Abstract
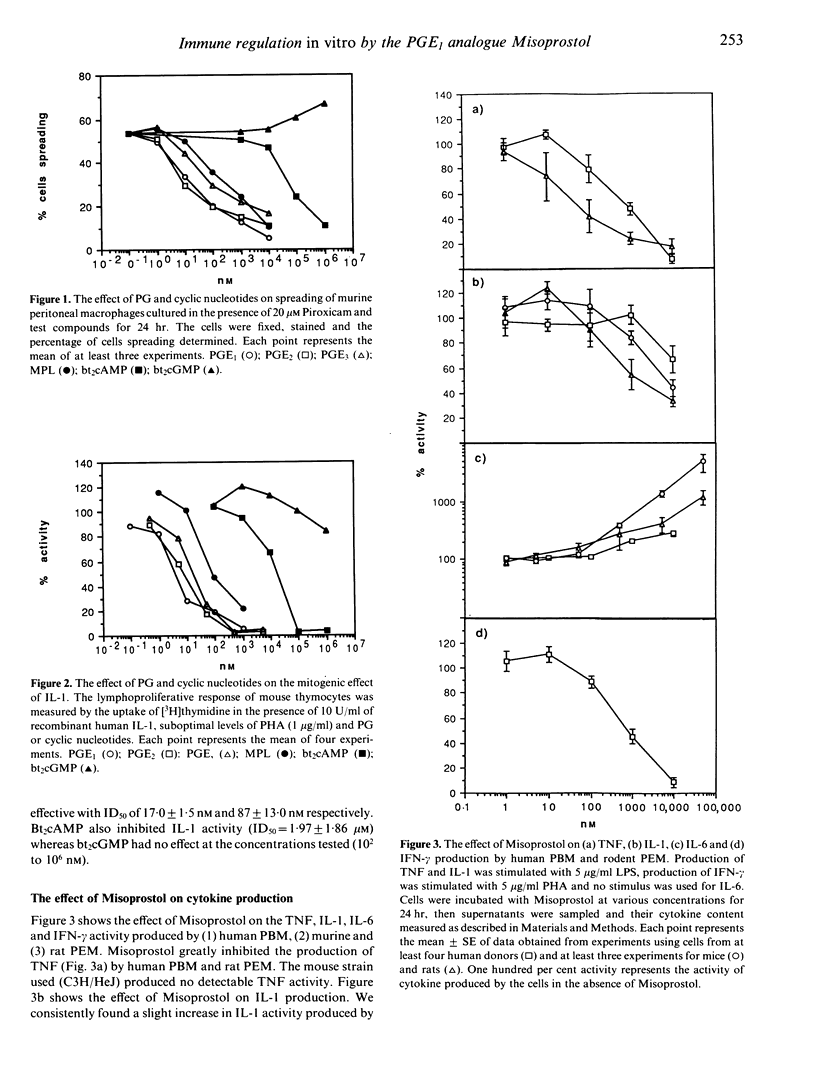
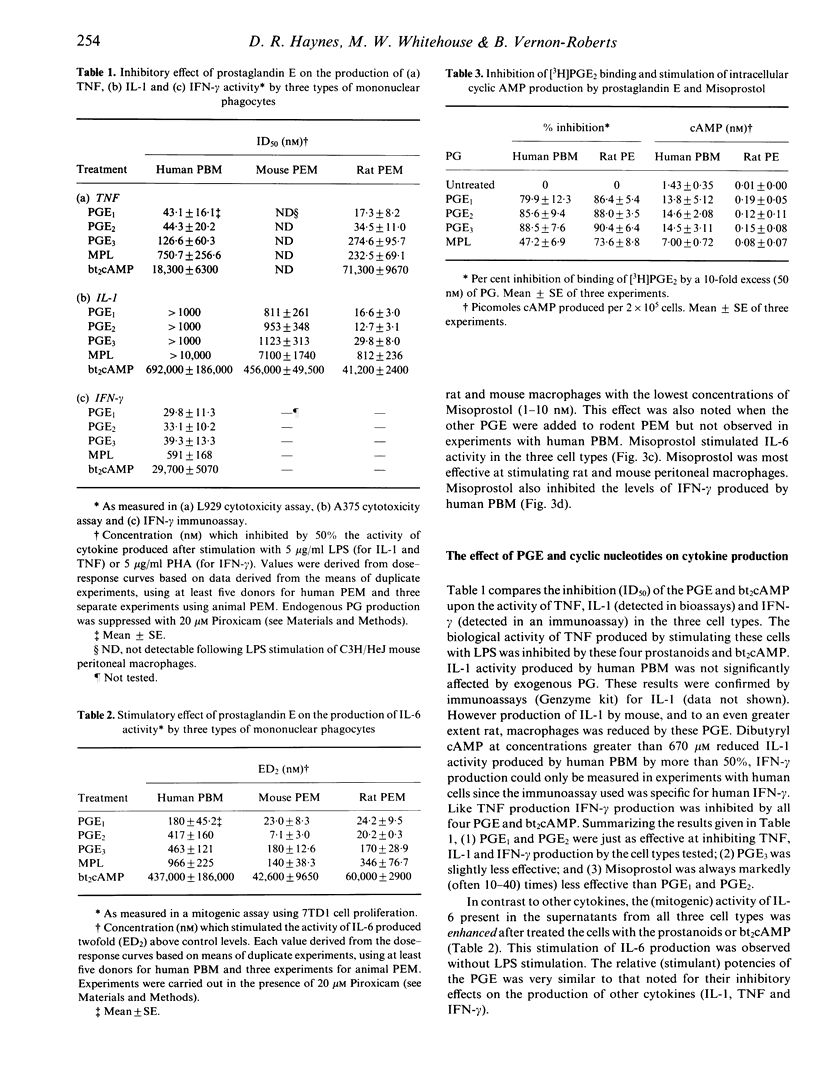
We examined whether some immune functions related to the action and production of cytokines could be regulated by the natural prostaglandins E (PGE) and the PGE1 (ester) analogue, Misoprostol. PGE1,2,3 and Misoprostol inhibited: (1) the mitogenic activity of interleukin-1 (IL-1) for mouse thymocytes; (2) spreading of mouse macrophages on glass; (3) tumour necrosis factor (TNF) (alpha and beta) production by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and rat macrophages; (4) IL-1 production by rat and mouse peritoneal macrophages; and (5) interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. These PGE had little effect on IL-1 production by human monocytes. By contrast, they all enhanced IL-6 production by rat and mouse macrophages and human monocytes. These effects were noted at concentrations below 500 nM (even as low as 10 nM). The relative potency of the prostanoids tested for both inhibitory and stimulatory effects was PGE1 = PGE2 = or greater than PGE3 greater than Misoprostol greater than PGA2 much greater than PGF1-alpha = PGF2-alpha = PGD2 (no effect). There is strong evidence that PGE1,2,3 and Misoprostol bind to the same receptor(s) and trigger the second messenger, cAMP, since dibutyryl cAMP (a lipophilic analogue of cAMP) had the same effects as the PGE. These PGE also induced elevated intracellular cAMP levels in and competed with [3H]PGE2 for binding to human and rat cells with the same relative potencies as described above.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Biology of multifunctional cytokines: IL 6 and related molecules (IL 1 and TNF). FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2860–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartold P. M., Haynes D. R. Interleukin-6 production by human gingival fibroblasts. J Periodontal Res. 1991 Jul;26(4):339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1991.tb02072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Tkacenko V., Milsark I., Krochin N., Cerami A. Effect of gamma interferon on cachectin expression by mononuclear phagocytes. Reversal of the lpsd (endotoxin resistance) phenotype. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1791–1796. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broughton K. S., Whelan J., Hardardottir I., Kinsella J. E. Effect of increasing the dietary (n-3) to (n-6) polyunsaturated fatty acid ratio on murine liver and peritoneal cell fatty acids and eicosanoid formation. J Nutr. 1991 Feb;121(2):155–164. doi: 10.1093/jn/121.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesario T. C., Yousefi S., Carandang G. The regulation of interferon production by aspirin, other inhibitors of the cyclooxygenase pathway and agents influencing calcium channel flux. