Abstract
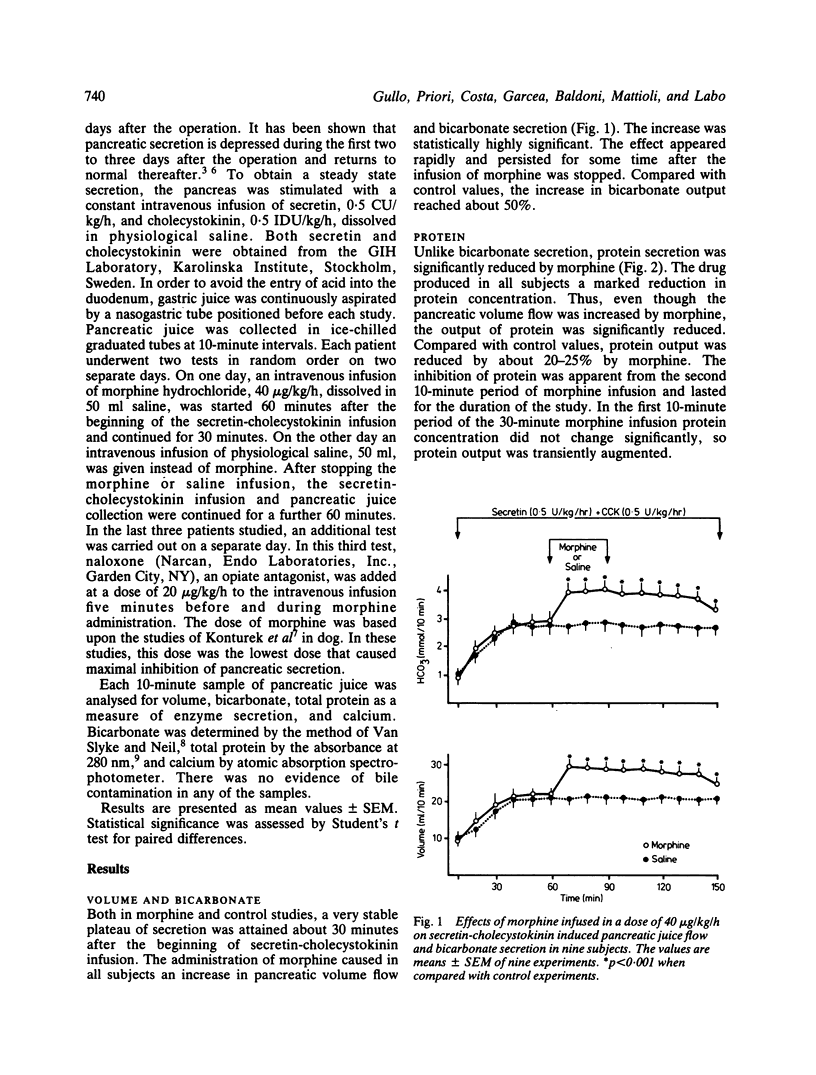
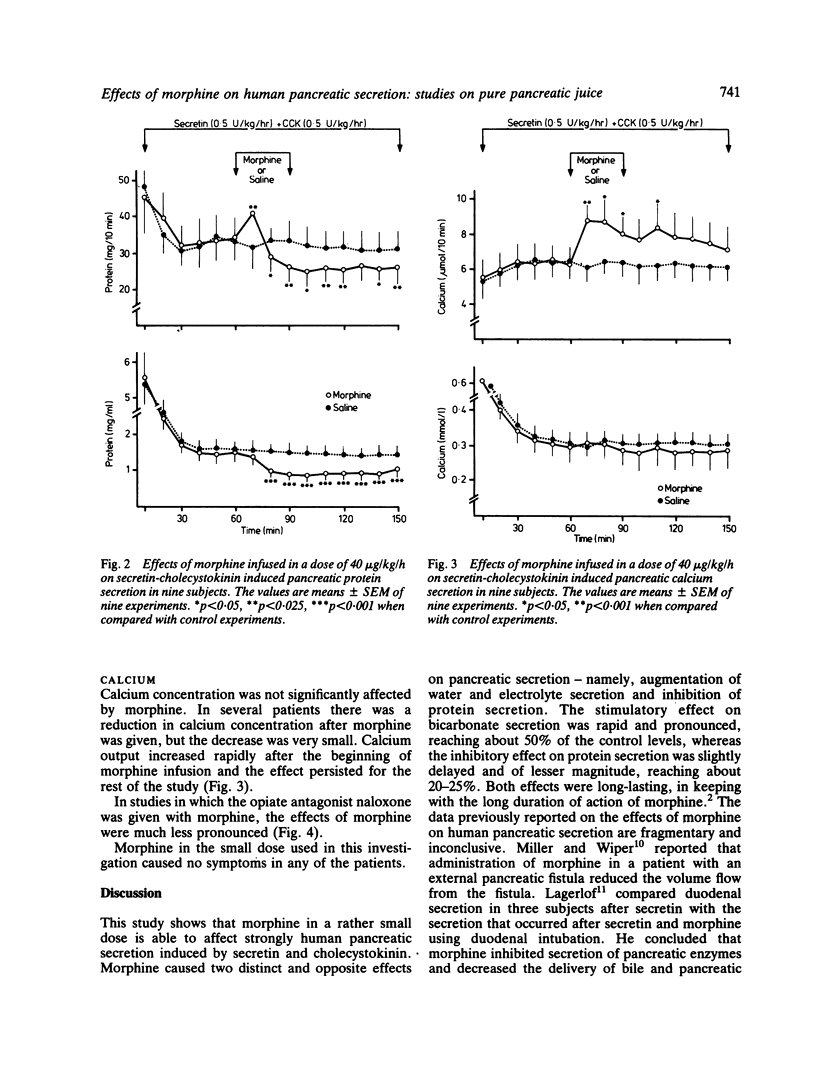
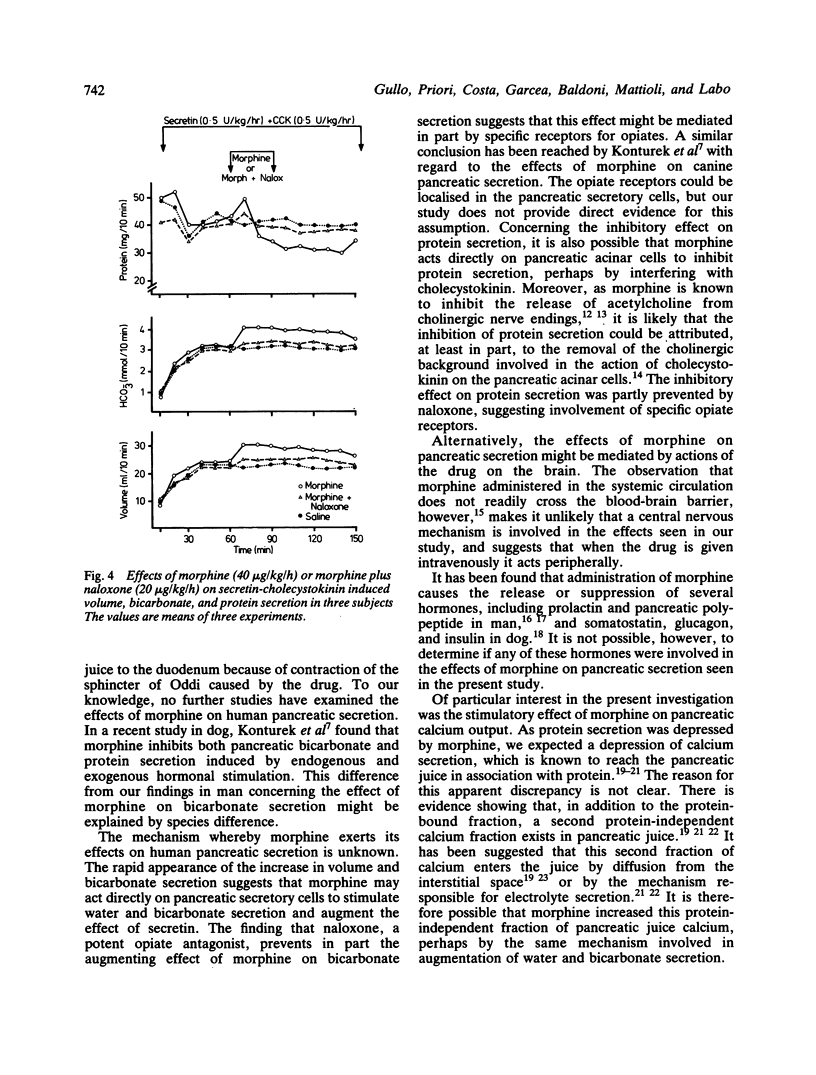
Data concerning the effects of morphine on human pancreatic secretion are fragmentary and inconclusive. In the present study, we evaluated the effects of morphine on pure pancreatic secretion in nine subjects with external transduodenal drainage of the main pancreatic duct performed after biliary tract surgery. Intravenous infusion of a small dose of morphine, 40 microgram/kg/h, during pancreatic stimulation with secretin and cholecystokinin, caused a significant increase in volume, bicarbonate, and calcium secretion, and a significant decrease in protein secretion. The stimulatory effect on water and electrolyte secretion was rapid and much more pronounced, reaching about 45-50% of the control levels, whereas the inhibition of protein output was slightly delayed and of lesser magnitude, reaching about 20-25% of the control values. Both effects were long-lasting. The addition of naloxone, potent opiate antagonist, prevented in part the effects of morphine on pancreatic secretion, suggesting that specific opiate receptors might be involved in these effects.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argent B. E., Case R. M., Scratcherd T. Amylase secretion by the perfused cat pancreas in relation to the secretion of calcium and other electrolytes and as influenced by the external ionic environment. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):575–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M. Calcium and gastrointestinal secretion. Digestion. 1973;8(3):269–288. doi: 10.1159/000197324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Clemente F., Meldolesi J. Secretion of calcium in pancreatic juice. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):617–638. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman M., Walsh J. H., Taylor I. L. Effect of naloxone and morphine on gastric acid secretion and on serum gastrin and pancreatic polypeptide concentrations in humans. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):294–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figarella C., Ribeiro T. The assay of human pancreatic phospholipase A in pancreatic juice and duodenal contents. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1971;6(2):133–137. doi: 10.3109/00365527109180682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebell H., Steffen C., Bode C. Stimulatory effect of pancreozymin-cholecystokinin on calcium secretion in pancreatic juice of dogs. Gut. 1972 Jun;13(6):477–482. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.6.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullo L., Costa P. L., Fontana G., Tessari R., Serra D., Labò G. Effect of adrenocorticotropic hormone on pure exocrine pancreatic secretion in man. Gastroenterology. 1977 Oct;73(4 Pt 1):762–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullo L., Costa P. L., Tessari R., Fontana G. Cortisol and pancreatic secretion. Observations on pure pancreatic juice. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1980;15(1):45–47. doi: 10.3109/00365528009181430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipp E., Dobbs R., Unger R. H. Morphine and beta-endorphin influence the secretion of the endocrine pancreas. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):190–191. doi: 10.1038/276190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhamandas K., Pinsky C., Phillis J. W. Effects of morphine and its antagonists on release of cerebral cortical acetylcholine. Nature. 