Abstract
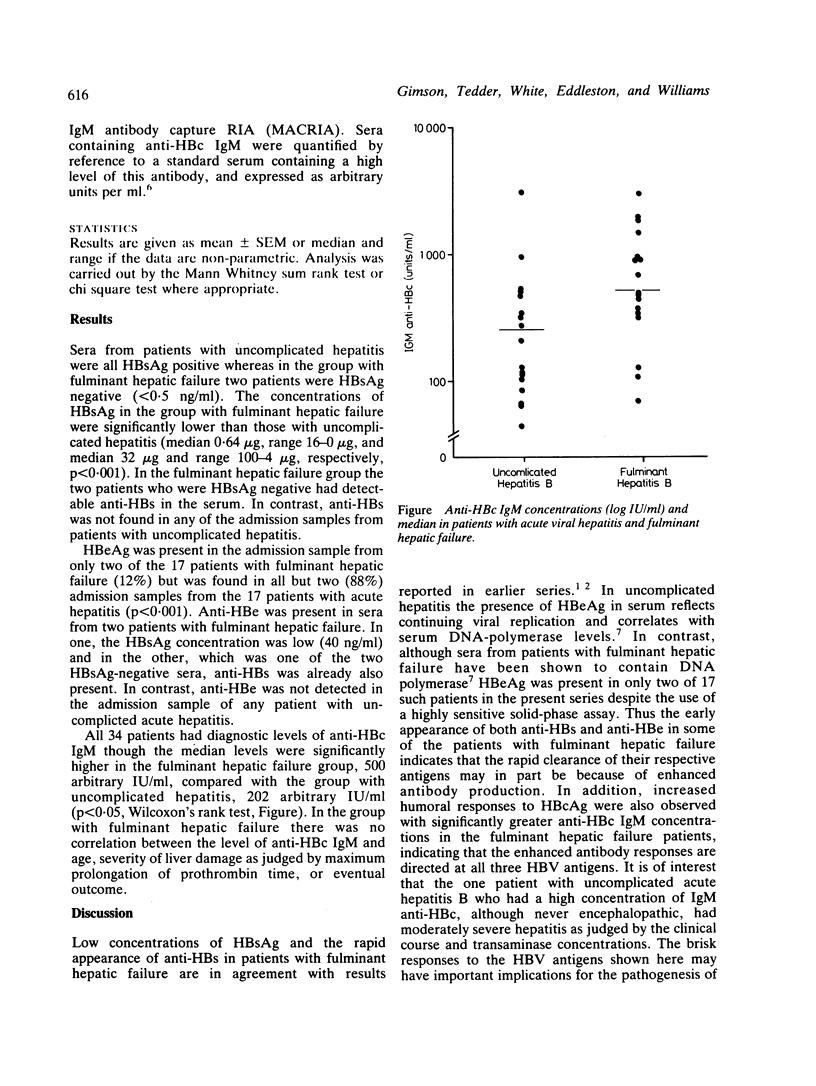
Serological markers for hepatitis B virus infection have been examined in 34 patients with acute hepatitis B, 17 of whom developed fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatitis B surface antigen concentrations were significantly lower and hepatitis Be antigen was less frequently detectable in patients with fulminant hepatic failure compared with those with acute hepatitis (median 0.64 micrograms, range 16-0 and median 32 micrograms and range 100-4 micrograms respectively, p less than 0.001; HBeAg detected in 12% and 88% respectively, p less than 0.001). The IgM component of hepatitis B core antibody was significantly higher in the patients with fulminant hepatic failure with median values of 500 IU/ml compared with those with uncomplicated hepatitis (median 202 IU/ml, p less than 0.05 Wilcoxon's rank test). Three patients who developed a fulminant course had detectable levels of either anti-HBs or anti-HBe. These results are consistent with enhanced antibody responses to all three hepatitis B virus antigens and more rapid clearance of the latter during fulminant hepatic failure.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti A., Diana S., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Changes in hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase in relation to the outcome of acute hepatitis type B. Gut. 1979 Mar;20(3):190–195. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.3.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbara J. A., Mijovic V., Cleghorn T. E., Tedder R. S., Briggs M. Liver enzyme concentrations as measure of possible infectivity in chronic asymptomatic carriers of hepatitis B. Br Med J. 1978 Dec 9;2(6152):1600–1602. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6152.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron C. H., Combridge B. S., Howell D. R., Barbara J. A. A sensitive immunoradiometric assay for the detection of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Virol Methods. 1980;1(6):311–323. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(80)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canalese J., Wyke R. J., Vergani D., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Circulating immune complexes in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Gut. 1981 Oct;22(10):845–848. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.10.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horney J. T., Galambos J. T. The liver during and after fulminant hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1977 Oct;73(4 Pt 1):639–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. A. The formation of circulating antibody in the splenectomized human being following intravenous injection of heterologous erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1950 Nov;65(5):515–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABESIN S. M. Electron microscopy of hypersensitivity reactions: allergic hepatic necrosis. Am J Pathol. 1963 Jun;42:743–757. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder R. S., Wilson-Croome R. Detection by radioimmunoassay of IgM class antibody to hepatitis B core antigen: a comparison of two methods. J Med Virol. 1980;6(3):235–247. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890060307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepo C. G., Robert D., Motin J., Trepo D., Sepetjian M., Prince A. M. Hepatitis B antigen (HBSAg) and/or antibodies (anti-HBS and anti-HBC) in fulminant hepatitis: pathogenic and prognostic significance. Gut. 1976 Jan;17(1):10–13. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trey C., Davidson C. S. The management of fulminant hepatic failure. Prog Liver Dis. 1970;3:282–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf I. L., El Sheikh N., Cullens H., Lee W. M., Eddleston A. L., Williams R., Zuckerman A. J. Enhanced HBsAb production in pathogenesis of fulminant viral hepatitis type B. Br Med J. 1976 Sep 18;2(6037):669–671. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6037.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


