Abstract
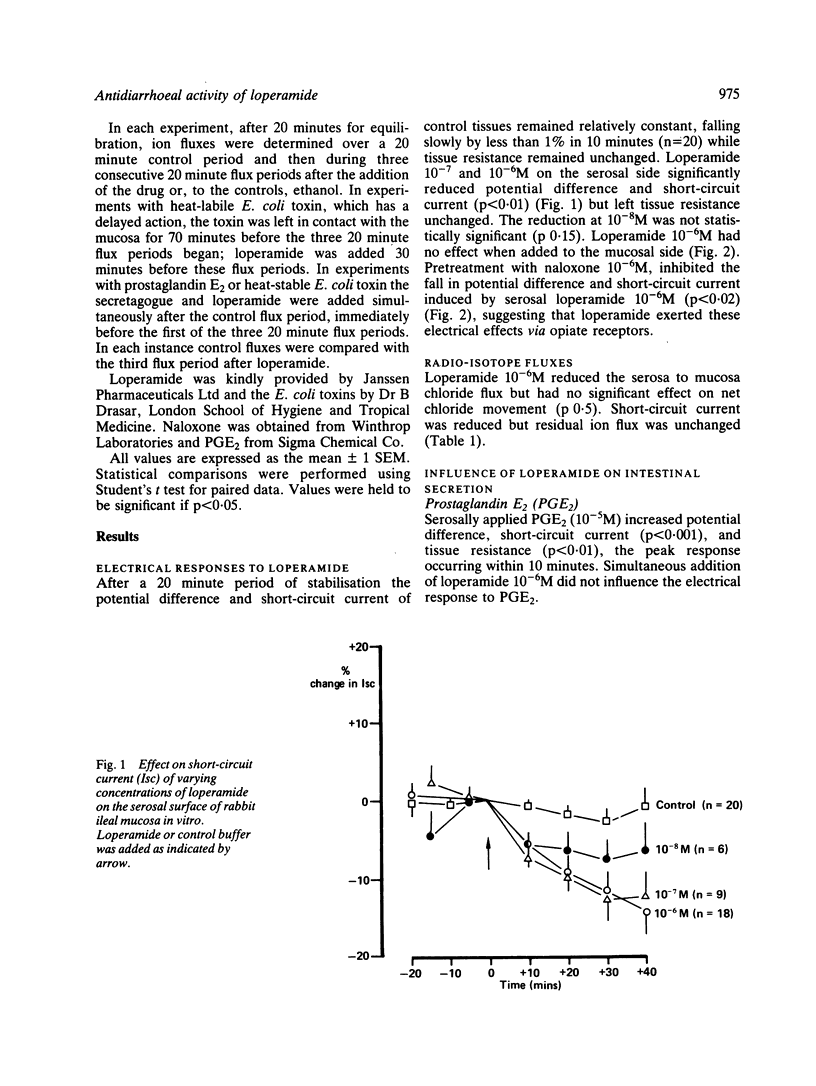
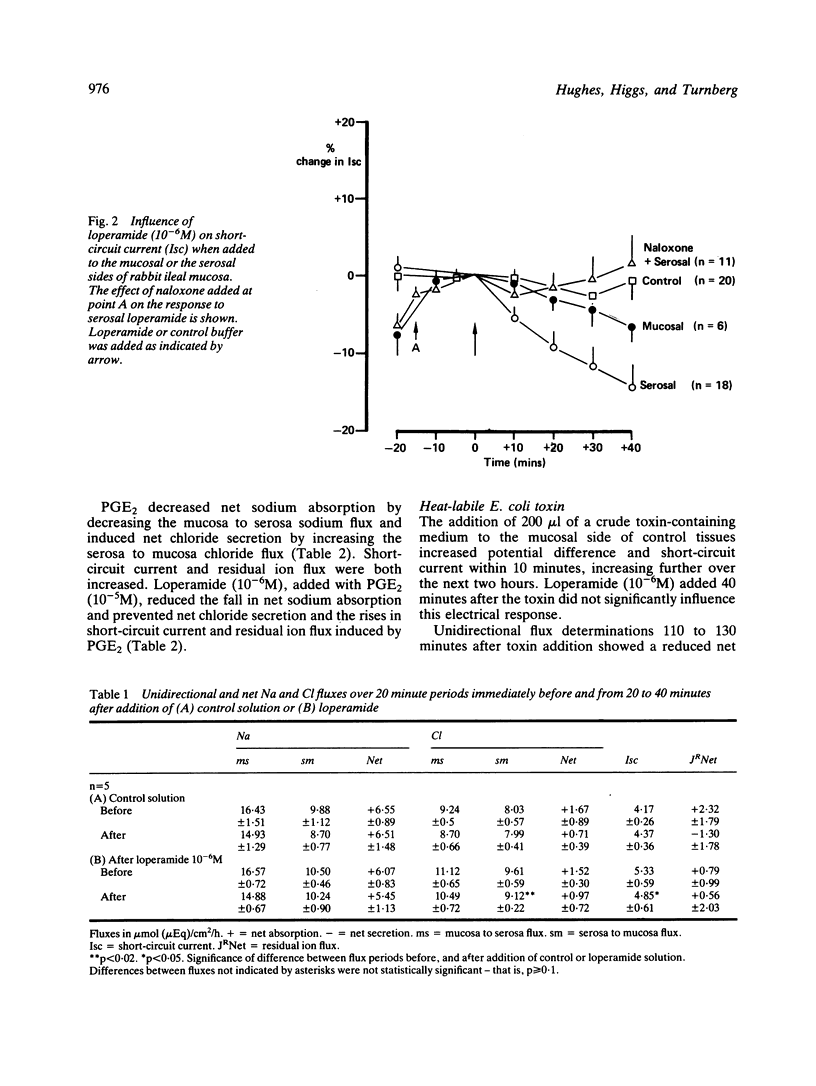
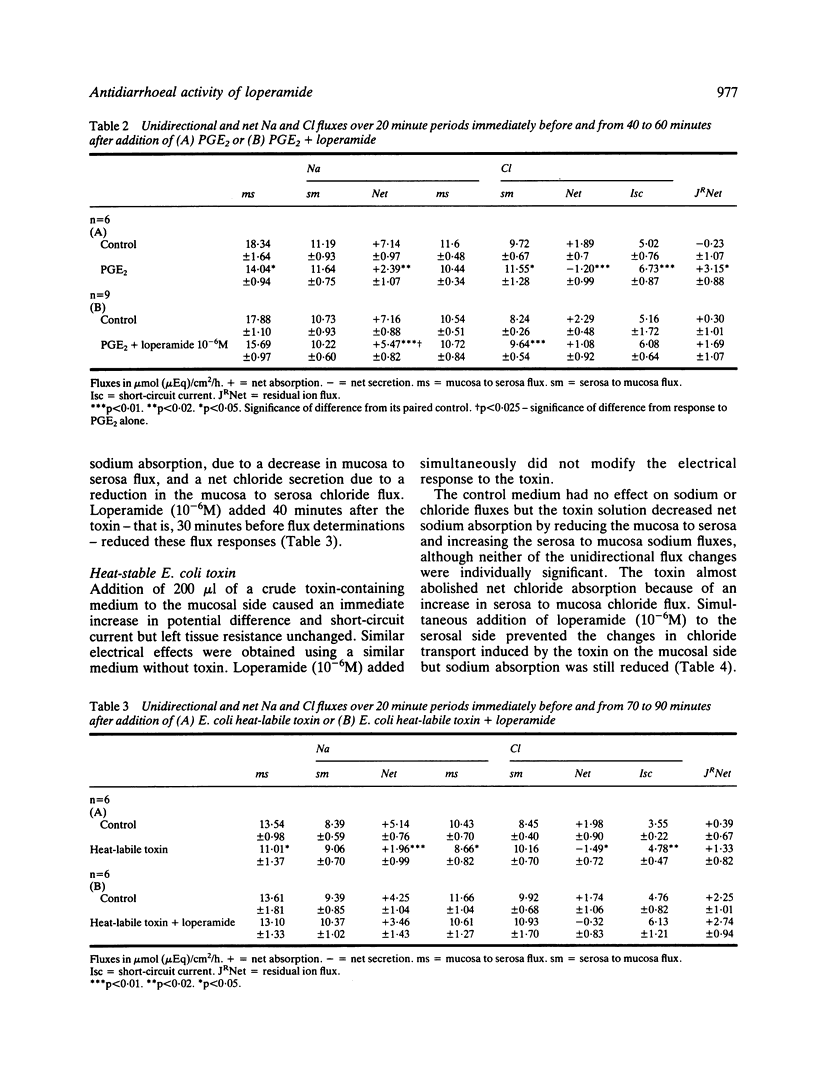
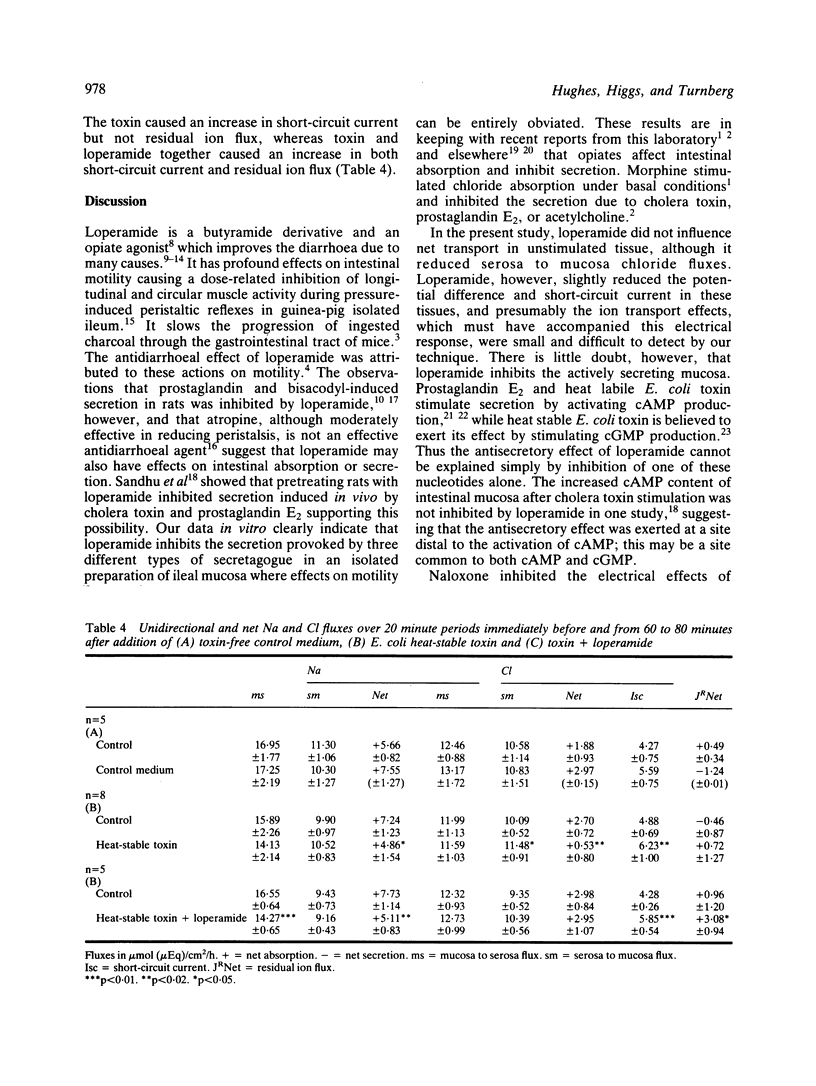
Loperamide is a well-established antidiarrhoeal agent with effects on gastrointestinal motility. We have now shown that the drug influences ion transport. In isolated rabbit ileal mucosa loperamide caused a dose-related fall in potential difference and short-circuit current and reduced the serosa to mucosa flux of chloride. The electrical effects were inhibited by naloxone (10(-6)M) suggesting that they were mediated by opiate receptors. Loperamide (10(-6)M) inhibited secretion provoked by heat stable and heat labile E. coli toxins and by prostaglandin E2. We conclude that loperamide is able to inhibit secretion mediated by cAMP or cGNP, and that this may be relevant to its antidiarrhoeal properties.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awouters F., Niemegeers C. J., Kuyps J., Janssen P. A. Loperamide antagonism of castor oil-induced diarrhea in rats: a quantitative study. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1975 Sep;217(1):29–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beubler E., Lembeck F. Inhibition of stimulated fluid secretion in the rat small and large intestine by opiate agonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;306(2):113–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00498980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins J., Racusen L., Binder H. J. Effect of D-alanine methionine enkephalin amide on ion transport in rabbit ileum. