Abstract
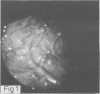
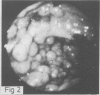
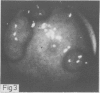
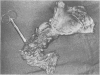
Upper gastrointestinal tract polyps were sought prospectively using endoscopy and biopsy in 34 patients with familial adenomatosis coli belonging to 18 unrelated families. Gastric and/or duodenal polyps, usually small and multiple, occurred in 28 patients (82%). Histologically verified extracolonic adenomas were present in 19 patients (56%). Gastric adenomas, all in the antrum, and duodenal adenomas occurred in four (12%) and 16 (48%) patients, respectively. In one patient, a duodenal adenocarcinoma and a bile duct adenoma were also found, and one patient had an adenocarcinoma of the bile ducts. Multiple non-neoplastic polyps were found in 19 patients (56%), most often in the stomach and also in the duodenum in 12 patients; they co-existed often with adenomas. In addition, there were nine patients with ileal polyps, most of them showing lymphoid hyperplasia but also one with adenomas. It is suggested that familial adenomatosis affects the whole gastrointestinal tract, not only the colon and rectum as believed earlier. Although upper gastrointestinal tract adenomas are not as consistent and multiple as those in the colon, and probably do not require prophylactic surgery, regular lifelong endoscopic follow up is warranted because of obviously increased cancer risk.
Full text
PDF


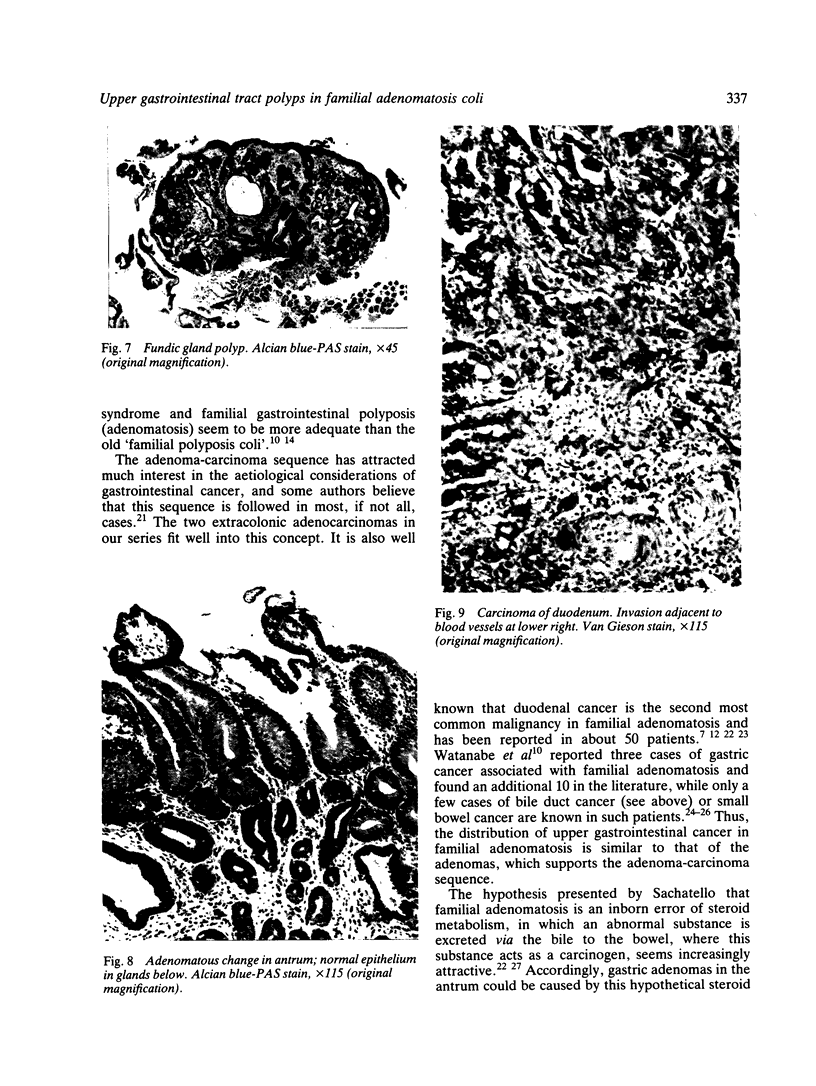


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burney B., Assor D. Polyposis coli with adenocarcinoma associated with carcinoma in situ of the gallbladder. Am J Surg. 1976 Jul;132(1):100–102. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H. J., Veale A. M., Morson B. C. Genetics of gastrointestinal polyposis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jun;74(6):1325–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B. R., Dohner V. A., Priest J. H. The Gardner syndrome: need for early diagnosis. J Pediatr. 1968 Apr;72(4):497–505. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALSTED J. A., HARRIS E. J., BARTLETT M. K. Involvement of the stomach in familial polyposis of the gastro-intestinal tract; report of a family. Gastroenterology. 1950 Aug;15(4):763–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEFFERNON E. W., METCALFE O., SCHWARZ H. J., Jr Polyposis of the small and large bowel with carcinoma in a villous polyp of the jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1962 Jan;42:60–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R., Bussey H. J., Mendelsohn G., Diamond M. P., Pavlides G., Hutcheon D., Harbison M., Shermeta D., Morson B. C., Yardley J. H. Ileal adenomas after colectomy in nine patients with adenomatous polyposis coli/Gardner's syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1979 Dec;77(6):1252–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann D. C., Goligher J. C. Polyposis of the stomach and small intestine in association with familia polyposis coli. Br J Surg. 1971 Feb;58(2):126–128. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Nance F. C. Periampullary malignancy in Gardner's syndrome. Ann Surg. 1977 May;185(5):565–573. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197705000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees C. D., Hermann R. E. Familial polyposis coli associated with bile duct cancer. Am J Surg. 1981 Mar;141(3):378–380. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYO C. W., DeWEERD J. H., JACKMAN R. J. Diffuse familial polyposis of the colon. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1951 Jul;93(1):87–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morson B. C. Evolution of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1974 Sep;34(3):suppl–suppl:849. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197409)34:3+<845::aid-cncr2820340710>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor E. W., Lebenthal E. Gardner's syndrome. Recent developments in research and management. