Abstract
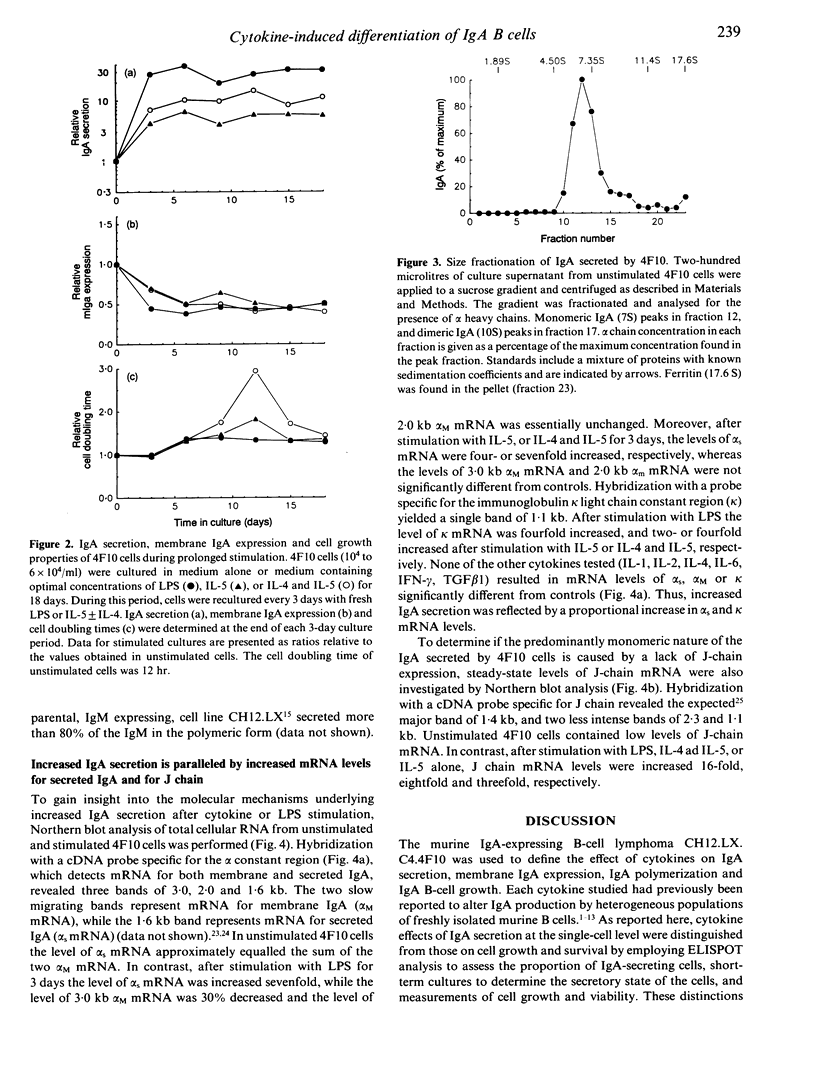
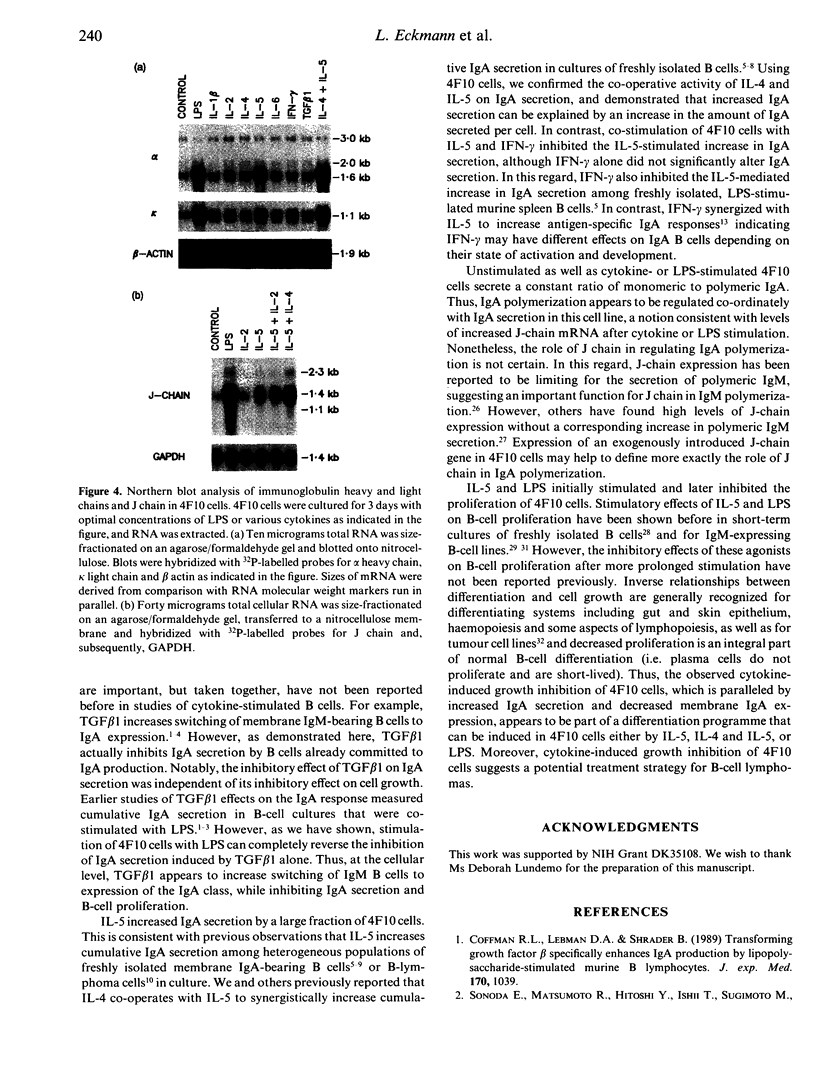
Cytokines such as interleukin-5 (IL-5) and transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF beta 1) increase IgA production by heterogeneous populations of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated murine B cells. We have used IgA expressing murine B-lymphoma cells CH12.LX.C4.4F10 (4F10) to define the activity of these and other cytokines on IgA secretion at the single-cell level, membrane IgA expression, IgA polymerization and cell growth. IL-5 as well as LPS significantly increases IgA secretion of 4F10 cells, whereas TGF beta 1, a cytokine known to stimulate isotype switching to IgA among surface IgM-bearing B cells, inhibits IgA secretion. When tested alone, IL-1 beta, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) do not significantly alter IgA secretion. However, there is a synergistic increase in IgA secretion when 4F10 cells are co-stimulated with IL-5 and IL-4, while IFN-gamma inhibits IL-5-stimulated up-regulation of IgA secretion. In parallel with increased IgA secretion after cytokine stimulation, 4F10 cells display less membrane IgA. Increased J-chain steady-state mRNA levels after IL-5 or LPS stimulation are paralleled by increased mRNA levels for secreted IgA, but are not accompanied by alterations in the ratio of monomeric to polymeric IgA. IL-5 and LPS initially stimulated but later inhibited 4F10 cell proliferation suggesting an inverse relationship between proliferation and differentiation in this cell line. 4F10 cells are a useful model for the characterization of discrete aspects of IgA B-cell differentiation, since the secretory and membrane Ig and proliferative responses of this IgA B-cell line to cytokines and LPS appear to parallel those of freshly isolated murine B cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold L. W., Grdina T. A., Whitmore A. C., Haughton G. Ig isotype switching in B lymphocytes. Isolation and characterization of clonal variants of the murine Ly-1+ B cell lymphoma, CH12, expressing isotypes other than IgM. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4355–4363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold L. W., LoCascio N. J., Lutz P. M., Pennell C. A., Klapper D., Haughton G. Antigen-induced lymphomagenesis: identification of a murine B cell lymphoma with known antigen specificity. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2064–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