1970 Oct 10;228(5267):176–177. doi: 10.1038/228176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Tasler J., Cieszkowski M., Jaworek J., Coy D. H., Schally A. V. Inhibition of pancreatic secretion by enkephalin and morphine in dogs. Gastroenterology. 1978 May;74(5 Pt 1):851–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhlouf G. M., Blum A. L. An assessment of models for pancreatic secretion. Gastroenterology. 1970 Dec;59(6):896–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Wiper T. B. Physiologic Observations on Patients With External Pancreatic Fistula. Ann Surg. 1944 Dec;120(6):852–872. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194412000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H., Hyman S., Braun L., Oldendorf S. Z. Blood-brain barrier: penetration of morphine, codeine, heroin, and methadone after carotid injection. Science. 1972 Dec 1;178(4064):984–986. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4064.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Sullivan S. N., Facer P., Pearse A. G. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the human gastrointestinal tract. Lancet. 1977 May 7;1(8019):972–974. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M., Webster P. D. Neurohormonal control of pancreatic secretion. A review. Gastroenterology. 1978 Feb;74(2 Pt 1):294–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolis G., Hickey J., Guyda H. Effects of morphine on serum growth hormone, cortisol, prolactin and thyroid stimulating hormone in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Oct;41(4):797–800. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-4-797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tournut R., White T. T. Water, electrolyte, and protein secretions of the human exocrine pancreas in the early postoperative period. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1972 Jul;135(1):17–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