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Dec;25(12):945–959. doi: 10.1007/BF01308046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsato K., Yao T., Watanabe H., Iida M., Itoh H. Small-intestinal involvement in familial polyposis diagnosed by operative intestinal fiberscopy: report of four cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(5):414–420. doi: 10.1007/BF02587374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks T. G., Bussey H. F., Lockhart-Mummery H. E. Familial polyposis coli associated with extracolonic abnormalities. Gut. 1970 Apr;11(4):323–329. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.4.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. G., Jr Polyposis and carcinoma of the small bowel and familial colonic polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1981 Sep;24(6):478–481. doi: 10.1007/BF02626789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranzi T., Castagnone D., Velio P., Bianchi P., Polli E. E. Gastric and duodenal polyps in familial polyposis coli. Gut. 1981 May;22(5):363–367. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.5.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Mastromarino A., Gustafson C., Lipkin M., Wynder E. L. Fecal bile acids and neutral sterols in patients with familial polyposis. Cancer. 1976 Oct;38(4):1694–1698. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197610)38:4<1694::aid-cncr2820380442>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. E., Mara J. E. Small bowel polyps and carcinoma in multiple intestinal polyposis. Arch Surg. 1974 May;108(5):736–738. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01350290098018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachatello C. R. Familial polyposis of the colon. A four-decade follow-up. Cancer. 1971 Sep;28(3):581–587. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197109)28:3<581::aid-cncr2820280309>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachatello C. R., Hedgecock H., Jr, Armstrong A. What can experimental colorectal cancer tell us about colorectal cancer in man? Dis Colon Rectum. 1980 Mar;23(2):80–85. doi: 10.1007/BF02587598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchardt W. A., Jr, Ponsky J. L. Familial polyposis and Gardner's syndrome. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 Jan;148(1):97–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman A. Gastric and small bowel polyps in Gardner's syndrome and familial polyposis coli. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1976 Sep;27(3):206–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull L. N., Jr, Fitts C. T. Lymphoid polyposis associated with familial polyposis and Gardner's syndrome. Ann Surg. 1974 Sep;180(3):319–322. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197409000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushio K., Sasagawa M., Doi H., Yamada T., Ichikawa H., Hojo K., Koyama Y., Sano R. Lesions associated with familial polyposis coli: studies of lesions of lesions of the stomach, duodenum, bones, and teeth. Gastrointest Radiol. 1976;1(1):67–80. doi: 10.1007/BF02256344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsunomiya J., Maki T., Iwama T., Matsunaga Y., Ichikawa T. Gastric lesion of familial polyposis coli. Cancer. 1974 Sep;34(3):745–754. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197409)34:3<745::aid-cncr2820340333>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Enjoji M., Yao T., Ohsato K. Gastric lesions in familial adenomatosis coli: their incidence and histologic analysis. Hum Pathol. 1978 May;9(3):269–283. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watne A. L., Lai H. Y., Mance T., Core S. Fecal steroids and bacterial flora in patients with polyposis coli. Am J Surg. 1976 Jan;131(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T., Ida M., Ohsato K., Watanabe H., Omae T. Duodenal lesions in familial polyposis of the colon. Gastroenterology. 1977 Nov;73(5):1086–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]