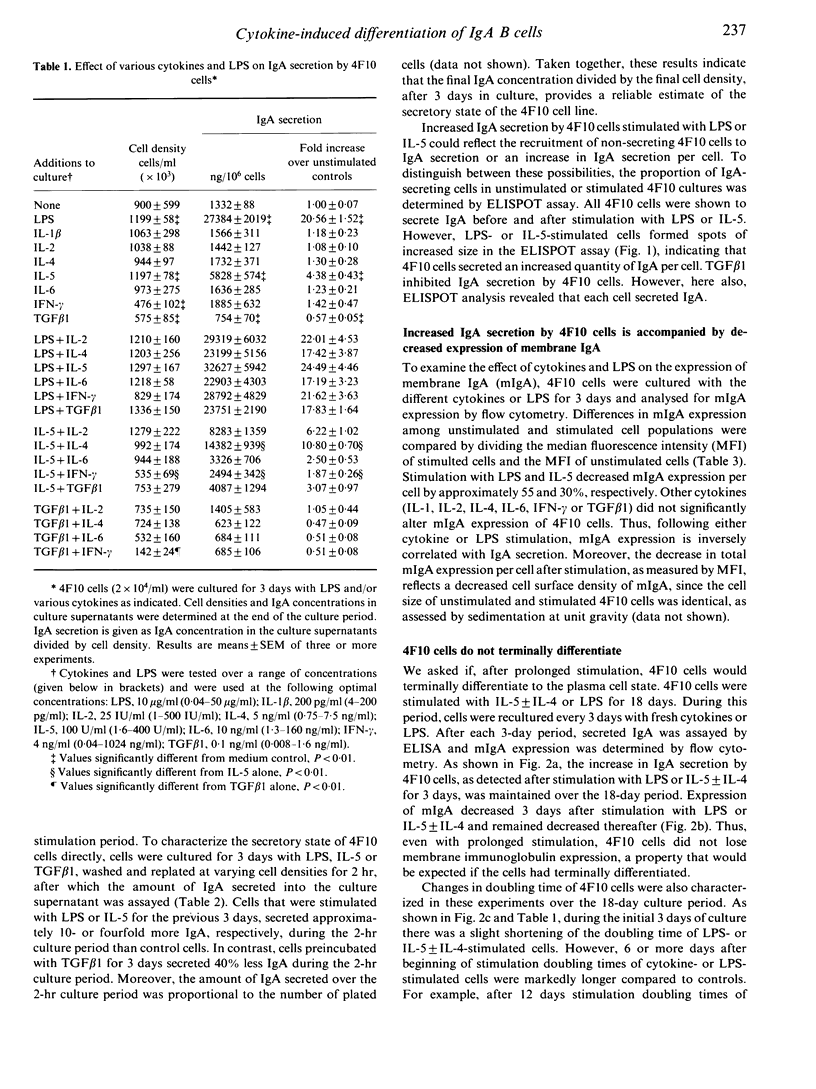
- Beagley K. W., Eldridge J. H., Kiyono H., Everson M. P., Koopman W. J., Honjo T., McGhee J. R. Recombinant murine IL-5 induces high rate IgA synthesis in cycling IgA-positive Peyer's patch B cells. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2035–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beagley K. W., Eldridge J. H., Lee F., Kiyono H., Everson M. P., Koopman W. J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., McGhee J. R. Interleukins and IgA synthesis. Human and murine interleukin 6 induce high rate IgA secretion in IgA-committed B cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2133–2148. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begley C. G., Metcalf D., Nicola N. A. Purified colony stimulating factors (G-CSF and GM-CSF) induce differentiation in human HL60 leukemic cells with suppression of clonogenicity. Int J Cancer. 1987 Jan 15;39(1):99–105. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman M. A., Tigges M. A., Minie M. E., Koshland M. E. A model system for peptide hormone action in differentiation: interleukin 2 induces a B lymphoma to transcribe the J chain gene. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):609–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90625-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Goding J. W., Schrader J. W. The regulation of growth and differentiation of a murine B cell lymphoma. I. Lipopolysaccharide-induced differentiation. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2461–2465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Lebman D. A., Shrader B. Transforming growth factor beta specifically enhances IgA production by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):1039–1044. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Shrader B., Carty J., Mosmann T. R., Bond M. W. A mouse T cell product that preferentially enhances IgA production. I. Biologic characterization. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3685–3690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harriman G. R., Kunimoto D. Y., Elliott J. F., Paetkau V., Strober W. The role of IL-5 in IgA B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3033–3039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughton G., Arnold L. W., Bishop G. A., Mercolino T. J. The CH series of murine B cell lymphomas: neoplastic analogues of Ly-1+ normal B cells. Immunol Rev. 1986 Oct;93:35–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Rolink A., Melchers F. Recombinant interleukin 2 or 5, but not 3 or 4, induces maturation of resting mouse B lymphocytes and propagates proliferation of activated B cell blasts. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1377–1390. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. H., Kagnoff M. F. Transforming growth factor beta 1 increases IgA isotype switching at the clonal level. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3773–3778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. H., Kagnoff M. F. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 is a costimulator for IgA production. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3411–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King L. B., Corley R. B. Characterization of a presecretory phase in B-cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp M. R., Severinson-Gronowicz E., Schröder J., Strober S. Characterization of a spontaneous murine B cell leukemia (BCL1). II. Tumor cell proliferation and IgM secretion after stimulation by LPS. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1000–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland M. E. The coming of age of the immunoglobulin J chain. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:425–453. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunimoto D. Y., Harriman G. R., Strober W. Regulation of IgA differentiation in CH12LX B cells by lymphokines. IL-4 induces membrane IgM-positive CH12LX cells to express membrane IgA and IL-5 induces membrane IgA-positive CH12LX cells to secrete IgA. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):713–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunimoto D. Y., Nordan R. P., Strober W. IL-6 is a potent cofactor of IL-1 in IgM synthesis and of IL-5 in IgA synthesis. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2230–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Rosenberg N., Alt F., Baltimore D. Continuing kappa-gene rearrangement in a cell line transformed by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. D., McKenzie D. T., Swain S. L., Kagnoff M. F. Interleukin 5 and interleukin 4 produced by Peyer's patch T cells selectively enhance immunoglobulin A expression. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2669–2674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. D., Swain S. L., Kagnoff M. P. Regulation of the IgM and IgA anti-dextran B1355S response: synergy between IFN-gamma, BCGF II, and IL 2. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4015–4020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbeck S., McKenzie D. T., Kagnoff M. F. Interleukin 5 is a differentiation factor for IgA B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jun;19(6):965–969. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher J. H., O'Garra A., Shrader B., van Kimmenade A., Bond M. W., Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. The characterization of four monoclonal antibodies specific for mouse IL-5 and development of mouse and human IL-5 enzyme-linked immunosorbent. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1576–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitia R., Rubartelli A., Kikutani H., Hammerling U., Stavnezer J. The regulation of membrane-bound and secreted alpha-chain biosynthesis during the differentiation of the B cell lymphoma I.29. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2859–2864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda E., Matsumoto R., Hitoshi Y., Ishii T., Sugimoto M., Araki S., Tominaga A., Yamaguchi N., Takatsu K. Transforming growth factor beta induces IgA production and acts additively with interleukin 5 for IgA production. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1415–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dutton R. W., McKenzie D., Helstrom H., English M. Role of antigen in the B cell response. Specific antigen and the lymphokine IL-5 synergize to drive B cell lymphoma proliferation and differentiation to Ig secretion. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4224–4230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Slightom J. L., Blattner F. R. Mouse IgA heavy chain gene sequence: implications for evolution of immunoglobulin hinge axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7684–7688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Word C. J., Mushinski J. F., Tucker P. W. The murine immunoglobulin alpha gene expresses multiple transcripts from a unique membrane exon. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):887–898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]