Abstract
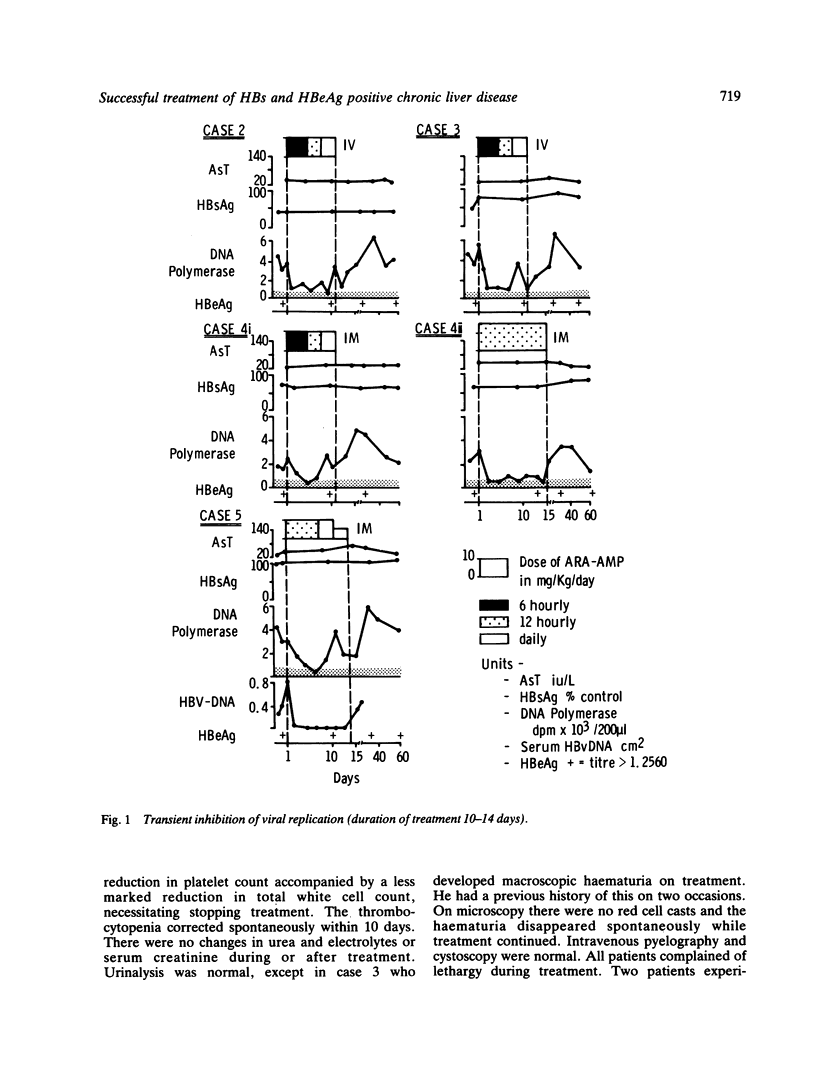
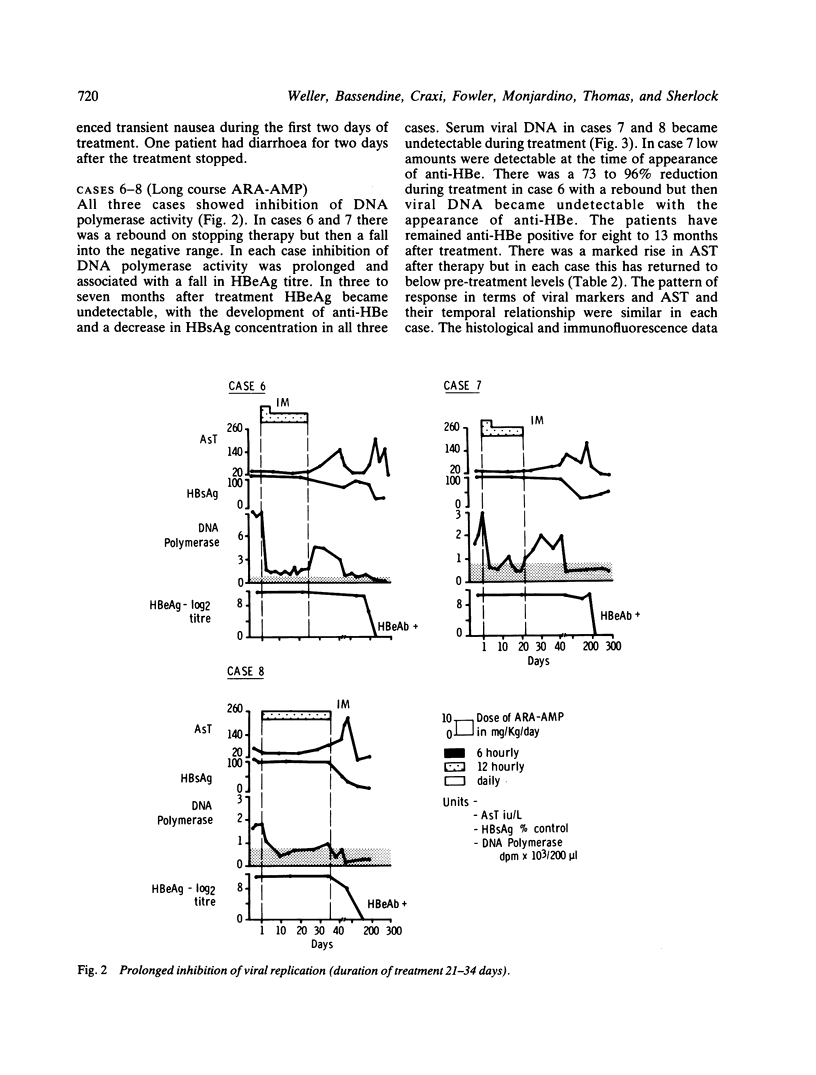
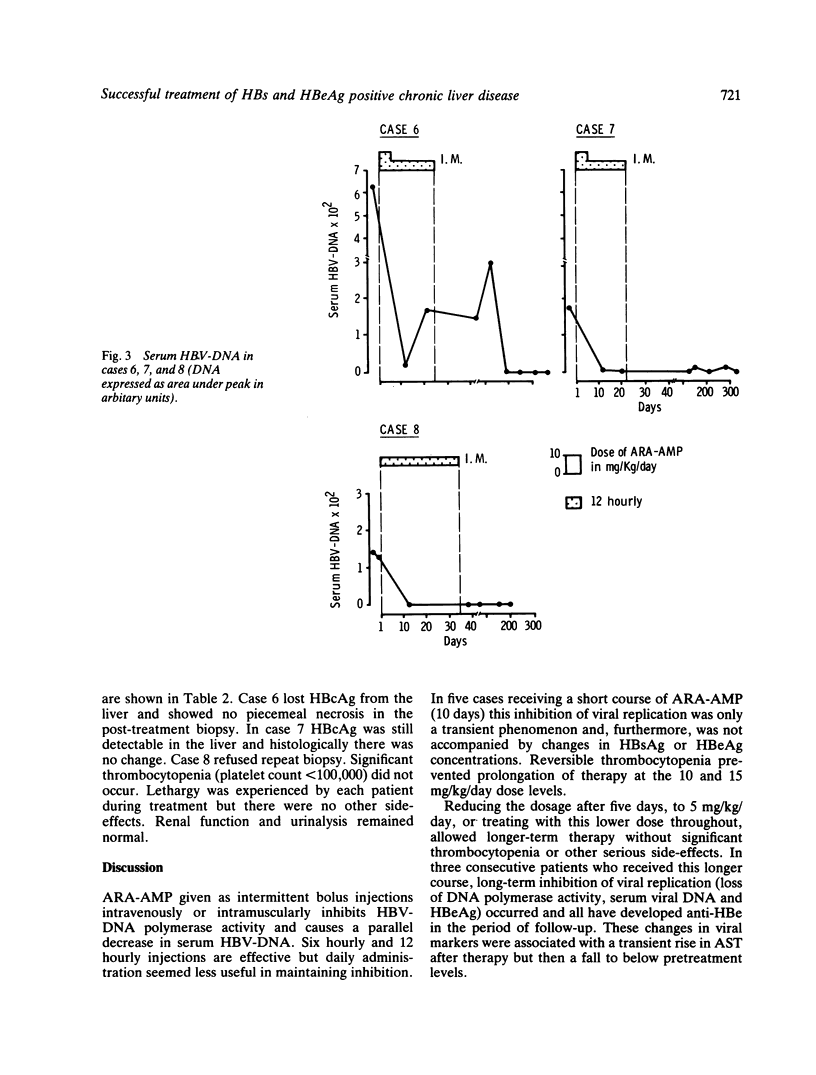
In eight HBs and HBe antigen positive patients with chronic active liver disease, adenine arabinoside 5'-monophosphate (ARA-AMP) given, intravenously or intramuscularly, six or 12 hours, produced inhibition of viral replication. In five patients given a short course of therapy with 10 or 15 mg/kg/day this effect was transient and in two thrombocytopenia occurred. In three further consecutive cases given a longer course with 5 mg/kg/day after five days of the high dose, thrombocytopenia was not seen and inhibition of viral replication for up to 13 months occurred. These patients lost HBV-DNA polymerase activity, serum viral DNA and HBeAg, developed anti-HBe, and HBsAg concentrations decreased. A course of twice daily intramuscular ARA-AMP given for three to five weeks as an outpatient may be expected to produce a long-term reduction in infectivity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Seeff L. B., Kaplan P. M., McAuliffe V. J., Wright E. C., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Holland P. V., Zimmerman H. J. Type B hepatitis: the infectivity of blood positive for e antigen and DNA polymerase after accidental needlestick exposure. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 21;295(17):909–913. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610212951701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassendine M. F., Chadwick R. G., Salmeron J., Shipton U., Thomas H. C., Sherlock S. Adenine arabinoside therapy in HBsAg-positive chronic liver disease: a controlled study. Gastroenterology. 1981 May;80(5 Pt 1):1016–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick R. G., Bassendine M. F., Crawford E. M., Thomas H. C., Sherlock S. HBsAg-positive chronic liver disease: inhibition of DNA polymerase activity by vidarabine. Br Med J. 1978 Aug 19;2(6136):531–533. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6136.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard R. B., Smith J. L., Neal A., Gregory P. B., Merigan T. C., Robinson W. S. Effect of vidarabine on chronic hepatitis B virus infection. JAMA. 1978 Apr 21;239(16):1648–1650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Realdi G., Alberti A., Rugge M., Bortolotti F., Rigoli A. M., Tremolada F., Ruol A. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to anti-HBe in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzetto M., Shih J. W., Verme G., Gerin J. L. A radioimmunoassay for HBcAg in the sera of HBsAg carriers: serum HBcAg, liver HBcAg immunofluorescence as markers of chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jun;80(6):1420–1427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. DNA and DNA polymerase in the core of the Dane particle of hepatitis B. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jul-Aug;270(1):151–159. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197507000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scullard G. H., Andres L. L., Greenberg H. B., Smith J. L., Sawhney V. K., Neal E. A., Mahal A. S., Popper H., Merigan T. C., Robinson W. S. Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: improvement in liver disease with interferon and adenine arabinoside. Hepatology. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):228–232. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viola L. A., Barrison I. G., Coleman J. C., Paradinas F. J., Fluker J. L., Evans B. A., Murray-Lyon I. M. Natural history of liver disease in chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carriers. Survey of 100 patients from Great Britain. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1156–1159. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90600-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


