Abstract
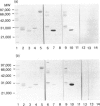
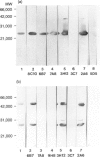
Limulus polyphemus C-reactive protein (CRP) (limulin) has approximately 30% amino acid sequence homology and shares at least one idiotypic determinant associated with ligand-binding activity with human CRP (hCRP); limulin also shares amino acid sequence homology and lectin activity with human serum amyloid P component (hSAP). In the present study panels of 14 anti-hCRP monoclonal antibodies (mAb) directed to distinct hCRP epitopes and 11 anti-hSAP mAb directed to distinct epitopes of hSAP were tested for reactivity with limulin and pentraxins of other species including rabbit CRP (raCRP), rat CRP and hamster female protein (FP) by ELISA and Western blot analyses. None of the anti-human pentraxin mAb showed strong cross-reactivity with limulin; only five mAb reacted with limulin at all, and cross-reactivities of these mAb with the other pentraxins, when present, also were weak. Cross-reactivity of limulin with hCRP and hSAP was similar, and in light of comparable amino acid sequence homology, suggests this molecule can be considered the limulus SAP as well as the limulus CRP. Several anti-hCRP mAb cross-reacted strongly with rabbit CRP and rat CRP; a few anti-hSAP cross-reacted strongly with FP; and weak cross-reactions were observed between hCRP and hSAP, but cross-reactivities between the pentraxins generally were limited and weak. A rabbit polyclonal antibody raised to highly conserved limulin peptide 141-156 and strongly reactive with limulin reacted weakly with hCRP and raCRP but failed to react with rat CRP, hSAP or FP. These studies emphasize a limited but distinct antigenic similarity between limulin, hCRP and other pentraxins, and identify mAb reactive with potential regions of shared structure and/or function between pentraxins of different species.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon R., Maron E. An immunological approach to the structural relationship between hen egg-white lysozyme and bovine -lactalbumin. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz M. L., de Beer F. C., Feinstein A., Munn E. A., Milstein C. P., Fletcher T. C., March J. F., Taylor J., Bruton C., Clamp J. R. Phylogenetic aspects of C-reactive protein and related proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:49–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabana V. G., Gewurz H., Siegel J. N. Interaction of very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) with rabbit C-reactive protein. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2342–2348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J. E., Margossian S. S., Slayter H. S., Sogn J. A. Hamster female protein. A new Pentraxin structurally and functionally similar to C-reactive protein and amyloid P component. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):977–991. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe J. E., Ross M. J. Amyloidosis and female protein in the Syrian hamster. Concurrent regulation by sex hormones. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1257–1267. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W., Mold C., Stump R. F. Identification of a polypeptide sequence that mediates nuclear localization of the acute phase protein C-reactive protein. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3869–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTSCHLICH E., STETSON C. A., Jr Immunologic cross-reactions among mammalian acute phase proteins. J Exp Med. 1960 Apr 1;111:441–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.4.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewurz H., Mold C., Siegel J., Fiedel B. C-reactive protein and the acute phase response. Adv Intern Med. 1982;27:345–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hind C. R., Collins P. M., Renn D., Cook R. B., Caspi D., Baltz M. L., Pepys M. B. Binding specificity of serum amyloid P component for the pyruvate acetal of galactose. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1058–1069. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurrell J. G., Smith J. A., Todd P. E., Leach S. J. Cross-reactivity between mammalian myoglobins: linear vs spatial antigenic determinants. Immunochemistry. 1977 Apr;14(4):283–288. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang H. X., Siegel J. N., Gewurz H. Binding and complement activation by C-reactive protein via the collagen-like region of C1q and inhibition of these reactions by monoclonal antibodies to C-reactive protein and C1q. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2324–2330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R., Li S. S., Kehoe J. M. Molecular characterization of limulin, a sialic acid binding lectin from the hemolymph of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4297–4303. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick J. M., Volanakis J. E. Molecular genetics, structure, and function of C-reactive protein. Immunol Res. 1991;10(1):43–53. doi: 10.1007/BF02918166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita C. M., Ying S. C., Hugli T. E., Siegel J. N., Potempa L. A., Jiang H., Houghten R. A., Gewurz H. Elucidation of a protease-sensitive site involved in the binding of calcium to C-reactive protein. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 12;28(25):9840–9848. doi: 10.1021/bi00451a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubak B. M., Potempa L. A., Anderson B., Mahklouf S., Venegas M., Gewurz H., Gewurz A. T. Evidence that serum amyloid P component binds to mannose-terminated sequences of polysaccharides and glycoproteins. Mol Immunol. 1988 Sep;25(9):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchialonis J. J., Edelman G. M. Isolation and characterization of a hemagglutinin from Limulus polyphemus. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):453–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley S., Pepys M. B. Immunochemical cross-reactions between pentraxins of different species. Immunology. 1987 Sep;62(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen N. Y., Suzuki A., Boykins R. A., Liu T. Y. The amino acid sequence of Limulus C-reactive protein. Evidence of polymorphism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10456–10465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen N. Y., Suzuki A., Cheng S. M., Zon G., Liu T. Y. Isolation and characterization of Limulus C-reactive protein genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10450–10455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira E. B., Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y. Comparative studies on the binding properties of human and rabbit C-reactive proteins. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1396–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmand A. P., Friedenson B., Gewurz H., Painter R. H., Hofmann T., Shelton E. Characterization of C-reactive protein and the complement subcomponent C1t as homologous proteins displaying cyclic pentameric symmetry (pentraxins). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):739–743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C., Fletcher T. C., Richardson N., Munn E. A., Feinstein A. Analogues in other mammals and in fish of human plasma proteins, C-reactive protein and amyloid P component. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):168–170. doi: 10.1038/273168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Liu T. Y. Limulin: a C-reactive protein from Limulus polyphemus. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):969–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Ohura K., Futaki S., Fujii N., Yajima H., Goldman N., Jones K. D., Wahl S. Proteolysis of human C-reactive protein produces peptides with potent immunomodulating activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7053–7057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluter S. F., Marchalonis J. J. Antibodies to synthetic joining segment peptide of the T-cell receptor beta-chain: serological cross-reaction between products of T-cell receptor genes, antigen binding T-cell receptors, and immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1872–1876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. N., Gewurz H. C-reactive protein in aging Lobund Wistar rats. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;287:127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson S. J., Mortensen R. F. Binding and immunological properties of a synthetic peptide corresponding to the phosphorylcholine-binding region of C-reactive protein. Mol Immunol. 1990 Jul;27(7):679–687. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90011-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson S. J., Mullenix M. C., Mortensen R. F. Monoclonal antibodies to the calcium-binding region peptide of human C-reactive protein alter its conformation. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2248–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasta G. R., Marchalonis J. J., Kohler H. Invertebrate recognition protein cross-reacts with an immunoglobulin idiotype. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1270–1276. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo P., Korenberg J. R., Whitehead A. S. Characterization of genomic and complementary DNA sequence of human C-reactive protein, and comparison with the complementary DNA sequence of serum amyloid P component. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13384–13388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying S. C., Gewurz H., Kinoshita C. M., Potempa L. A., Siegel J. N. Identification and partial characterization of multiple native and neoantigenic epitopes of human C-reactive protein by using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):221–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]