Abstract
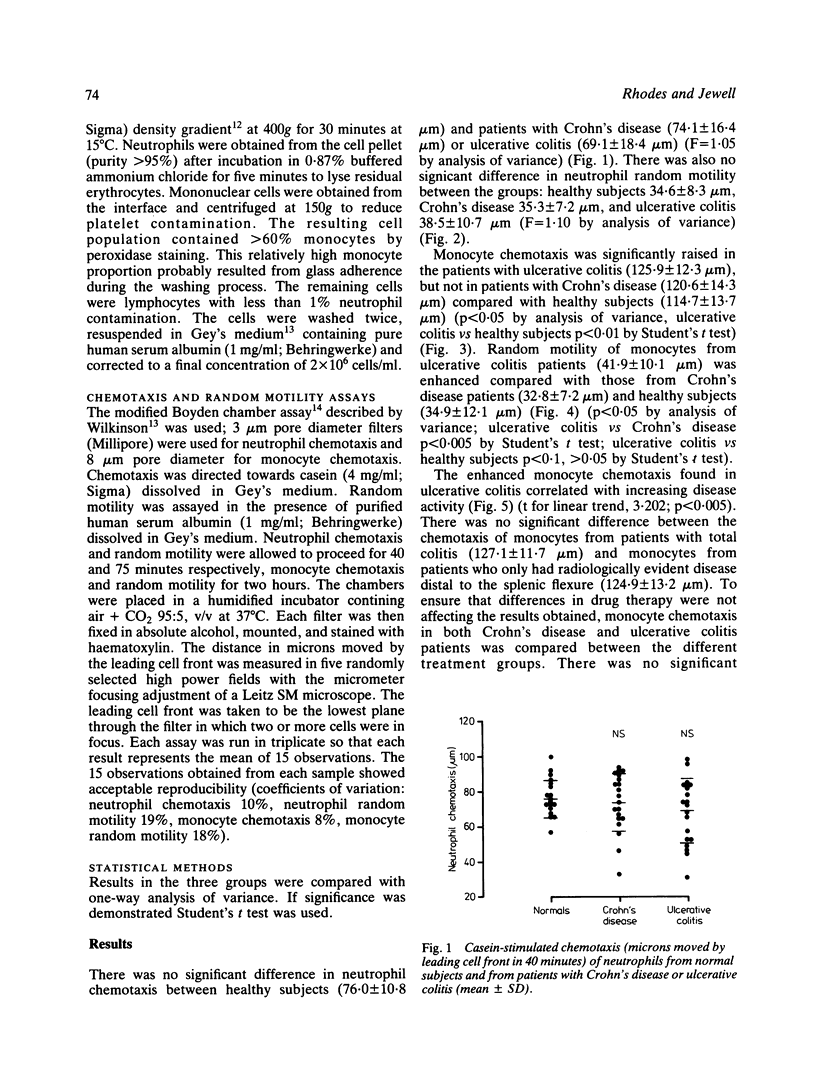
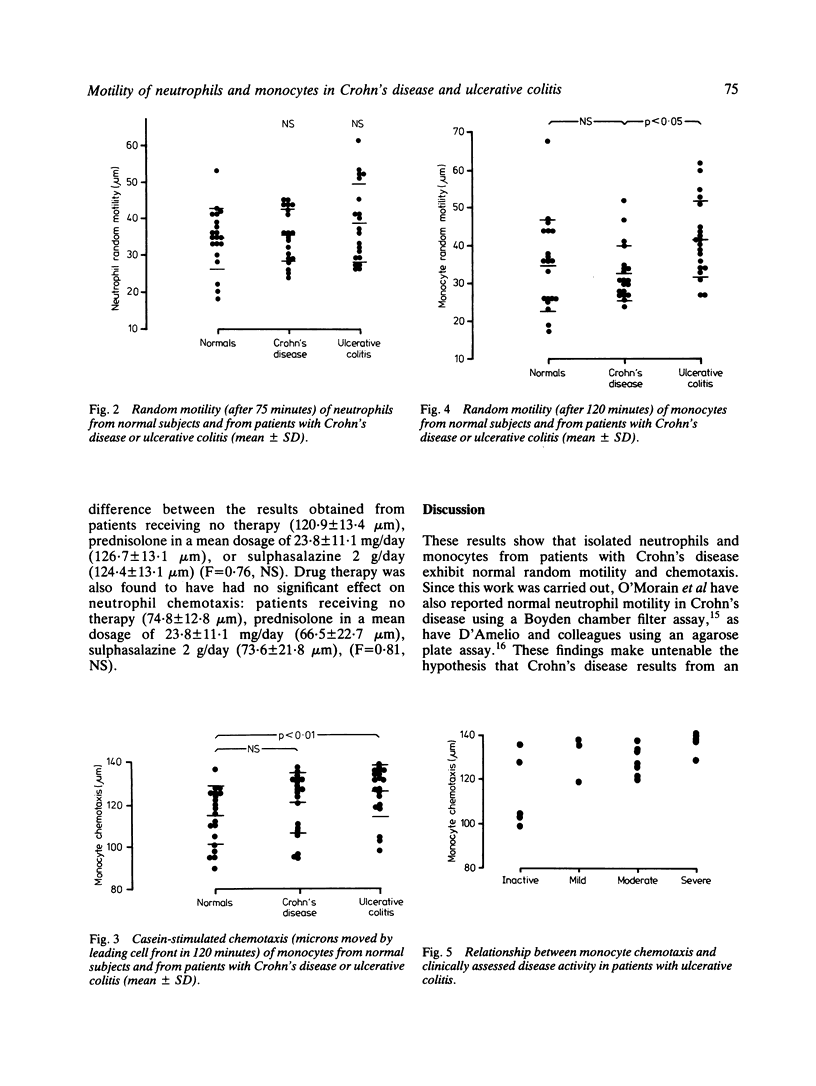
Random motility and chemotaxis of peripheral blood neutrophils and monocytes from patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis have been measured using a modified Boyden Chamber filter assay. Increased random motility and chemotaxis of monocytes were found in patients with active ulcerative colitis. Monocyte motility was normal in Crohn's disease and no abnormality of neutrophil motility or chemotaxis was found in either disease. Drug therapy with prednisolone or sulphasalazine received in vivo was found to have no effect on the motility of the washed neutrophils and monocytes in vitro. This work adds to the evidence that monocytes are activated in ulcerative colitis but does not support the hypothesis that Crohn's disease is due to an inherent defect in phagocyte motility.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder V., Riis P. The leucocyte chemotactic function in patients with ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(2):141–144. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199404000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. Further observations. Methylcellulose, dextran, and ficoll as erythrocyteaggregating agents. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:31–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Gallin J. I., Fauci A. S. Effects of in vivo prednisone on in vitro eosinophil and neutrophil adherence and chemotaxis. Blood. 1979 Apr;53(4):633–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amelio R., Rossi P., Le Moli S., Ricci R., Montano S., Pallone F. In vitro studies on cellular and humoral chemotaxis in Crohn's disease using the under agarose gel technique. Gut. 1981 Jul;22(7):566–570. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.7.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Dombal F. T., Burton I. L., Clamp S. E., Goligher J. C. Short-term course and prognosis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1974 Jun;15(6):435–443. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermanowicz A., Nawarska Z. Chemotaxis and random migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in ulcerative colitis examined by the agarose method. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1981;16(8):961–966. doi: 10.3109/00365528109181011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause U., Michaëlsson G., Juhlin L. Skin reactivity and phagocytic function of neutrophil leucocytes in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1978;13(1):71–75. doi: 10.3109/00365527809179808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee A. S., Jewell D. P. Monocytes in inflammatory bowel disease: monocyte and serum lysosomal enzyme activity. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Apr;58(4):295–300. doi: 10.1042/cs0580295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee A. S., Szawatakowski M., Jewell D. P. Monocytes in inflammatory bowel disease: phagocytosis and intracellular killing. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Oct;33(10):921–925. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.10.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuret G., Bitzi A., Hammer B. Macrophage turnover in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):501–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moráin C. O., Segal A. A., Walker D., Levi A. J. Abnormalities of neutrophil function do not cause the migration defect in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1981 Oct;22(10):817–822. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.10.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M., Ward M., Eastwood M. A., Harkness R. A. Letter: Neutrophil function and myeloperoxidase activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1976 Sep 11;2(7985):584–584. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91845-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. M., Bartholomew T. C., Jewell D. P. Inhibition of leucocyte motility by drugs used in ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1981 Aug;22(8):642–647. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.8.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. M., Potter B. J., Brown D. J., Jewell D. P. Serum inhibitors of leukocyte chemotaxis in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jun;82(6):1327–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Loewi G. Neutrophil dysfunction in Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1976 Jul 31;2(7979):219–221. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector W. G., Lykke A. W. The cellular evolution of inflammatory granulomata. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):163–167. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUELOVE S. C., WITTS L. J. Cortisone in ulcerative colitis; final report on a therapeutic trial. Br Med J. 1955 Oct 29;2(4947):1041–1048. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4947.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M., Eastwood M. A. The nitroblue tetrazolium test in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Digestion. 1976;14(2):179–183. doi: 10.1159/000197924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A. The chemosuppression of chemotaxis. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):209–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogman M. W., Touloukian R. J., Gallagher R. Letter: Intestinal granulomatosis in chronic granulomatous disease and in Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jan 24;290(4):228–228. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197401242900414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


