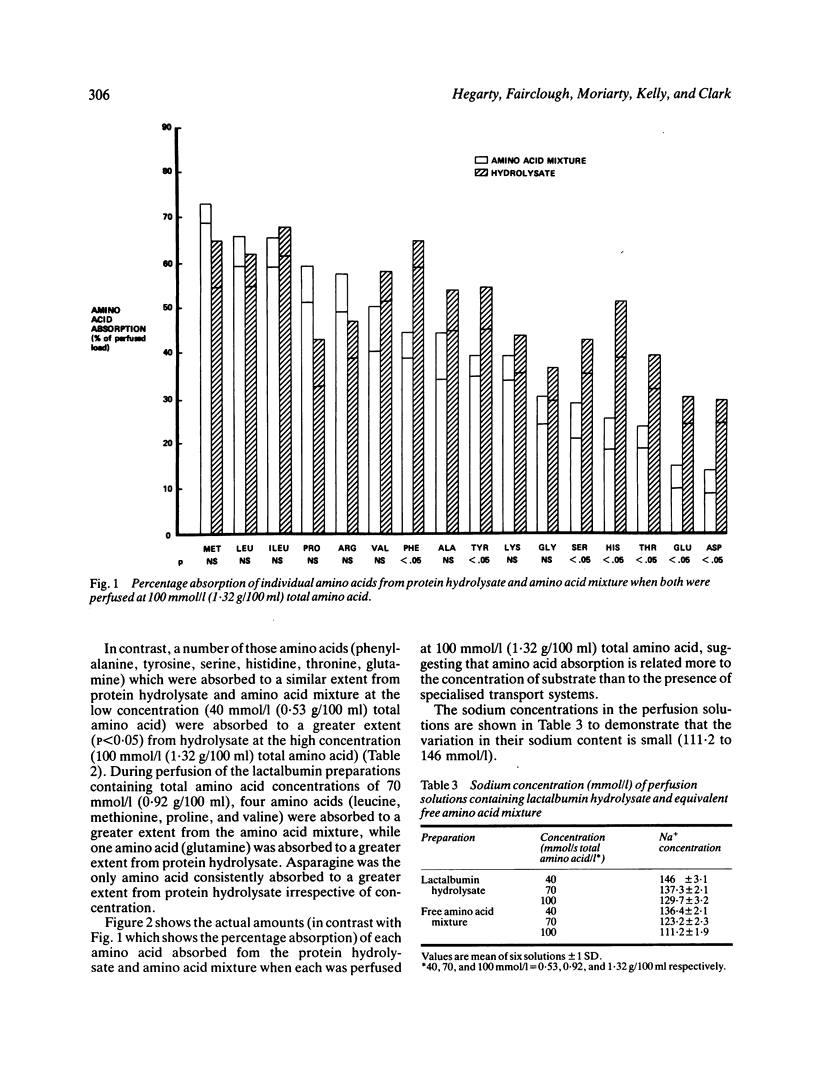
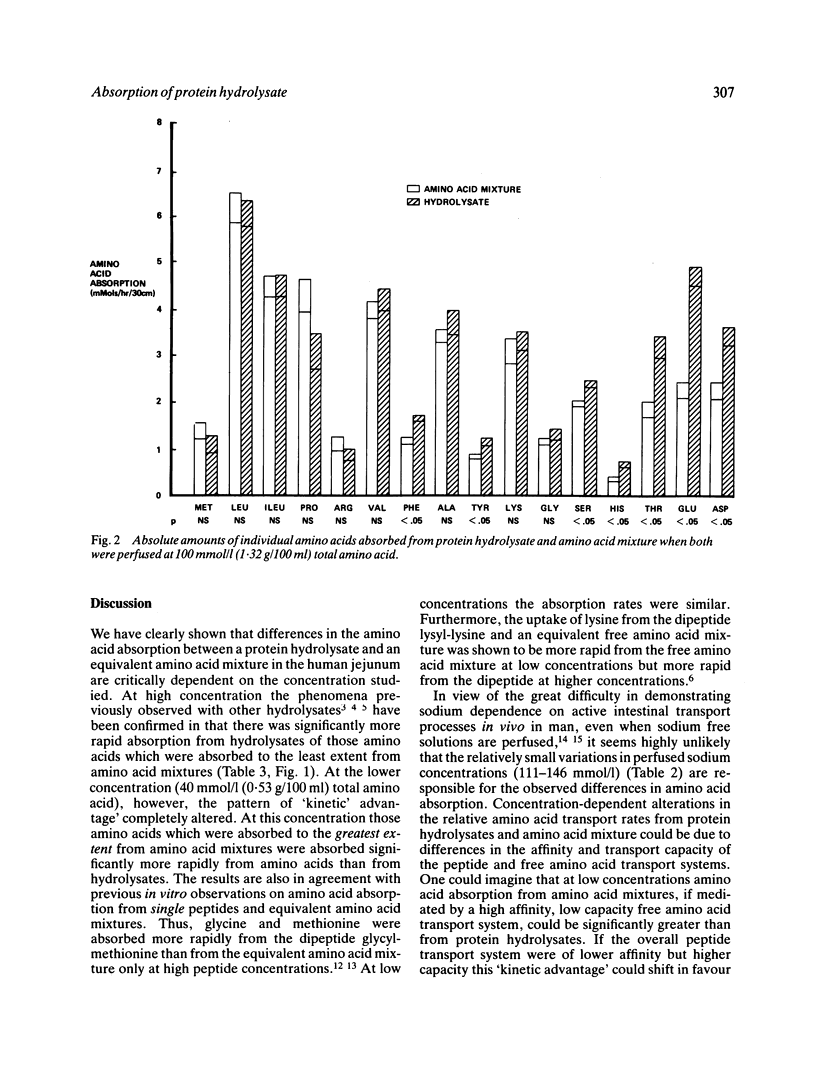
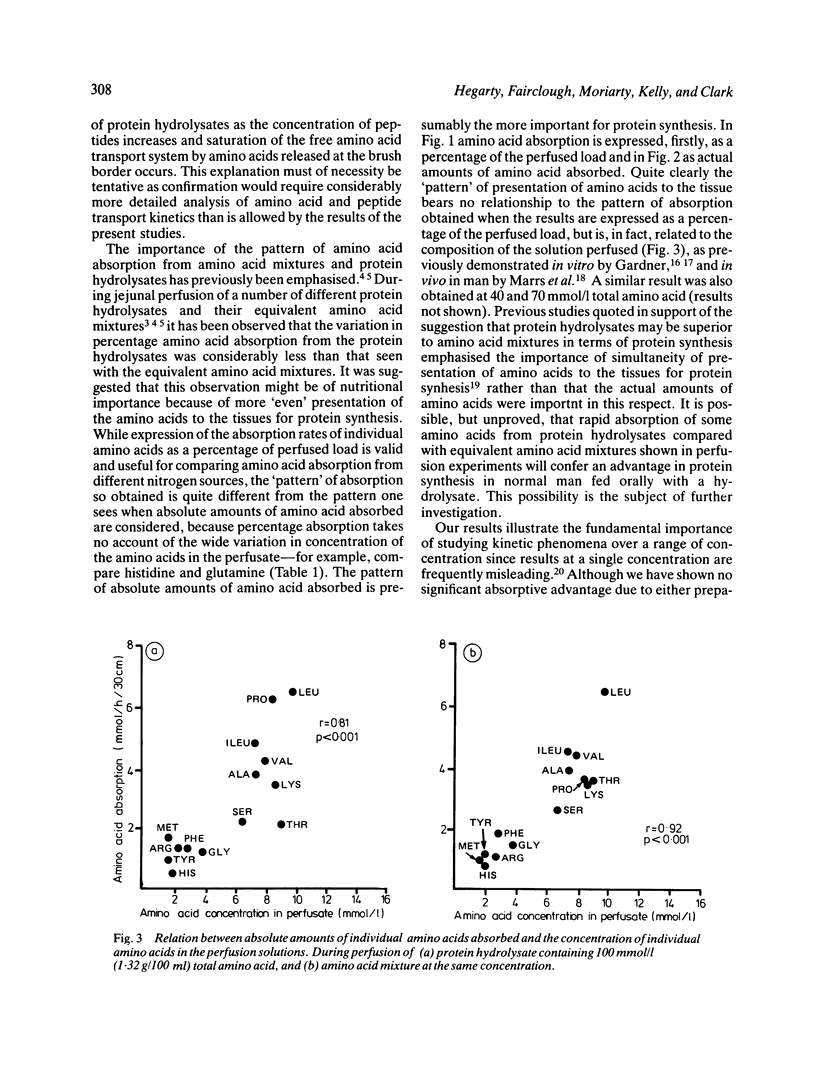
Amino acid absorption from a peptide-containing protein hydrolysate and an equivalent amino acid mixture over a range of concentrations of the two--such as is thought to be found in the normal intestine after a meal--has been studied using a jejunal perfusion technique in man. The relative rates of amino acid absorption from the protein hydrolysate and amino acid mixture varied markedly with concentration, demonstrating that the global hypothesis that peptides confer an advantage in amino acid absorption in vivo is too simple. There is a highly significant correlation between amino acid absorption and the concentrations of amino acid in the perfusate, whether this contained amino acid or protein hydrolysate, suggesting that, under these experimental conditions at least, the presence of distinct amino acid and peptide transport systems is relatively unimportant. Doubt is thus cast upon suggestions derived from previous intestinal perfusion experiments that intact peptide transport may be nutritionally significant in man.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adibi S. A. Leucine absorption rate and net movements of sodium and water in human jejunum. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Jun;28(6):753–757. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adibi S. A., Mercer D. W. Protein digestion in human intestine as reflected in luminal, mucosal, and plasma amino acid concentrations after meals. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1586–1594. doi: 10.1172/JCI107335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burston D., Taylor E., Matthews D. M. Kinetics of uptake of lysine and lysyl-lysine by hamster jejunum in vitro. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Oct;59(4):285–287. doi: 10.1042/cs0590285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairclough P. D., Hegarty J. E., Silk D. B., Clark M. L. Comparison of the absorption of two protein hydrolysates and their effects on water and electrolyte movements in the human jejunum. Gut. 1980 Oct;21(10):829–834. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.10.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. L. Absorption from a mixture of seventeen free amino acids by the isolated small intestine of the rat. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(2):563–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. L. Absorption of amino acids and peptides from a complex mixture in the isolated small intestine of the rat. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(1):233–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs T. C., Addison J. M., Burston D., Matthews D. M. Changes in plasma amino acid concentrations in man after ingestion of an amino acid mixture simulating casein, and a tryptic hydrolysate of casein. Br J Nutr. 1975 Sep;34(2):259–265. doi: 10.1017/s000711457500030x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. M., Craft I. L., Geddes D. M., Wise I. J., Hyde C. W. Absorption of glycine and glycine peptides from the small intestine of the rat. Clin Sci. 1968 Dec;35(3):415–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. M. Intestinal absorption of peptides. Physiol Rev. 1975 Oct;55(4):537–608. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1975.55.4.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. M., Lis M. T., Cheng B., Crampton R. F. Observations on the intestinal absorption of some oligopeptides of methionine and glycine in the rat. Clin Sci. 1969 Dec;37(3):751–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen W. A., Ingelfinger F. J. The role of sodium in intestinal glucose absorption in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1133–1142. doi: 