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):19–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI109830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., McColl I. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. I. Na and Cl fluxes and short-circuit current. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1388–1396. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galambos J. T., Hersh T., Schroder S., Wenger J. Loperamide: a new antidiarrheal agent in the treatment of chronic diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1026–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs P. E., Corbett C. L., Riley A. K., Hawker P. C., Turnberg L. A. In vitro behavior of human intestinal mucosa. The influence of acetyl choline on ion transport. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):535–542. doi: 10.1172/JCI108498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim S. M., Adaikan P. G. The effect of loperamide on prostaglandin induced diarrhoea in rat and man. Prostaglandins. 1977 Feb;13(2):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karle J. Triplet phase invariants: Formula for acentric case from fourth-order determinantal joint probability distributions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):5–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. Effect of antidiarrheal and antimotility drugs on ileal excreta. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Apr;22(4):327–332. doi: 10.1007/BF01072190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackerer C. R., Clay G. A., Dajani E. Z. Loperamide binding to opiate receptor sites of brain and myenteric plexus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Oct;199(1):131–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainguet P., Fiasse R. Double-blind placebo-controlled study of loperamide (Imodium) in chronic diarrhoea caused by ileocolic disease or resection. Gut. 1977 Jul;18(7):575–579. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.7.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay J. S., Linaker B. D., Higgs N. B., Turnberg L. A. Studies of the antisecretory activity of morphine in rabbit ileum in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1982 Feb;82(2):243–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay J. S., Linaker B. D., Turnberg L. A. Influence of opiates on ion transport across rabbit ileal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):279–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama S., Yamasato T., Mizutani M. [Effects of loperamide on the motility of the isolated intestine in guinea pigs, rats and dogs (author's transl)]. Nihon Heikatsukin Gakkai Zasshi. 1977 Jun;13(2):69–74. doi: 10.1540/jsmr1965.13.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemegeers C. J., Lenaerts F. M., Janssen P. A. Loperamide (R 18 553), a novel type of antidiarrheal agent. Part 1: in vivo oral pharmacology and acute toxicity. Comparison with morphine, codeine, diphenoxylate and difenoxine. Arzneimittelforschung. 1974 Oct;24(10):1633–1636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemegeers C. J., Lenaerts F. M., Janssen P. A. Loperamide (R 18 553), a novel type of antidiarrheal agent. Part 2: in vivo parenteral pharmacology and acute toxicity in mice. Comparison with morphine, codeine and diphenoxylate. Arzneimittelforschung. 1974 Oct;24(10):1636–1641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu B. K., Tripp J. H., Candy D. C., Harries J. T. Loperamide: studies on its mechanism of action. Gut. 1981 Aug;22(8):658–662. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.8.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat G. N., Huibregtse K. Loperamide and ileostomy output--placebo-controled double-blind crossover study. Br Med J. 1975 Jun 21;2(5972):667–667. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5972.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat G. N., Huibregtse K., Meuwissen S. G. Loperamide in chronic diarrhea and after ileostomy: a placebo-controlled double-blind cross-over study. Arch Chir Neerl. 1976;28(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nueten J. M., Janssen P. A., Fontaine J. Loperamide (R 18 553), a novel type of antidiarrheal agent. Part 3: in vitro studies on the peristaltic reflex and other experiments on isolated tissues. Arzneimittelforschung. 1974 Oct;24(10):1641–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


