Abstract
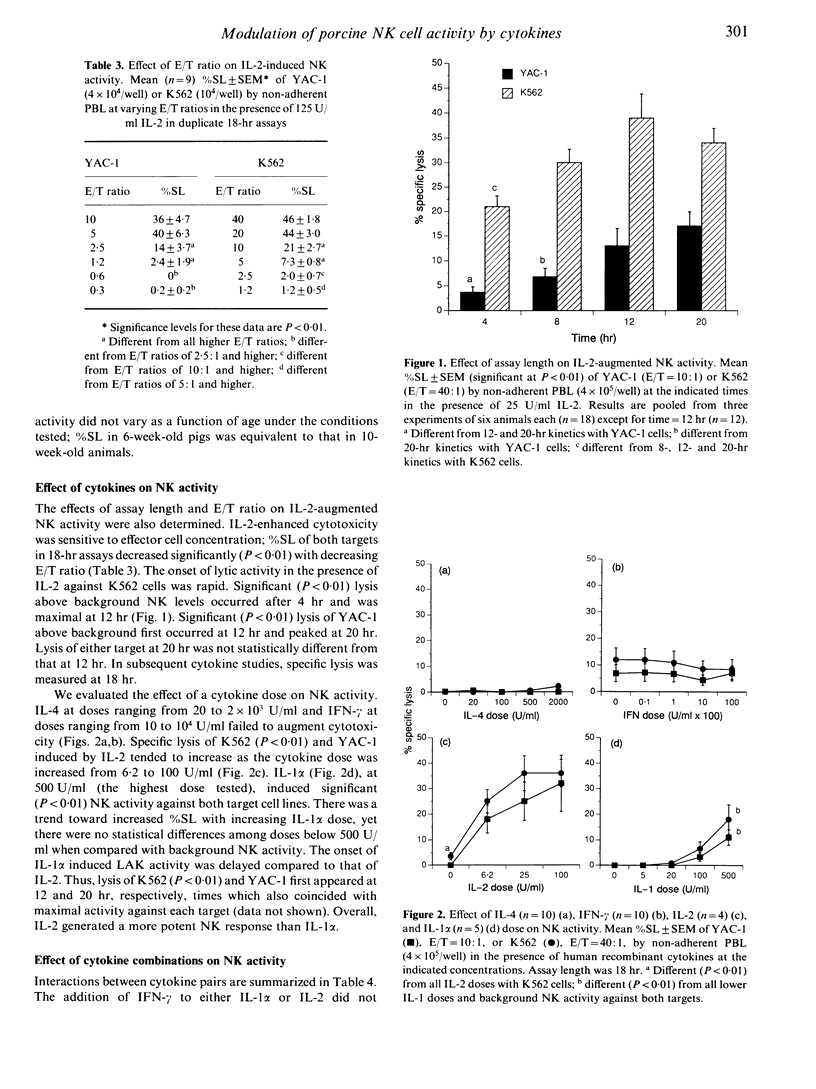
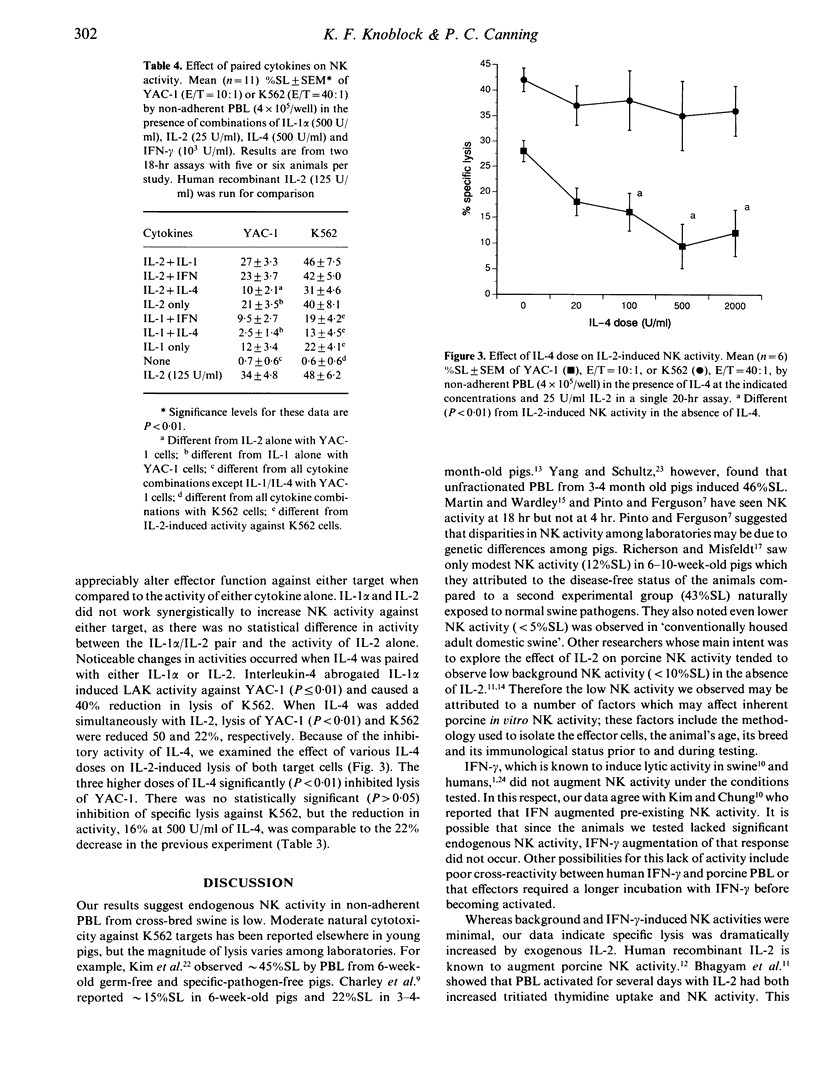
In order to understand better how cytokines modulate porcine lymphocyte-mediated natural cytotoxicity and to develop a rapid and reliable colorimetric assay to study that activity in young pigs, we studied inherent and cytokine induced in vitro natural killer (NK) activity. The cytokines we studied were human recombinant interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha), IL-2, IL-4 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). Natural killer activity by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), reported as per cent specific lysis (%SL), was determined by the colorimetric measurement of lactate dehydrogenase released from tumour cell targets, YAC-1 and K562. Inherent NK activity was low and remained relatively unchanged by alterations of assay length or effector cell concentration. Low NK activity was also observed in response to IL-4 and IFN-gamma. IL-2 and, to a lesser extent, IL-1 alpha induced significant NK activity with trends towards increasing %SL with increasing cytokine dose. Optimal IL-1 alpha- and IL-2-induced NK activity could be observed at 18 hr, with significant activity stimulated by IL-2 as early as 4 hr. IL-2-induced NK activity was sensitive to effector cell concentration; %SL decreased as the effector to target ratio decreased. IL-1 alpha- and IL-2-induced NK activities were decreased in the presence of IL-4. These results indicate porcine PBMC are sensitive to in vitro modulation by human recombinant IL-1 alpha, IL-2 and IL-4. The ability of IL-1 alpha and IL-2 to induce swine NK activity and the ability of IL-4 to inhibit that activity are similar to the actions of those cytokines in human NK systems.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderson M. R., Sassenfeld H. M., Widmer M. B. Interleukin 7 enhances cytolytic T lymphocyte generation and induces lymphokine-activated killer cells from human peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):577–587. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhagyam R. C., Jarrett-Zaczek D., Ferguson F. G. Activation of swine peripheral blood lymphocytes with human recombinant interleukin-2. Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):607–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepica A., Derbyshire J. B. Characterisation of the effector cells in antibody-dependent and spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity in swine against target cells infected with transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Res Vet Sci. 1986 Jul;41(1):70–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charley B., Fradelizi D. Differential effects of human and porcine interleukin 2 on natural killing (NK) activity of newborn piglets and adult pigs lymphocytes. Ann Rech Vet. 1987;18(3):227–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charley B., Petit E., La Bonnardière C. Interferon-induced enhancement of newborn pig natural killing (NK) activity. Ann Rech Vet. 1985;16(4):399–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S., Doyle M. V. Response of bovine and porcine peripheral blood mononuclear cells to human recombinant interleukin 2(125). Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jan;11(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Mizel S. B. T-Cell lymphoma model for the analysis of interleukin 1-mediated T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1133–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han X., Itoh K., Balch C. M., Pellis N. R. Recombinant interleukin 4 (RIL4) inhibits interleukin 2-induced activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes. Lymphokine Res. 1988 Fall;7(3):227–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K. J., Blecha F., Fenwick B. W., Thaler R. C., Nelssen J. L. Human recombinant interleukin-2 augments porcine natural killer cell cytotoxicity in vivo. Ann Rech Vet. 1990;21(2):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. R., Ortaldo J. R., Bonnard G. D. Augmentation by interferon of human natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):221–223. doi: 10.1038/277221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi C. M., Thompson J. A., Lindgren C. G., Gillis S., Widmer M. B., Kern D. E., Fefer A. Induction of lymphokine-activated killer activity by interleukin 4 in human lymphocytes preactivated by interleukin 2 in vivo or in vitro. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 1;49(23):6487–6492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh N. D., Kim Y. B., Koren H. S., Amos D. B. Natural killing and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in specific-pathogen-free miniature swine and germ-free piglets. II. Ontogenic development development of NK and ADCC. Int J Cancer. 1981 Aug 15;28(2):175–178. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Shiiba K., Shimizu Y., Suzuki R., Kumagai K. Generation of activated killer (AK) cells by recombinant interleukin 2 (rIL 2) in collaboration with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3124–3129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J., Schultz R. D. Bovine natural cell mediated cytotoxicity (NCMC): activation by cytokines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Feb;24(2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(90)90014-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B., Chung T. J. Effect of recombinant human interferons on NK and K cell activities of gnotobiotic miniature swine. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;181:329–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B. Effect of biological response modifier-streptococcal preparation OK-432 on NK/K cell system of gnotobiotic miniature swine. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;181:337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korzeniewski C., Callewaert D. M. An enzyme-release assay for natural cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 25;64(3):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90438-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Cerottini J. C., MacDonald H. R. Interleukin 1-dependent induction of both interleukin 2 secretion and interleukin 2 receptor expression by thymoma cells. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1226–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubinski J., Fong T. C., Babbitt J. T., Ransone L., Yodoi J. J., Bloom E. T. Increased binding of IL-2 and increased IL-2 receptor mRNA synthesis are expressed by an NK-like cell line in response to IL-1. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1903–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Wardley R. C. Natural cytotoxicity detected in swine using Aujeszky's disease virus infected targets. Res Vet Sci. 1984 Sep;37(2):211–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler A., Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H. The effects of IL-4 on human natural killer cells. A potent regulator of IL-2 activation and proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2349–2351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Heterogeneity of natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:359–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostensen M. E., Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. Enhancement of human natural killer cell function by the combined effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha or interleukin-1 and interferon-alpha or interleukin-2. J Biol Response Mod. 1989 Feb;8(1):53–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto A., Ferguson F. Characteristics of Yorkshire swine natural killer cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Dec;20(1):15–29. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(88)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richerson J. T., Misfeldt M. L. Host environment as a modulating factor of swine natural killer cell activity. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Dec;23(3-4):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(89)90143-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Tanaka Y., Eto S., Suzuki H., Yodoi J., Yamashita U. Effect of interleukin 1 on the expression of interleukin 2 receptor (Tac antigen) on human natural killer cells and natural killer-like cell line (YT cells). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):551–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamatsu H., Koide F. Augmentation of porcine spontaneous cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Oct;47(5):749–759. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Matsumoto-Kobayashi M., Clark S. C., Seehra J., London L., Perussia B. Response of resting human peripheral blood natural killer cells to interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1147–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer M. B., Acres R. B., Sassenfeld H. M., Grabstein K. H. Regulation of cytolytic cell populations from human peripheral blood by B cell stimulatory factor 1 (interleukin 4). J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1447–1455. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W. C., Schultz R. D. Ontogeny of natural killer cell activity and antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity in pigs. Dev Comp Immunol. 1986 Summer;10(3):405–418. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(86)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W. C., Schultz R. D., Spano J. S. Isolation and characterization of porcine natural killer (NK) cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Apr;14(4):345–356. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(87)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