10.1172/JCI105802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk D. B., Clark M. L., Marrs T. C., Addison J. M., Burston D., Matthews D. M., Clegg K. M. Jejunal absorption of an amino acid mixture simulating casein and an enzymic hydrolysate of casein prepared for oral administration to normal adults. Br J Nutr. 1975 Jan;33(1):95–100. doi: 10.1079/bjn19750012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk D. B., Fairclough P. D., Park N. J., Lane A. E., Webb J. P., Clark M. L., Dawson A. M. A study of relations between the absorption of amino acids, dipeptides, water and electrolytes in the normal human jejunum. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Nov;49(5):401–408. doi: 10.1042/cs0490401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk D. B., Marrs T. C., Addison J. M., Burston D., Clark M. L., Matthews D. M. Absorption of amino acids from an amino acid mixture simulating casein and a tryptic hydrolysate of casein in man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Nov;45(5):715–719. doi: 10.1042/cs0450715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Dawson A. M. Further studies on the perfusion method for measuring intestinal absorption in man: the effects of a proximal occlusive balloon and a mixing segment. Gut. 1970 Nov;11(11):947–954. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.11.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Dawson A. M. Interrelationships between the absorptions of glucose, sodium and water by the normal human jejunum. Clin Sci. 1969 Feb;36(1):119–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Sandberg R. J., Phillips S. F. A comparison of stable and 14 C-labelled polyethylene glycol as volume indicators in the human jejunum. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):812–815. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.10.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