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1989 Jan;65(1):26–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland L. G., French J. K., Betts W. H., Murphy G. A., Elliott M. J. Clinical and biochemical effects of dietary fish oil supplements in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Oct;15(10):1471–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres S., Ghorbani R., Kelley V. E., Georgilis K., Lonnemann G., van der Meer J. W., Cannon J. G., Rogers T. S., Klempner M. S., Weber P. C. The effect of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by mononuclear cells. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 2;320(5):265–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902023200501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Guy G. R., Michell R. H., Gordon J., Dugas B., Rigley K. P., Callard R. E. Interleukin 4 activates human B lymphocytes via transient inositol lipid hydrolysis and delayed cyclic adenosine monophosphate generation. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):151–156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Bird C. R., Bristow A., Poole S., Thorpe R. A simple sensitive bioassay for interleukin-1 which is unresponsive to 10(3) U/ml of interleukin-2. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 4;99(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. R., Garrett I. R., Vernon-Roberts B. Effect of gold salt treatment on the receptor binding activity of monocytes and macrophages isolated from rats with adjuvant arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1988;8(4):159–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00270454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. R., Garrett I. R., Whitehouse M. W., Vernon-Roberts B. Do gold drugs inhibit interleukin-1? Evidence from an in vitro lymphocyte activating factor assay. J Rheumatol. 1988;15(5):775–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. R., Wright P. F., Whitehouse M. W., Vernon-Roberts B. The cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, piroxicam, enhances cytokine-induced lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Immunol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;68(Pt 4):225–230. doi: 10.1038/icb.1990.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horrobin D. F. Prostaglandin E1: physiological significance and clinical use. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1988 Jul 15;100(14):471–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis S., Lee J. C., Hanna N. Effects of prostaglandins and cAMP levels on monocyte IL-1 production. Agents Actions. 1989 Jun;27(3-4):274–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01972795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I., Coleman R. A., Humphrey P. P., Levy G. P., Lumley P. Studies on the characterisation of prostanoid receptors: a proposed classification. Prostaglandins. 1982 Nov;24(5):667–689. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen P. J., Dinarello C. A., Strom T. B. Prostaglandins posttranscriptionally inhibit monocyte expression of interleukin 1 activity by increasing intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3189–3194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W. Arachidonic acid metabolites regulate interleukin-1 production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):892–897. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Wiggins R. C., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. Regulation of macrophage tumor necrosis factor production by prostaglandin E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. P., Barrett M. L. Immunosuppressive actions of prostaglandins and the possible increase in chronic inflammation after cyclo-oxygenase inhibitors. Agents Actions. 1986 Oct;19(1-2):59–65. doi: 10.1007/BF01977259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai S., Mizuno K., Kaneta M., Hirai Y. A simple, sensitive bioassay for the detection of interleukin-1 using human melanoma A375 cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):1189–1196. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson P. A. Recent advances in defining the role of misoprostol in rheumatology. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1990 Feb;20:50–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otterness I. G., Bliven M. L., Eskra J. D., Reinke M., Hanson D. C. The pharmacologic regulation of interleukin-1 production: the role of prostaglandins. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jul;114(2):385–397. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rola-Pleszczynski M., Lemaire I. Leukotrienes augment interleukin 1 production by human monocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3958–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales W. E., Chensue S. W., Otterness I., Kunkel S. L. Regulation of monokine gene expression: prostaglandin E2 suppresses tumor necrosis factor but not interleukin-1 alpha or beta-mRNA and cell-associated bioactivity. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 May;45(5):416–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirko S. P., Schindler R., Doyle M. J., Weisman S. M., Dinarello C. A. Transcription, translation and secretion of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor: effects of tebufelone, a dual cyclooxygenase/5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):243–250. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederkehr J. C., Dumble L., Pollak R., Moran M. Immunosuppressive effect of misoprostol: a new synthetic prostaglandin E1 analogue. Aust N Z J Surg. 1990 Feb;60(2):121–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Synthesis of interleukin 6 (interferon-beta 2/B cell stimulatory factor 2) in human fibroblasts is triggered by an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6177–6182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


